Akansha Gautam
Fake News Detection System using XLNet model with Topic Distributions: CONSTRAINT@AAAI2021 Shared Task
Jan 12, 2021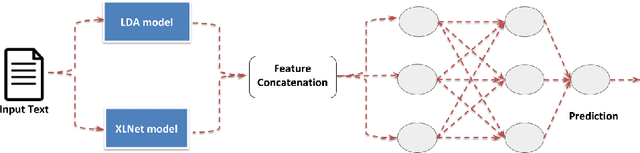

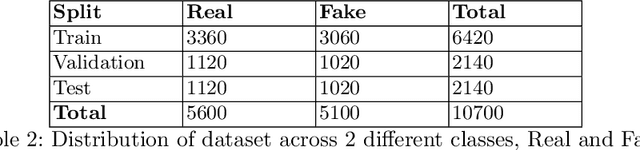
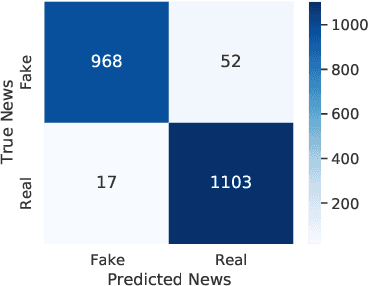
Abstract:With the ease of access to information, and its rapid dissemination over the internet (both velocity and volume), it has become challenging to filter out truthful information from fake ones. The research community is now faced with the task of automatic detection of fake news, which carries real-world socio-political impact. One such research contribution came in the form of the Constraint@AAA12021 Shared Task on COVID19 Fake News Detection in English. In this paper, we shed light on a novel method we proposed as a part of this shared task. Our team introduced an approach to combine topical distributions from Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) with contextualized representations from XLNet. We also compared our method with existing baselines to show that XLNet + Topic Distributions outperforms other approaches by attaining an F1-score of 0.967.
SGG: Spinbot, Grammarly and GloVe based Fake News Detection
Aug 16, 2020


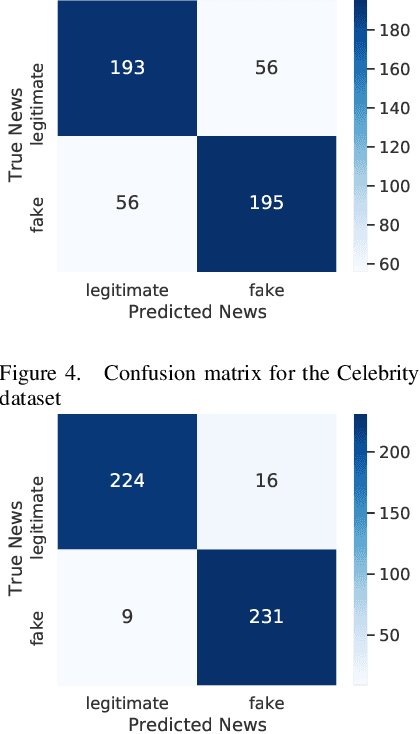
Abstract:Recently, news consumption using online news portals has increased exponentially due to several reasons, such as low cost and easy accessibility. However, such online platforms inadvertently also become the cause of spreading false information across the web. They are being misused quite frequently as a medium to disseminate misinformation and hoaxes. Such malpractices call for a robust automatic fake news detection system that can keep us at bay from such misinformation and hoaxes. We propose a robust yet simple fake news detection system, leveraging the tools for paraphrasing, grammar-checking, and word-embedding. In this paper, we try to the potential of these tools in jointly unearthing the authenticity of a news article. Notably, we leverage Spinbot (for paraphrasing), Grammarly (for grammar-checking), and GloVe (for word-embedding) tools for this purpose. Using these tools, we were able to extract novel features that could yield state-of-the-art results on the Fake News AMT dataset and comparable results on Celebrity datasets when combined with some of the essential features. More importantly, the proposed method is found to be more robust empirically than the existing ones, as revealed in our cross-domain analysis and multi-domain analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge