Alberto Jesu
Reinforcement Learning on Encrypted Data
Sep 16, 2021
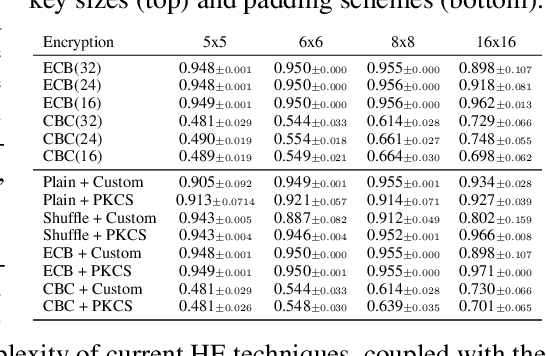
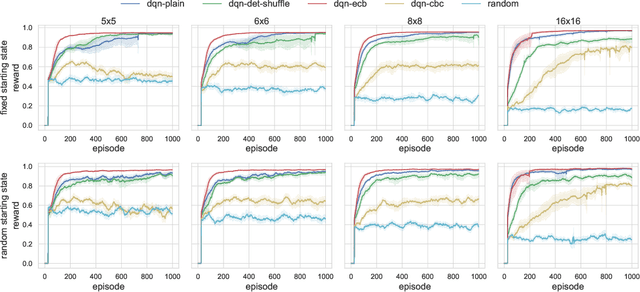
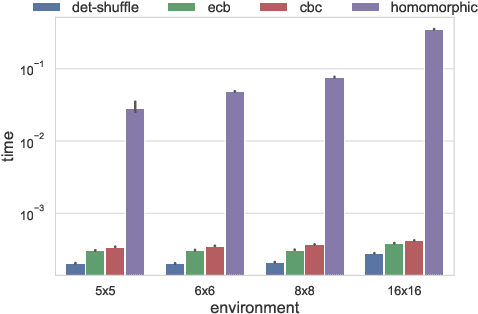
Abstract:The growing number of applications of Reinforcement Learning (RL) in real-world domains has led to the development of privacy-preserving techniques due to the inherently sensitive nature of data. Most existing works focus on differential privacy, in which information is revealed in the clear to an agent whose learned model should be robust against information leakage to malicious third parties. Motivated by use cases in which only encrypted data might be shared, such as information from sensitive sites, in this work we consider scenarios in which the inputs themselves are sensitive and cannot be revealed. We develop a simple extension to the MDP framework which provides for the encryption of states. We present a preliminary, experimental study of how a DQN agent trained on encrypted states performs in environments with discrete and continuous state spaces. Our results highlight that the agent is still capable of learning in small state spaces even in presence of non-deterministic encryption, but performance collapses in more complex environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge