Akond Rahman
Large Language Models for IT Automation Tasks: Are We There Yet?
May 26, 2025Abstract:LLMs show promise in code generation, yet their effectiveness for IT automation tasks, particularly for tools like Ansible, remains understudied. Existing benchmarks rely primarily on synthetic tasks that fail to capture the needs of practitioners who use IT automation tools, such as Ansible. We present ITAB (IT Automation Task Benchmark), a benchmark of 126 diverse tasks (e.g., configuring servers, managing files) where each task accounts for state reconciliation: a property unique to IT automation tools. ITAB evaluates LLMs' ability to generate functional Ansible automation scripts via dynamic execution in controlled environments. We evaluate 14 open-source LLMs, none of which accomplish pass@10 at a rate beyond 12%. To explain these low scores, we analyze 1,411 execution failures across the evaluated LLMs and identify two main categories of prevalent semantic errors: failures in state reconciliation related reasoning (44.87% combined from variable (11.43%), host (11.84%), path(11.63%), and template (9.97%) issues) and deficiencies in module-specific execution knowledge (24.37% combined from Attribute and parameter (14.44%) and module (9.93%) errors). Our findings reveal key limitations in open-source LLMs' ability to track state changes and apply specialized module knowledge, indicating that reliable IT automation will require major advances in state reasoning and domain-specific execution understanding.
Case Study-Based Approach of Quantum Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Quantum Support Vector Machine for Malware Classification and Protection
Jun 01, 2023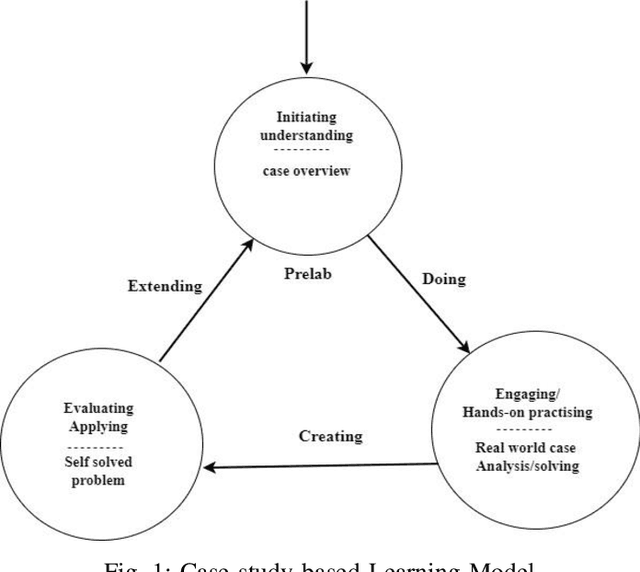
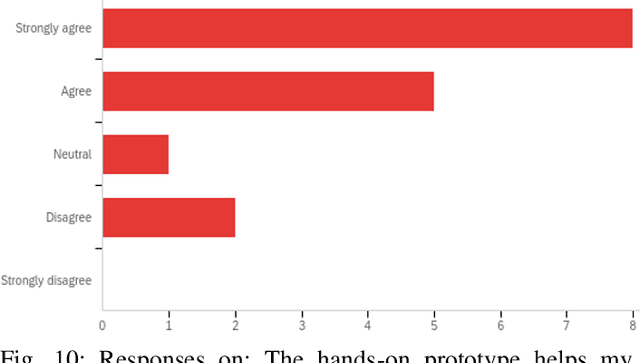
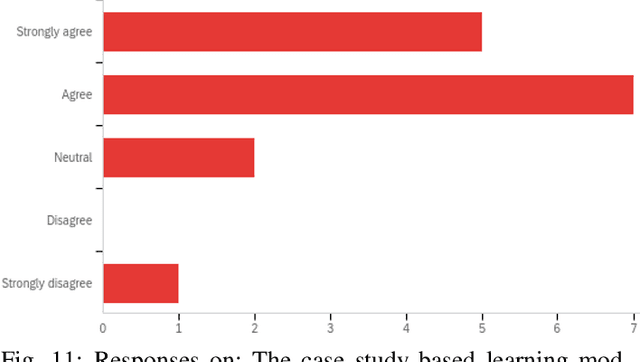

Abstract:Quantum machine learning (QML) is an emerging field of research that leverages quantum computing to improve the classical machine learning approach to solve complex real world problems. QML has the potential to address cybersecurity related challenges. Considering the novelty and complex architecture of QML, resources are not yet explicitly available that can pave cybersecurity learners to instill efficient knowledge of this emerging technology. In this research, we design and develop QML-based ten learning modules covering various cybersecurity topics by adopting student centering case-study based learning approach. We apply one subtopic of QML on a cybersecurity topic comprised of pre-lab, lab, and post-lab activities towards providing learners with hands-on QML experiences in solving real-world security problems. In order to engage and motivate students in a learning environment that encourages all students to learn, pre-lab offers a brief introduction to both the QML subtopic and cybersecurity problem. In this paper, we utilize quantum support vector machine (QSVM) for malware classification and protection where we use open source Pennylane QML framework on the drebin215 dataset. We demonstrate our QSVM model and achieve an accuracy of 95% in malware classification and protection. We will develop all the modules and introduce them to the cybersecurity community in the coming days.
Software Supply Chain Vulnerabilities Detection in Source Code: Performance Comparison between Traditional and Quantum Machine Learning Algorithms
May 31, 2023



Abstract:The software supply chain (SSC) attack has become one of the crucial issues that are being increased rapidly with the advancement of the software development domain. In general, SSC attacks execute during the software development processes lead to vulnerabilities in software products targeting downstream customers and even involved stakeholders. Machine Learning approaches are proven in detecting and preventing software security vulnerabilities. Besides, emerging quantum machine learning can be promising in addressing SSC attacks. Considering the distinction between traditional and quantum machine learning, performance could be varies based on the proportions of the experimenting dataset. In this paper, we conduct a comparative analysis between quantum neural networks (QNN) and conventional neural networks (NN) with a software supply chain attack dataset known as ClaMP. Our goal is to distinguish the performance between QNN and NN and to conduct the experiment, we develop two different models for QNN and NN by utilizing Pennylane for quantum and TensorFlow and Keras for traditional respectively. We evaluated the performance of both models with different proportions of the ClaMP dataset to identify the f1 score, recall, precision, and accuracy. We also measure the execution time to check the efficiency of both models. The demonstration result indicates that execution time for QNN is slower than NN with a higher percentage of datasets. Due to recent advancements in QNN, a large level of experiments shall be carried out to understand both models accurately in our future research.
Malware Detection and Prevention using Artificial Intelligence Techniques
Jun 26, 2022



Abstract:With the rapid technological advancement, security has become a major issue due to the increase in malware activity that poses a serious threat to the security and safety of both computer systems and stakeholders. To maintain stakeholders, particularly, end users security, protecting the data from fraudulent efforts is one of the most pressing concerns. A set of malicious programming code, scripts, active content, or intrusive software that is designed to destroy intended computer systems and programs or mobile and web applications is referred to as malware. According to a study, naive users are unable to distinguish between malicious and benign applications. Thus, computer systems and mobile applications should be designed to detect malicious activities towards protecting the stakeholders. A number of algorithms are available to detect malware activities by utilizing novel concepts including Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning. In this study, we emphasize Artificial Intelligence (AI) based techniques for detecting and preventing malware activity. We present a detailed review of current malware detection technologies, their shortcomings, and ways to improve efficiency. Our study shows that adopting futuristic approaches for the development of malware detection applications shall provide significant advantages. The comprehension of this synthesis shall help researchers for further research on malware detection and prevention using AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge