Alexey Unagaev
Optimal Use of Multi-spectral Satellite Data with Convolutional Neural Networks
Sep 15, 2020

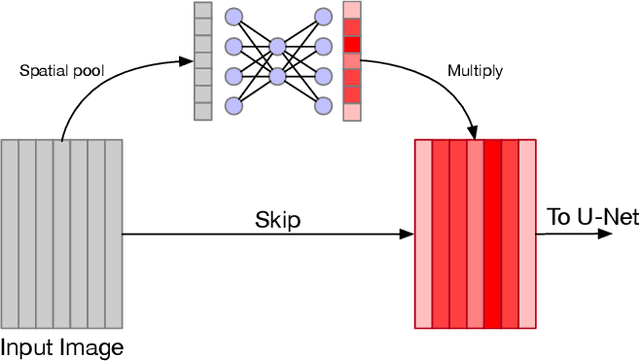
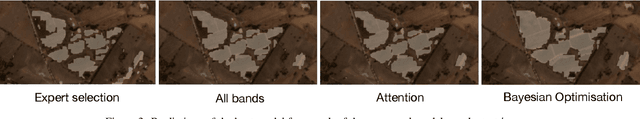
Abstract:The analysis of satellite imagery will prove a crucial tool in the pursuit of sustainable development. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have made large gains in natural image analysis, their application to multi-spectral satellite images (wherein input images have a large number of channels) remains relatively unexplored. In this paper, we compare different methods of leveraging multi-band information with CNNs, demonstrating the performance of all compared methods on the task of semantic segmentation of agricultural vegetation (vineyards). We show that standard industry practice of using bands selected by a domain expert leads to a significantly worse test accuracy than the other methods compared. Specifically, we compare: using bands specified by an expert; using all available bands; learning attention maps over the input bands; and leveraging Bayesian optimisation to dictate band choice. We show that simply using all available band information already increases test time performance, and show that the Bayesian optimisation, first applied to band selection in this work, can be used to further boost accuracy.
SMArtCast: Predicting soil moisture interpolations into the future using Earth observation data in a deep learning framework
Mar 16, 2020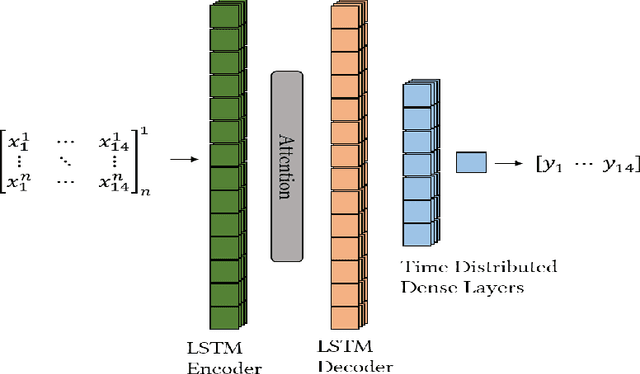
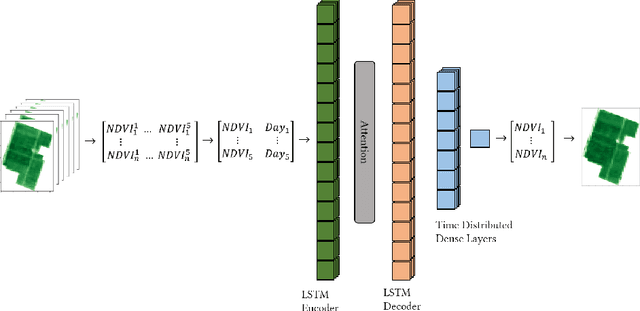
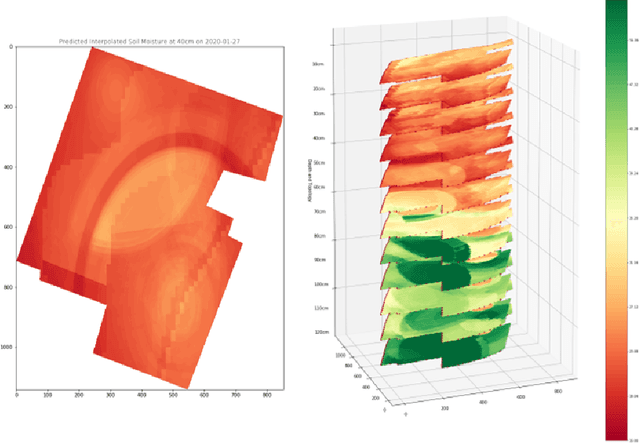
Abstract:Soil moisture is critical component of crop health and monitoring it can enable further actions for increasing yield or preventing catastrophic die off. As climate change increases the likelihood of extreme weather events and reduces the predictability of weather, and non-optimal soil moistures for crops may become more likely. In this work, we a series of LSTM architectures to analyze measurements of soil moisture and vegetation indiced derived from satellite imagery. The system learns to predict the future values of these measurements. These spatially sparse values and indices are used as input features to an interpolation method that infer spatially dense moisture map for a future time point. This has the potential to provide advance warning for soil moistures that may be inhospitable to crops across an area with limited monitoring capacity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge