Alexis Bose
Path Loss Prediction Using Machine Learning with Extended Features
Jan 14, 2025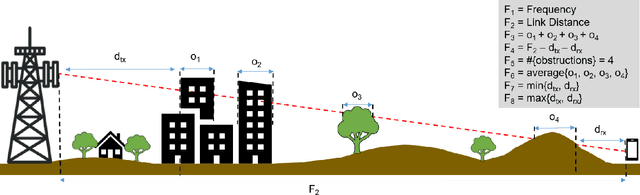
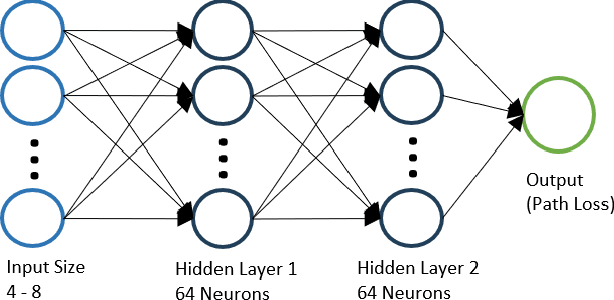
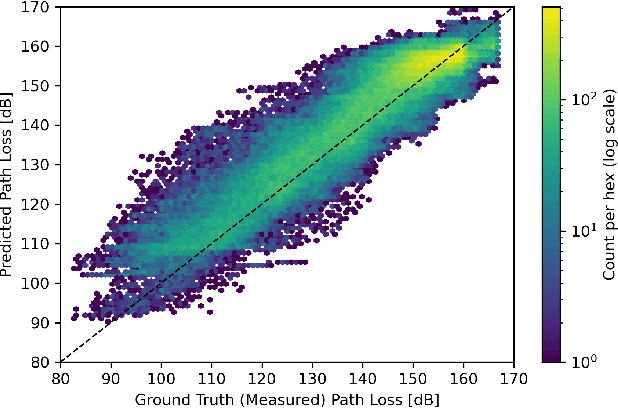
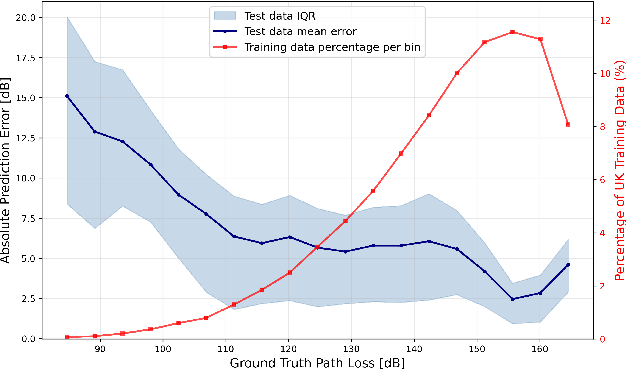
Abstract:Wireless communications rely on path loss modeling, which is most effective when it includes the physical details of the propagation environment. Acquiring this data has historically been challenging, but geographic information system data is becoming increasingly available with higher resolution and accuracy. Access to such details enables propagation models to more accurately predict coverage and minimize interference in wireless deployments. Machine learning-based modeling can significantly support this effort, with feature-based approaches allowing for accurate, efficient, and scalable propagation modeling. Building on previous work, we introduce an extended set of features that improves prediction accuracy while, most importantly, maintaining model generalization across a broad range of environments.
Uncertainty Estimation for Path Loss and Radio Metric Models
Jan 10, 2025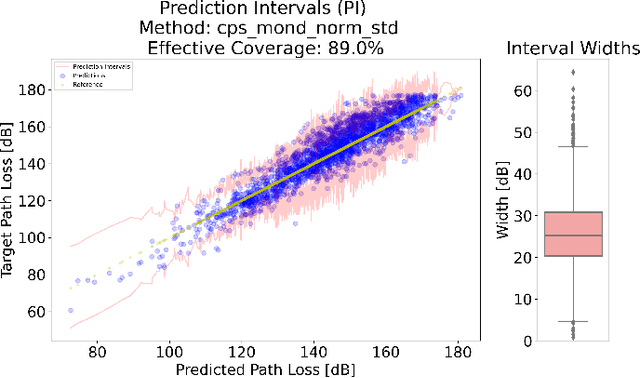
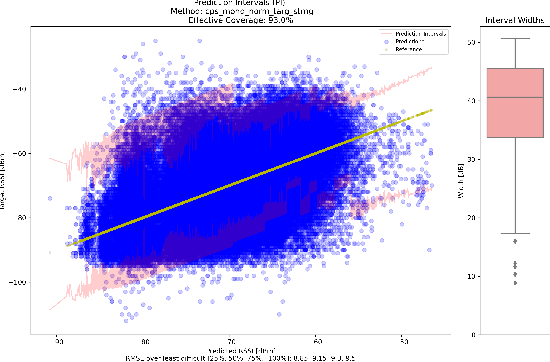
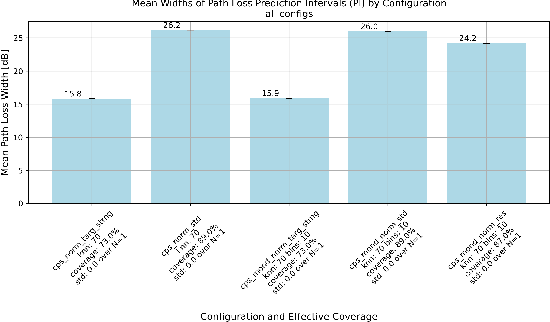
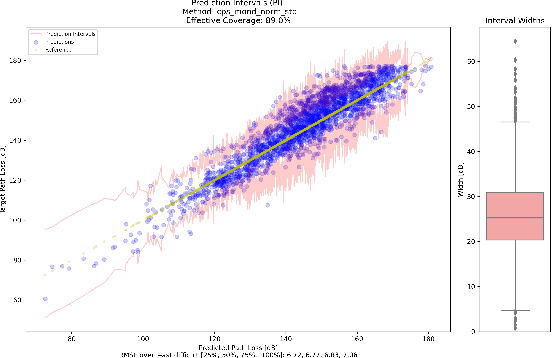
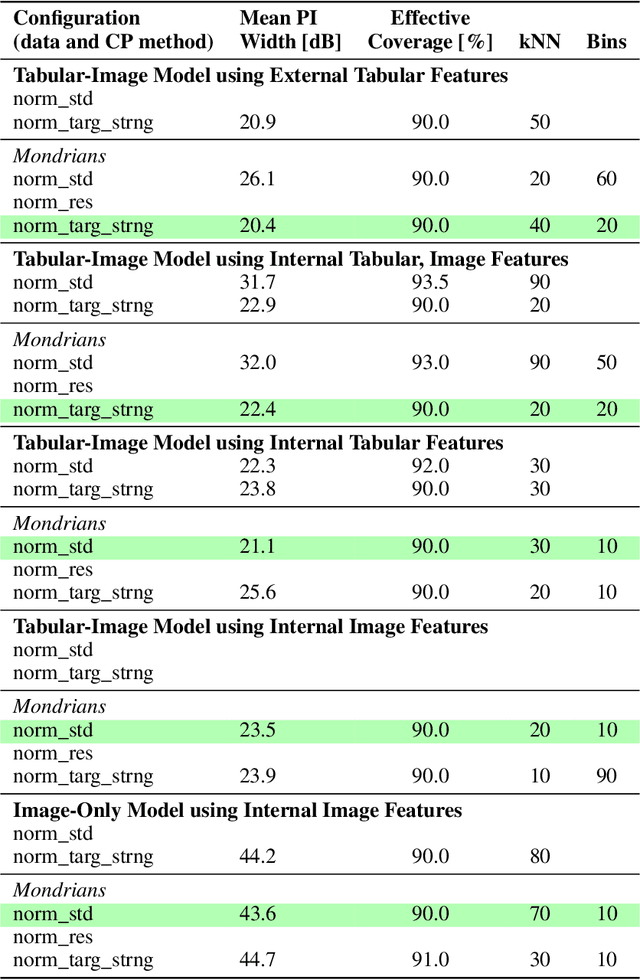
Abstract:This research leverages Conformal Prediction (CP) in the form of Conformal Predictive Systems (CPS) to accurately estimate uncertainty in a suite of machine learning (ML)-based radio metric models [1] as well as in a 2-D map-based ML path loss model [2]. Utilizing diverse difficulty estimators, we construct 95% confidence prediction intervals (PIs) that are statistically robust. Our experiments demonstrate that CPS models, trained on Toronto datasets, generalize effectively to other cities such as Vancouver and Montreal, maintaining high coverage and reliability. Furthermore, the employed difficulty estimators identify challenging samples, leading to measurable reductions in RMSE as dataset difficulty decreases. These findings highlight the effectiveness of scalable and reliable uncertainty estimation through CPS in wireless network modeling, offering important potential insights for network planning, operations, and spectrum management.
Machine Learning for Modeling Wireless Radio Metrics with Crowdsourced Data and Local Environment Features
Jan 02, 2025

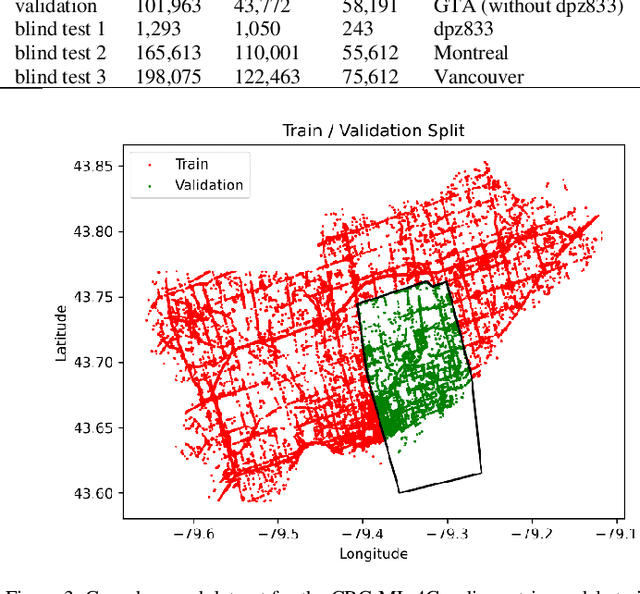

Abstract:This paper presents a suite of machine learning models, CRC-ML-Radio Metrics, designed for modeling RSRP, RSRQ, and RSSI wireless radio metrics in 4G environments. These models utilize crowdsourced data with local environmental features to enhance prediction accuracy across both indoor at elevation and outdoor urban settings. They achieve RMSE performance of 9.76 to 11.69 dB for RSRP, 2.90 to 3.23 dB for RSRQ, and 9.50 to 10.36 dB for RSSI, evaluated on over 300,000 data points in the Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver areas. These results demonstrate the robustness and adaptability of the models, supporting precise network planning and quality of service optimization in complex Canadian urban environments.
Conformal Prediction for Multimodal Regression
Oct 25, 2024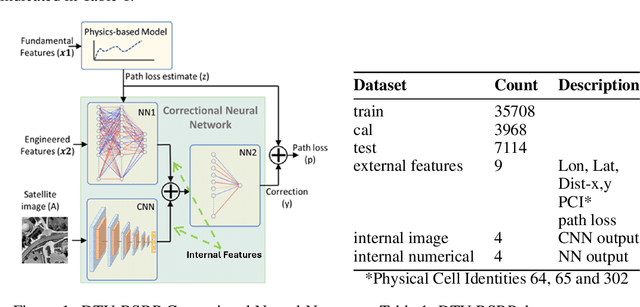
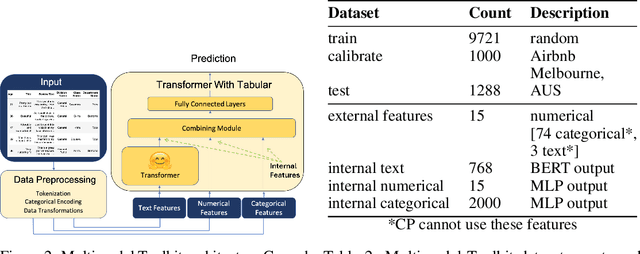
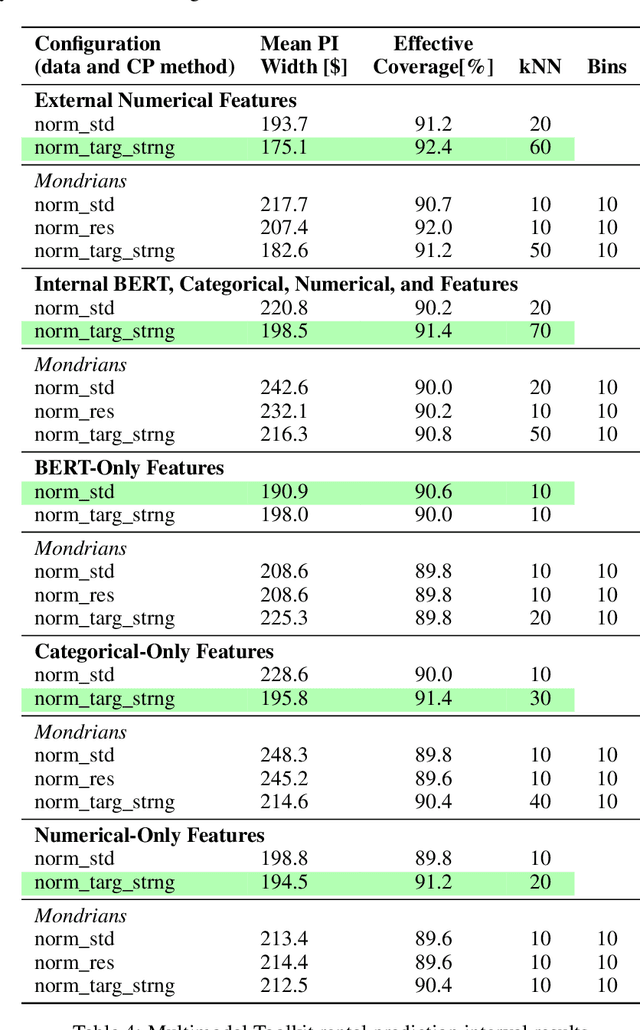
Abstract:This paper introduces multimodal conformal regression. Traditionally confined to scenarios with solely numerical input features, conformal prediction is now extended to multimodal contexts through our methodology, which harnesses internal features from complex neural network architectures processing images and unstructured text. Our findings highlight the potential for internal neural network features, extracted from convergence points where multimodal information is combined, to be used by conformal prediction to construct prediction intervals (PIs). This capability paves new paths for deploying conformal prediction in domains abundant with multimodal data, enabling a broader range of problems to benefit from guaranteed distribution-free uncertainty quantification.
Target Strangeness: A Novel Conformal Prediction Difficulty Estimator
Oct 24, 2024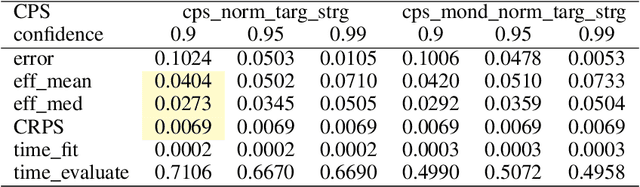
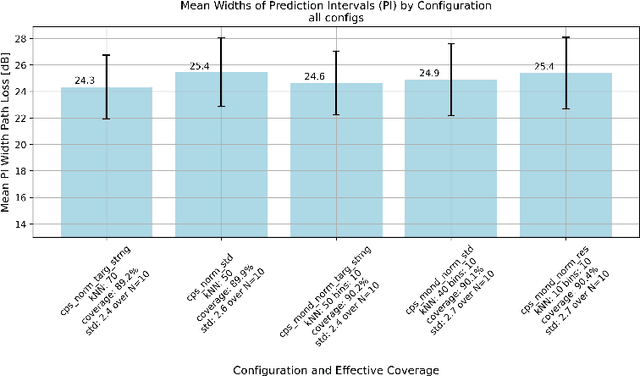
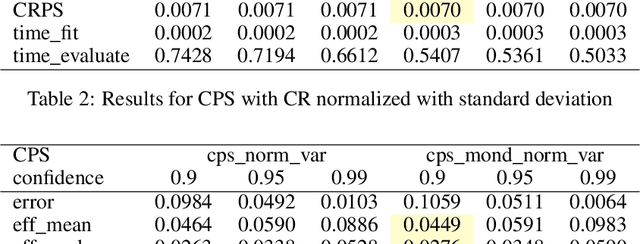
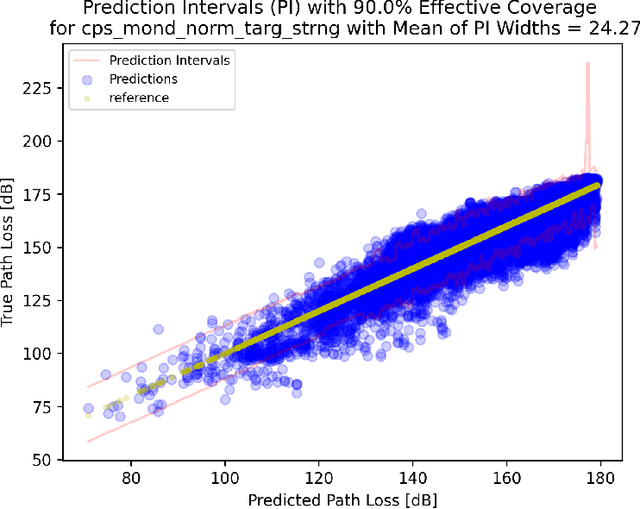
Abstract:This paper introduces Target Strangeness, a novel difficulty estimator for conformal prediction (CP) that offers an alternative approach for normalizing prediction intervals (PIs). By assessing how atypical a prediction is within the context of its nearest neighbours' target distribution, Target Strangeness can surpass the current state-of-the-art performance. This novel difficulty estimator is evaluated against others in the context of several conformal regression experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge