Alex Bogun
Saliency Diversified Deep Ensemble for Robustness to Adversaries
Dec 07, 2021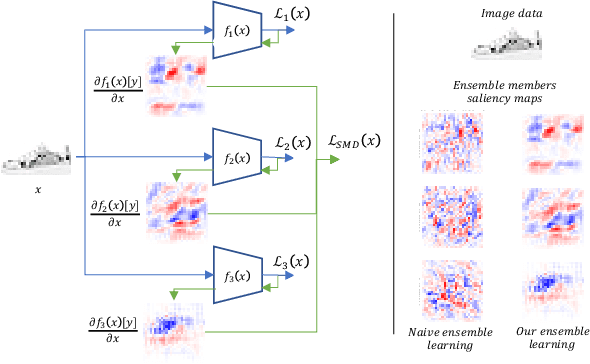
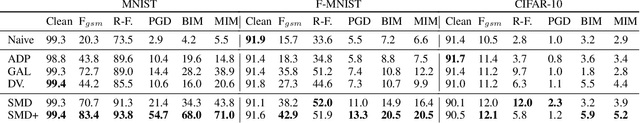
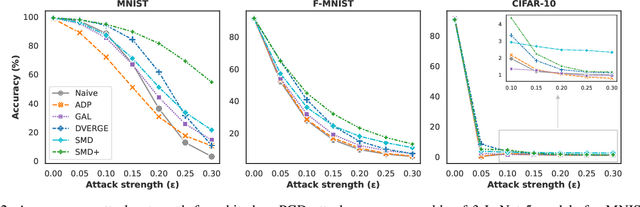
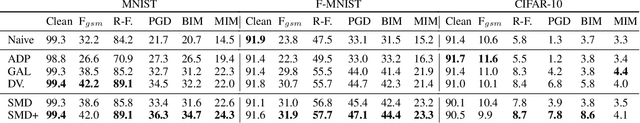
Abstract:Deep learning models have shown incredible performance on numerous image recognition, classification, and reconstruction tasks. Although very appealing and valuable due to their predictive capabilities, one common threat remains challenging to resolve. A specifically trained attacker can introduce malicious input perturbations to fool the network, thus causing potentially harmful mispredictions. Moreover, these attacks can succeed when the adversary has full access to the target model (white-box) and even when such access is limited (black-box setting). The ensemble of models can protect against such attacks but might be brittle under shared vulnerabilities in its members (attack transferability). To that end, this work proposes a novel diversity-promoting learning approach for the deep ensembles. The idea is to promote saliency map diversity (SMD) on ensemble members to prevent the attacker from targeting all ensemble members at once by introducing an additional term in our learning objective. During training, this helps us minimize the alignment between model saliencies to reduce shared member vulnerabilities and, thus, increase ensemble robustness to adversaries. We empirically show a reduced transferability between ensemble members and improved performance compared to the state-of-the-art ensemble defense against medium and high strength white-box attacks. In addition, we demonstrate that our approach combined with existing methods outperforms state-of-the-art ensemble algorithms for defense under white-box and black-box attacks.
Heterogeneous Ensemble for ESG Ratings Prediction
Sep 21, 2021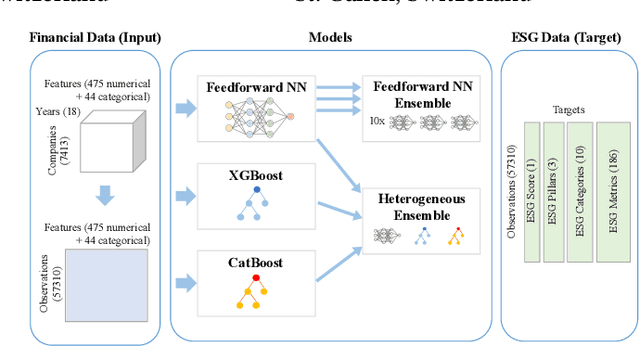
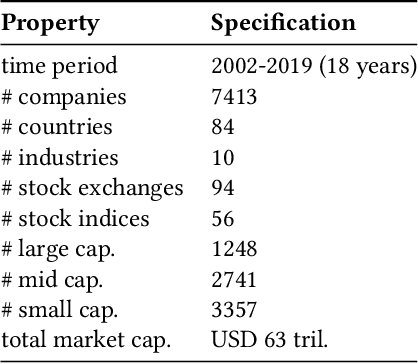
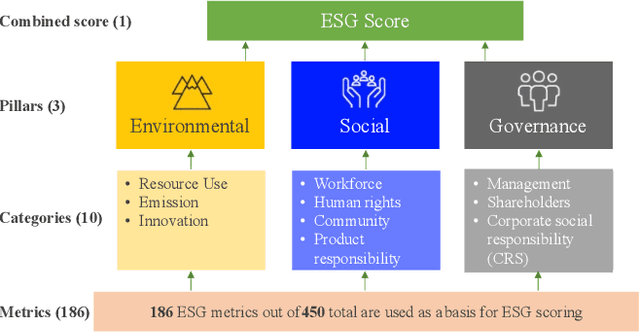

Abstract:Over the past years, topics ranging from climate change to human rights have seen increasing importance for investment decisions. Hence, investors (asset managers and asset owners) who wanted to incorporate these issues started to assess companies based on how they handle such topics. For this assessment, investors rely on specialized rating agencies that issue ratings along the environmental, social and governance (ESG) dimensions. Such ratings allow them to make investment decisions in favor of sustainability. However, rating agencies base their analysis on subjective assessment of sustainability reports, not provided by every company. Furthermore, due to human labor involved, rating agencies are currently facing the challenge to scale up the coverage in a timely manner. In order to alleviate these challenges and contribute to the overall goal of supporting sustainability, we propose a heterogeneous ensemble model to predict ESG ratings using fundamental data. This model is based on feedforward neural network, CatBoost and XGBoost ensemble members. Given the public availability of fundamental data, the proposed method would allow cost-efficient and scalable creation of initial ESG ratings (also for companies without sustainability reporting). Using our approach we are able to explain 54% of the variation in ratings R2 using fundamental data and outperform prior work in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge