Alexandros Fragkiadakis
Evaluating Short-Term Forecasting of Multiple Time Series in IoT Environments
Jun 15, 2022
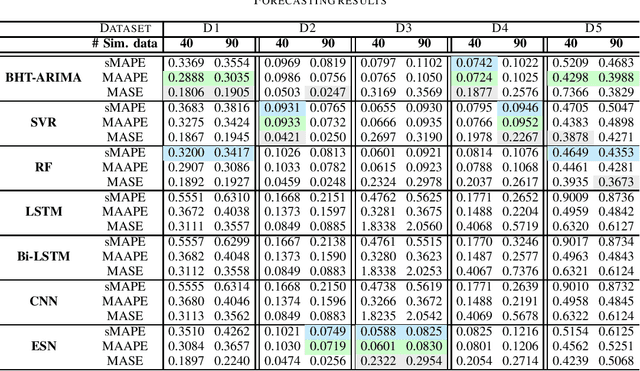
Abstract:Modern Internet of Things (IoT) environments are monitored via a large number of IoT enabled sensing devices, with the data acquisition and processing infrastructure setting restrictions in terms of computational power and energy resources. To alleviate this issue, sensors are often configured to operate at relatively low sampling frequencies, yielding a reduced set of observations. Nevertheless, this can hamper dramatically subsequent decision-making, such as forecasting. To address this problem, in this work we evaluate short-term forecasting in highly underdetermined cases, i.e., the number of sensor streams is much higher than the number of observations. Several statistical, machine learning and neural network-based models are thoroughly examined with respect to the resulting forecasting accuracy on five different real-world datasets. The focus is given on a unified experimental protocol especially designed for short-term prediction of multiple time series at the IoT edge. The proposed framework can be considered as an important step towards establishing a solid forecasting strategy in resource constrained IoT applications.
Autonomous Maintenance in IoT Networks via AoI-driven Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 31, 2020


Abstract:Internet of Things (IoT) with its growing number of deployed devices and applications raises significant challenges for network maintenance procedures. In this work, we formulate a problem of autonomous maintenance in IoT networks as a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process. Subsequently, we utilize Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithms (DRL) to train agents that decide if a maintenance procedure is in order or not and, in the former case, the proper type of maintenance needed. To avoid wasting the scarce resources of IoT networks we utilize the Age of Information (AoI) metric as a reward signal for the training of the smart agents. AoI captures the freshness of the sensory data which are transmitted by the IoT sensors as part of their normal service provision. Numerical results indicate that AoI integrates enough information about the past and present states of the system to be successfully used in the training of smart agents for the autonomous maintenance of the network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge