Alireza Vafaei Sadr
Learning to Detect Interesting Anomalies
Oct 28, 2022Abstract:Anomaly detection algorithms are typically applied to static, unchanging, data features hand-crafted by the user. But how does a user systematically craft good features for anomalies that have never been seen? Here we couple deep learning with active learning -- in which an Oracle iteratively labels small amounts of data selected algorithmically over a series of rounds -- to automatically and dynamically improve the data features for efficient outlier detection. This approach, AHUNT, shows excellent performance on MNIST, CIFAR10, and Galaxy-DESI data, significantly outperforming both standard anomaly detection and active learning algorithms with static feature spaces. Beyond improved performance, AHUNT also allows the number of anomaly classes to grow organically in response to Oracle's evaluations. Extensive ablation studies explore the impact of Oracle question selection strategy and loss function on performance. We illustrate how the dynamic anomaly class taxonomy represents another step towards fully personalized rankings of different anomaly classes that reflect a user's interests, allowing the algorithm to learn to ignore statistically significant but uninteresting outliers (e.g., noise). This should prove useful in the era of massive astronomical datasets serving diverse sets of users who can only review a tiny subset of the incoming data.
U-Net-based Models for Skin Lesion Segmentation: More Attention and Augmentation
Oct 28, 2022



Abstract:According to WHO[1], since the 1970s, diagnosis of melanoma skin cancer has been more frequent. However, if detected early, the 5-year survival rate for melanoma can increase to 99 percent. In this regard, skin lesion segmentation can be pivotal in monitoring and treatment planning. In this work, ten models and four augmentation configurations are trained on the ISIC 2016 dataset. The performance and overfitting are compared utilizing five metrics. Our results show that the U-Net-Resnet50 and the R2U-Net have the highest metrics value, along with two data augmentation scenarios. We also investigate CBAM and AG blocks in the U-Net architecture, which enhances segmentation performance at a meager computational cost. In addition, we propose using pyramid, AG, and CBAM blocks in a sequence, which significantly surpasses the results of using the two individually. Finally, our experiments show that models that have exploited attention modules successfully overcome common skin lesion segmentation problems. Lastly, in the spirit of reproducible research, we implement models and codes publicly available.
Recommendations on test datasets for evaluating AI solutions in pathology
Apr 21, 2022
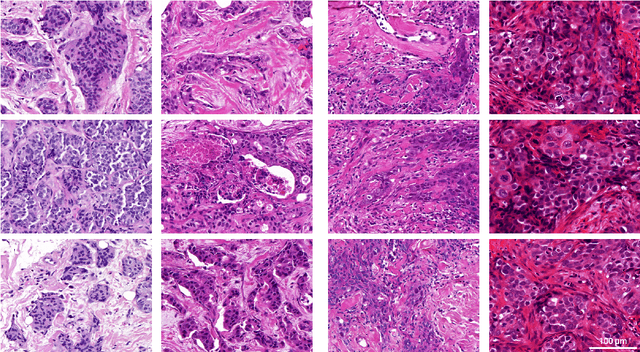

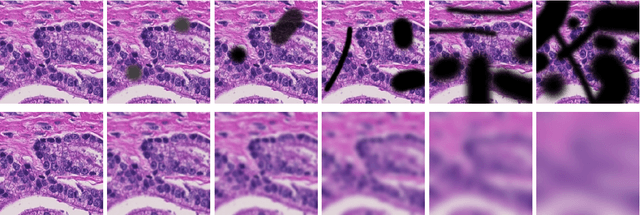
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) solutions that automatically extract information from digital histology images have shown great promise for improving pathological diagnosis. Prior to routine use, it is important to evaluate their predictive performance and obtain regulatory approval. This assessment requires appropriate test datasets. However, compiling such datasets is challenging and specific recommendations are missing. A committee of various stakeholders, including commercial AI developers, pathologists, and researchers, discussed key aspects and conducted extensive literature reviews on test datasets in pathology. Here, we summarize the results and derive general recommendations for the collection of test datasets. We address several questions: Which and how many images are needed? How to deal with low-prevalence subsets? How can potential bias be detected? How should datasets be reported? What are the regulatory requirements in different countries? The recommendations are intended to help AI developers demonstrate the utility of their products and to help regulatory agencies and end users verify reported performance measures. Further research is needed to formulate criteria for sufficiently representative test datasets so that AI solutions can operate with less user intervention and better support diagnostic workflows in the future.
Inpainting via Generative Adversarial Networks for CMB data analysis
Apr 21, 2020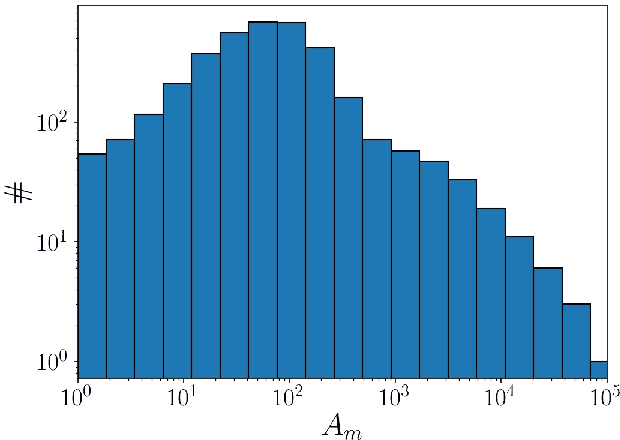
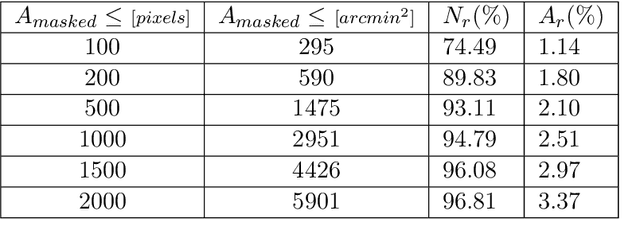
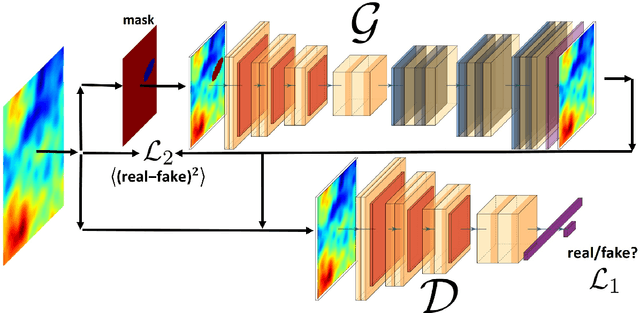
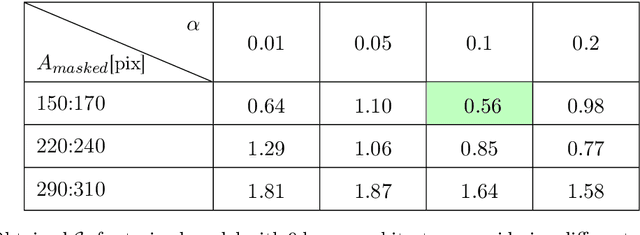
Abstract:In this work, we propose a new method to inpaint the CMB signal in regions masked out following a point source extraction process. We adopt a modified Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and compare different combinations of internal (hyper-)parameters and training strategies. We study the performance using a suitable $\mathcal{C}_r$ variable in order to estimate the performance regarding the CMB power spectrum recovery. We consider a test set where one point source is masked out in each sky patch with a 1.83 $\times$ 1.83 squared degree extension, which, in our gridding, corresponds to 64 $\times$ 64 pixels. The GAN is optimized for estimating performance on Planck 2018 total intensity simulations. The training makes the GAN effective in reconstructing a masking corresponding to about 1500 pixels with $1\%$ error down to angular scales corresponding to about 5 arcminutes.
A Flexible Framework for Anomaly Detection via Dimensionality Reduction
Sep 09, 2019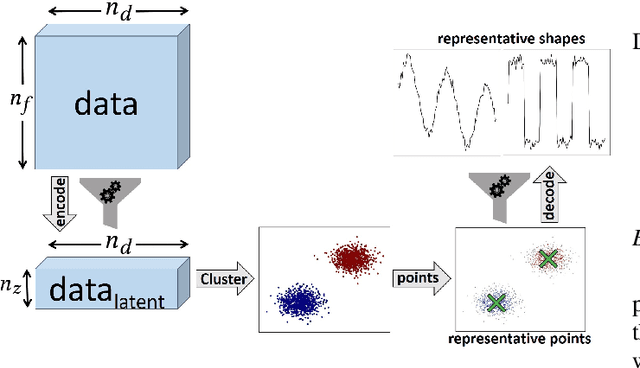
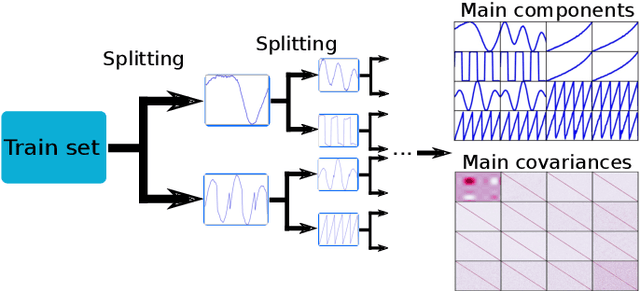
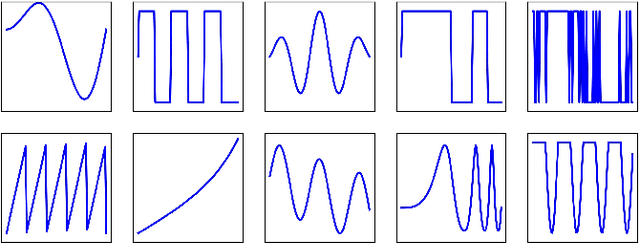
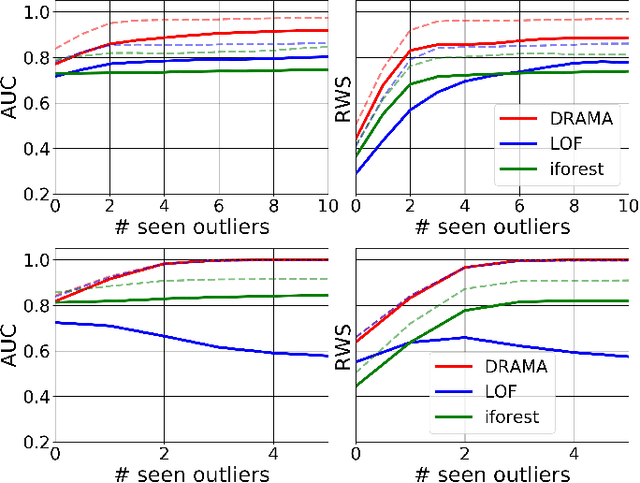
Abstract:Anomaly detection is challenging, especially for large datasets in high dimensions. Here we explore a general anomaly detection framework based on dimensionality reduction and unsupervised clustering. We release DRAMA, a general python package that implements the general framework with a wide range of built-in options. We test DRAMA on a wide variety of simulated and real datasets, in up to 3000 dimensions, and find it robust and highly competitive with commonly-used anomaly detection algorithms, especially in high dimensions. The flexibility of the DRAMA framework allows for significant optimization once some examples of anomalies are available, making it ideal for online anomaly detection, active learning and highly unbalanced datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge