Alexander Rietzler
ANLS* -- A Universal Document Processing Metric for Generative Large Language Models
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Traditionally, discriminative models have been the predominant choice for tasks like document classification and information extraction. These models make predictions that fall into a limited number of predefined classes, facilitating a binary true or false evaluation and enabling the direct calculation of metrics such as the F1 score. However, recent advancements in generative large language models (GLLMs) have prompted a shift in the field due to their enhanced zero-shot capabilities, which eliminate the need for a downstream dataset and computationally expensive fine-tuning. However, evaluating GLLMs presents a challenge as the binary true or false evaluation used for discriminative models is not applicable to the predictions made by GLLMs. This paper introduces a new metric for generative models called ANLS* for evaluating a wide variety of tasks, including information extraction and classification tasks. The ANLS* metric extends existing ANLS metrics as a drop-in-replacement and is still compatible with previously reported ANLS scores. An evaluation of 7 different datasets and 3 different GLLMs using the ANLS* metric is also provided, demonstrating the importance of the proposed metric. We also benchmark a novel approach to generate prompts for documents, called SFT, against other prompting techniques such as LATIN. In 15 out of 21 cases, SFT outperforms other techniques and improves the state-of-the-art, sometimes by as much as $15$ percentage points. Sources are available at https://github.com/deepopinion/anls_star_metric
Adapt or Get Left Behind: Domain Adaptation through BERT Language Model Finetuning for Aspect-Target Sentiment Classification
Aug 30, 2019
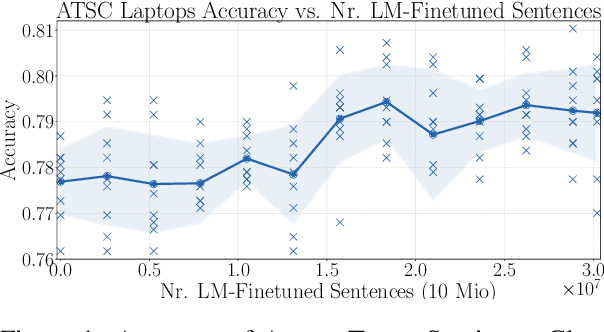
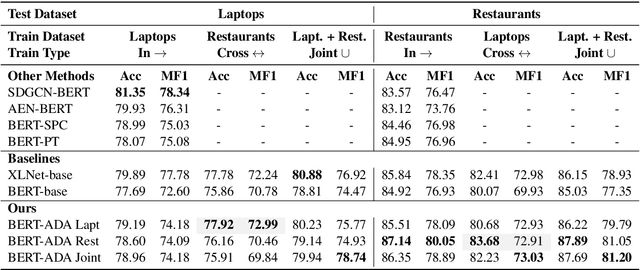
Abstract:Aspect-Target Sentiment Classification (ATSC) is a subtask of Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA), which has many applications e.g. in e-commerce, where data and insights from reviews can be leveraged to create value for businesses and customers. Recently, deep transfer-learning methods have been applied successfully to a myriad of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, including ATSC. Building on top of the prominent the BERT language model, we approach ATSC by using a two-step procedure: Self-supervised domain-specific BERT language model finetuning, followed by supervised task-specific finetuning. Our findings on how to best exploit domain-specific language model finetuning enables us to produce new state-of-the-art performance on the SemEval 2014 Task 4 restaurants dataset. In addition, to explore the real-world robustness of our models, we perform cross-domain evaluation. We show that a cross-domain adapted BERT language model performs significantly better compared to strong baseline models like vanilla BERT-base and XLNet-base.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge