Alex Spaeth
Modular Self-Lock Origami: design, modeling, and simulation to improve the performance of a rotational joint
Jul 31, 2023Abstract:Origami structures have been widely explored in robotics due to their many potential advantages. Origami robots can be very compact, as well as cheap and efficient to produce. In particular, they can be constructed in a flat format using modern manufacturing techniques. Rotational motion is essential for robotics, and a variety of origami rotational joints have been proposed in the literature. However, few of these are even approximately flat-foldable. One potential enabler of flat origami rotational joints is the inclusion of lightweight pneumatic pouches which actuate the origami's folds; however, pouch actuators only enable a relatively small amount of rotational displacement. The previously proposed Four-Vertex Origami is a flat-foldable structure which provides an angular multiplier for a pouch actuator, but suffers from a degenerate state. This paper presents a novel rigid origami, the Self-Lock Origami, which eliminates this degeneracy by slightly relaxing the assumption of flat-foldability. This joint is analysed in terms of a trade-off between the angular multiplier and the mechanical advantage. Furthermore, the Self-Lock Origami is a modular joint which can be connected to similar or different joints to produce complex movements for various applications; three different manipulator designs are introduced as a proof of concept.
A Geometric Kinematic Model for Flexible Voxel-Based Robots
Aug 21, 2021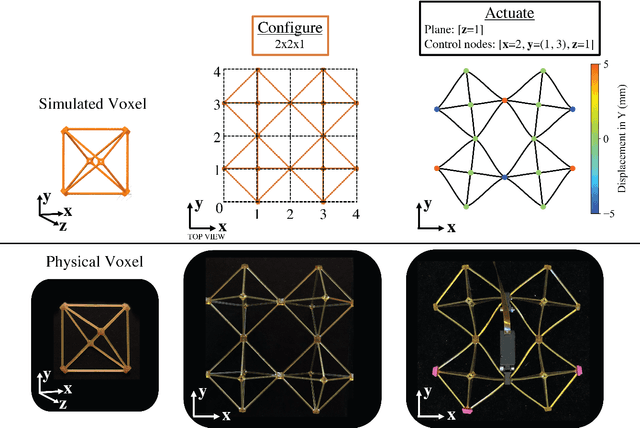
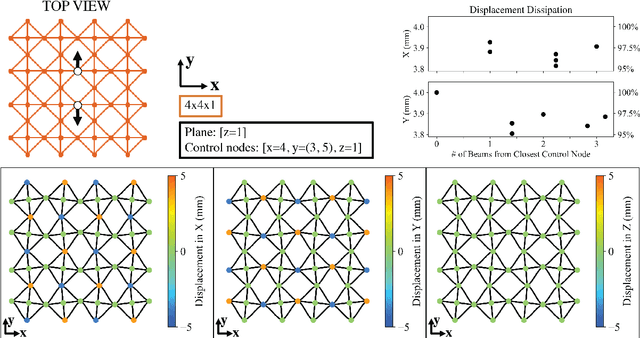
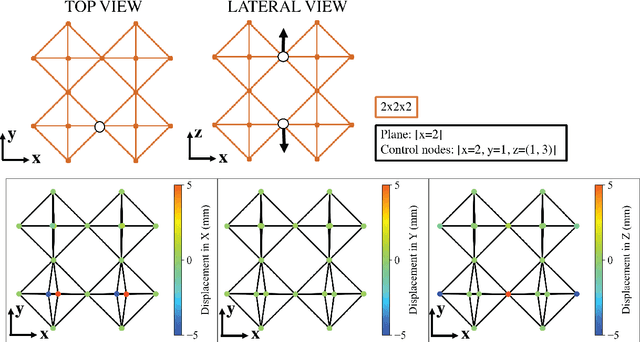
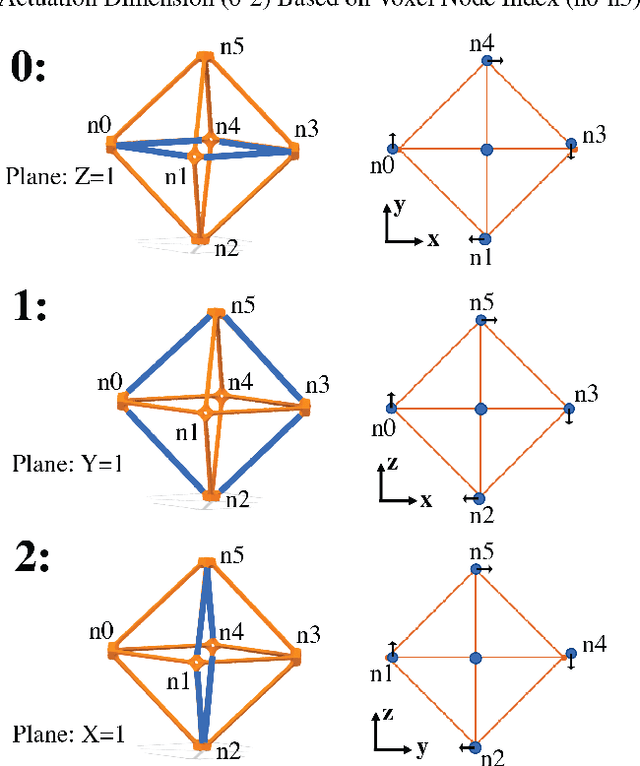
Abstract:Voxel-based structures provide a modular, mechanically flexible periodic lattice which can be used as a soft robot through internal deformations. To engage these structures for robotic tasks, we use a finite element method to characterize the motion caused by deforming single degrees of freedom and develop a reduced kinematic model. We find that node translations propagate periodically along geometric planes within the lattice, and briefly show that translational modes dominate the energy usage of the actuators. The resulting kinematic model frames the structural deformations in terms of user-defined control and end effector nodes, which further reduces the model size. The derived Planes of Motion (POM) model can be equivalently used for forward and inverse kinematics, as demonstrated by the design of a tripod stable gait for a locomotive voxel robot and validation of the quasi-static model through physical experiments.
Spiking neural state machine for gait frequency entrainment in a flexible modular robot
Jul 14, 2020



Abstract:We propose a modular architecture for neuromorphic closed-loop control based on bistable relaxation oscillator modules consisting of three spiking neurons each. Like its biological prototypes, this basic component is robust to parameter variation but can be modulated by external inputs. By combining these modules, we can construct a neural state machine capable of generating the cyclic or repetitive behaviors necessary for legged locomotion. A concrete case study for the approach is provided by a modular robot constructed from flexible plastic volumetric pixels, in which we produce a forward crawling gait entrained to the natural frequency of the robot by a minimal system of twelve neurons organized into four modules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge