Alexander Krolicki
Supervised DKRC with Images for Offline System Identification
Sep 06, 2021



Abstract:Koopman spectral theory has provided a new perspective in the field of dynamical systems in recent years. Modern dynamical systems are becoming increasingly non-linear and complex, and there is a need for a framework to model these systems in a compact and comprehensive representation for prediction and control. The central problem in applying Koopman theory to a system of interest is that the choice of finite-dimensional basis functions is typically done apriori, using expert knowledge of the systems dynamics. Our approach learns these basis functions using a supervised learning approach where a combination of autoencoders and deep neural networks learn the basis functions for any given system. We demonstrate this approach on a simple pendulum example in which we obtain a linear representation of the non-linear system and then predict the future state trajectories given some initial conditions. We also explore how changing the input representation of the dynamic systems time series data can impact the quality of learned basis functions. This alternative representation is compared to the traditional raw time series data approach to determine which method results in lower reconstruction and prediction error of the true non-linear dynamics of the system.
Cell A* for Navigation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Partially-known Environments
Sep 16, 2020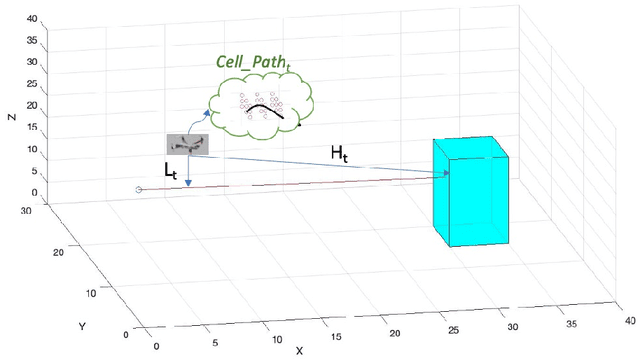


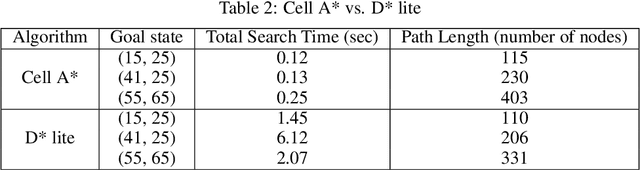
Abstract:Proper path planning is the first step of robust and efficient autonomous navigation for mobile robots. Meanwhile, it is still challenging for robots to work in a complex environment without complete prior information. This paper presents an extension to the A* search algorithm and its variants to make the path planning stable with less computational burden while handling long-distance tasks. The implemented algorithm is capable of online searching for a collision-free and smooth path when heading to the defined goal position. This paper deploys the algorithm on the autonomous drone platform and implements it on a remote control car for algorithm efficiency validation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge