Ali Nauman
Artificial Intelligence, Ambient Backscatter Communication and Non-Terrestrial Networks: A 6G Commixture
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:The advent of Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) represents a compelling response to the International Mobile Telecommunications 2030 (IMT-2030) framework, enabling the delivery of advanced, seamless connectivity that supports reliable, sustainable, and resilient communication systems. Nevertheless, the integration of NTN with Terrestrial Networks (TN) necessitates considerable alterations to the existing cellular infrastructure in order to address the challenges intrinsic to NTN implementation. Additionally, Ambient Backscatter Communication (AmBC), which utilizes ambient Radio Frequency (RF) signals to transmit data to the intended recipient by altering and reflecting these signals, exhibits considerable potential for the effective integration of NTN and TN. Furthermore, AmBC is constrained by its limitations regarding power, interference, and other related factors. In contrast, the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) within wireless networks demonstrates significant potential for predictive analytics through the use of extensive datasets. AI techniques enable the real-time optimization of network parameters, mitigating interference and power limitations in AmBC. These predictive models also enhance the adaptive integration of NTN and TN, driving significant improvements in network reliability and Energy Efficiency (EE). In this paper, we present a comprehensive examination of how the commixture of AI, AmBC, and NTN can facilitate the integration of NTN and TN. We also provide a thorough analysis indicating a marked enhancement in EE predicated on this triadic relationship.
Efficient Resource Allocation and User Association in NOMA-Enabled Vehicular-Aided HetNets with High Altitude Platforms
Jan 22, 2024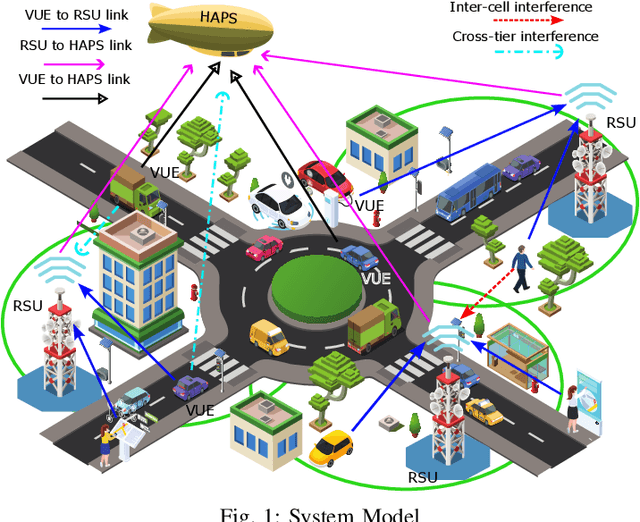
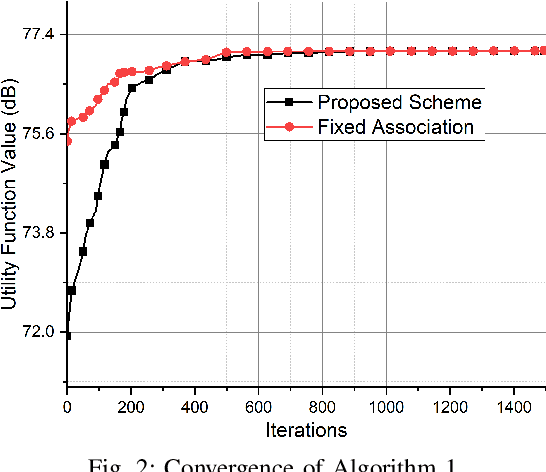
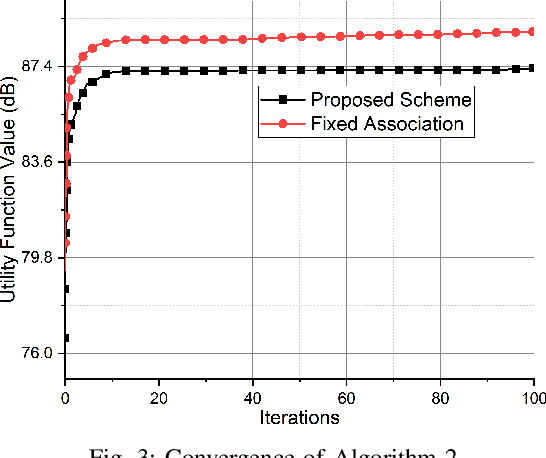
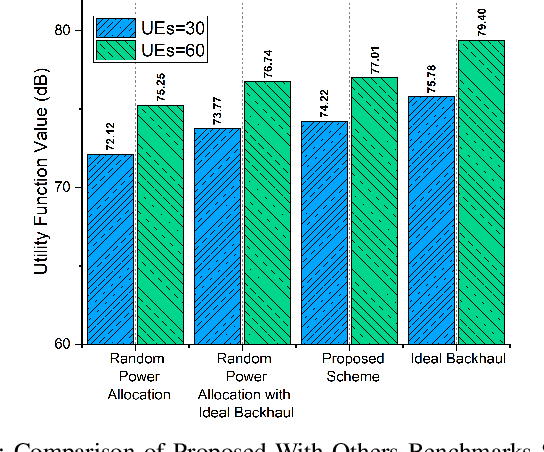
Abstract:The increasing demand for massive connectivity and high data rates has made the efficient use of existing spectrum resources an increasingly challenging problem. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) is a potential solution for future heterogeneous networks (HetNets) due to its high capacity and spectrum efficiency. In this study, we analyze an uplink NOMA-enabled vehicular-aided HetNet, where multiple vehicular user equipment (VUEs) share the access link spectrum, and a high-altitude platform (HAP) communicates with roadside units (RSUs) through a backhaul communication link. We propose an improved algorithm for user association that selects VUEs for HAPs based on channel coefficient ratios and terrestrial VUEs based on a caching-state backhaul communication link. The joint optimization problems aim to maximize a utility function that considers VUE transmission rates and cross-tier interference while meeting the constraints of backhaul transmission rates and QoS requirements of each VUE. The joint resource allocation optimization problem consists of three sub-problems: bandwidth allocation, user association, and transmission power allocation. We derive a closed-form solution for bandwidth allocation and solve the transmission power allocation sub-problem iteratively using Taylor expansion to transform a non-convex term into a convex one. Our proposed three-stage iterative algorithm for resource allocation integrates all three sub-problems and is shown to be effective through simulation results. Specifically, the results demonstrate that our solution achieves performance improvements over existing approaches.
Dynamic Resource Management in Integrated NOMA Terrestrial-Satellite Networks using Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:This study introduces a resource allocation framework for integrated satellite-terrestrial networks to address these challenges. The framework leverages local cache pool deployments and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) to reduce time delays and improve energy efficiency. Our proposed approach utilizes a multi-agent enabled deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm (MADDPG) to optimize user association, cache design, and transmission power control, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency. The approach comprises two phases: User Association and Power Control, where users are treated as agents, and Cache Optimization, where the satellite (Bs) is considered the agent. Through extensive simulations, we demonstrate that our approach surpasses conventional single-agent deep reinforcement learning algorithms in addressing cache design and resource allocation challenges in integrated terrestrial-satellite networks. Specifically, our proposed approach achieves significantly higher energy efficiency and reduced time delays compared to existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge