Alexander Thoms
Distributed Certifiably Correct Range-Aided SLAM
Mar 05, 2025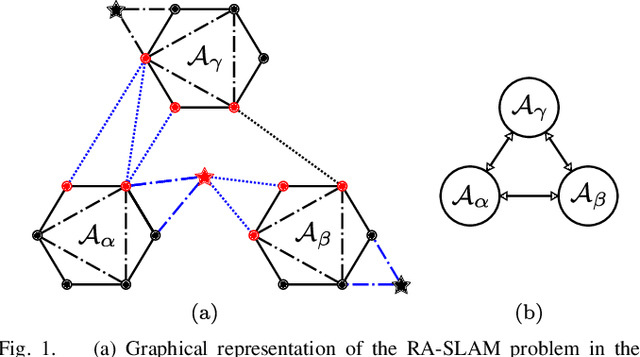
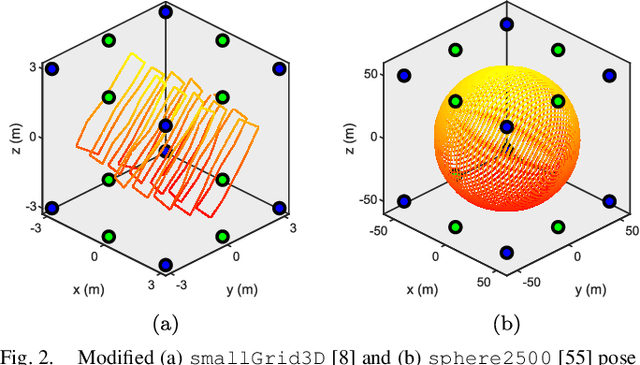
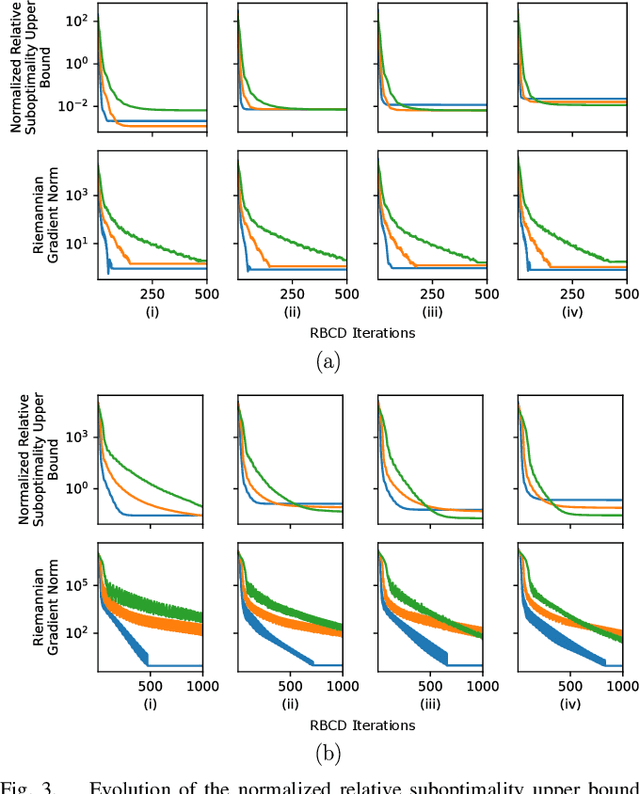
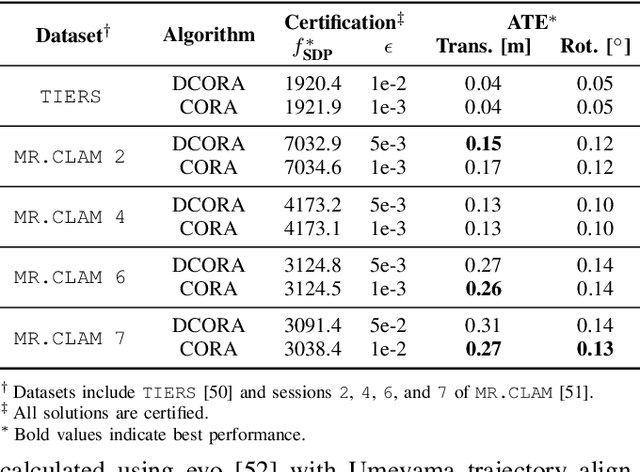
Abstract:Reliable simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms are necessary for safety-critical autonomous navigation. In the communication-constrained multi-agent setting, navigation systems increasingly use point-to-point range sensors as they afford measurements with low bandwidth requirements and known data association. The state estimation problem for these systems takes the form of range-aided (RA) SLAM. However, distributed algorithms for solving the RA-SLAM problem lack formal guarantees on the quality of the returned estimate. To this end, we present the first distributed algorithm for RA-SLAM that can efficiently recover certifiably globally optimal solutions. Our algorithm, distributed certifiably correct RA-SLAM (DCORA), achieves this via the Riemannian Staircase method, where computational procedures developed for distributed certifiably correct pose graph optimization are generalized to the RA-SLAM problem. We demonstrate DCORA's efficacy on real-world multi-agent datasets by achieving absolute trajectory errors comparable to those of a state-of-the-art centralized certifiably correct RA-SLAM algorithm. Additionally, we perform a parametric study on the structure of the RA-SLAM problem using synthetic data, revealing how common parameters affect DCORA's performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge