Alessandro Ottino
Partitioning Distributed Compute Jobs with Reinforcement Learning and Graph Neural Networks
Jan 31, 2023Abstract:From natural language processing to genome sequencing, large-scale machine learning models are bringing advances to a broad range of fields. Many of these models are too large to be trained on a single machine, and instead must be distributed across multiple devices. This has motivated the research of new compute and network systems capable of handling such tasks. In particular, recent work has focused on developing management schemes which decide how to allocate distributed resources such that some overall objective, such as minimising the job completion time (JCT), is optimised. However, such studies omit explicit consideration of how much a job should be distributed, usually assuming that maximum distribution is desirable. In this work, we show that maximum parallelisation is sub-optimal in relation to user-critical metrics such as throughput and blocking rate. To address this, we propose PAC-ML (partitioning for asynchronous computing with machine learning). PAC-ML leverages a graph neural network and reinforcement learning to learn how much to partition computation graphs such that the number of jobs which meet arbitrary user-defined JCT requirements is maximised. In experiments with five real deep learning computation graphs on a recently proposed optical architecture across four user-defined JCT requirement distributions, we demonstrate PAC-ML achieving up to 56.2% lower blocking rates in dynamic job arrival settings than the canonical maximum parallelisation strategy used by most prior works.
RAMP: A Flat Nanosecond Optical Network and MPI Operations for Distributed Deep Learning Systems
Nov 28, 2022Abstract:Distributed deep learning (DDL) systems strongly depend on network performance. Current electronic packet switched (EPS) network architectures and technologies suffer from variable diameter topologies, low-bisection bandwidth and over-subscription affecting completion time of communication and collective operations. We introduce a near-exascale, full-bisection bandwidth, all-to-all, single-hop, all-optical network architecture with nanosecond reconfiguration called RAMP, which supports large-scale distributed and parallel computing systems (12.8~Tbps per node for up to 65,536 nodes). For the first time, a custom RAMP-x MPI strategy and a network transcoder is proposed to run MPI collective operations across the optical circuit switched (OCS) network in a schedule-less and contention-less manner. RAMP achieves 7.6-171$\times$ speed-up in completion time across all MPI operations compared to realistic EPS and OCS counterparts. It can also deliver a 1.3-16$\times$ and 7.8-58$\times$ reduction in Megatron and DLRM training time respectively} while offering 42-53$\times$ and 3.3-12.4$\times$ improvement in energy consumption and cost respectively.
Experimental Demonstration of Learned Time-Domain Digital Back-Propagation
Dec 23, 2019
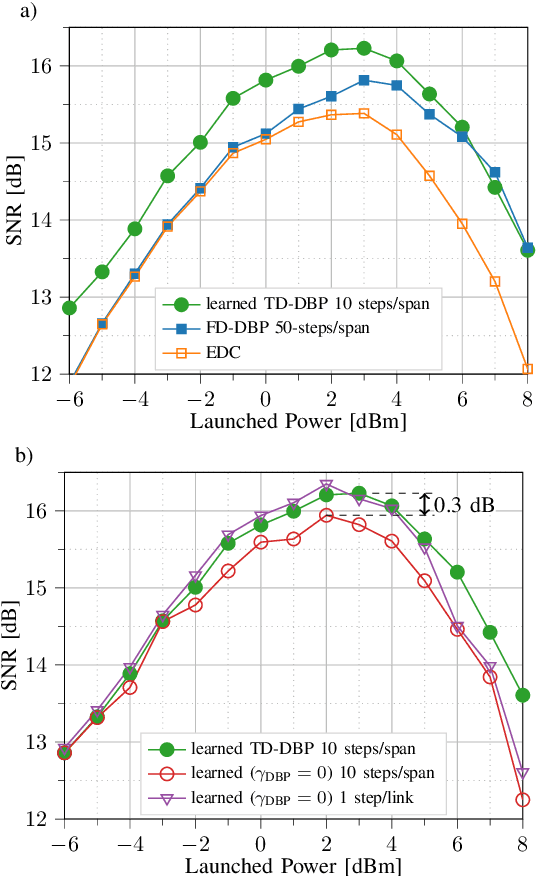

Abstract:We present the first experimental demonstration of learned time-domain digital back-propagation (DBP), in 64-GBd dual-polarization 64-QAM signal transmission over 1014 km. Performance gains were comparable to those obtained with conventional, higher complexity, frequency-domain DBP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge