Aishwarya Sivaraman
FETA: Fairness Enforced Verifying, Training, and Predicting Algorithms for Neural Networks
Jun 01, 2022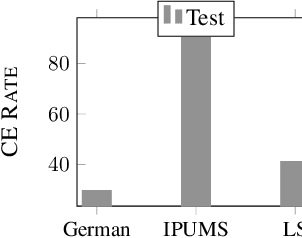
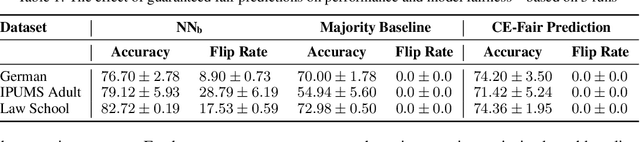
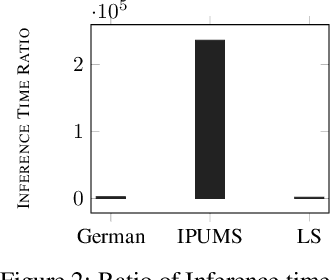
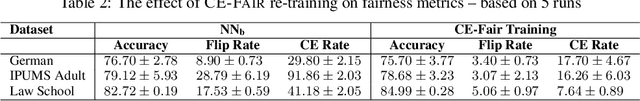
Abstract:Algorithmic decision making driven by neural networks has become very prominent in applications that directly affect people's quality of life. In this paper, we study the problem of verifying, training, and guaranteeing individual fairness of neural network models. A popular approach for enforcing fairness is to translate a fairness notion into constraints over the parameters of the model. However, such a translation does not always guarantee fair predictions of the trained neural network model. To address this challenge, we develop a counterexample-guided post-processing technique to provably enforce fairness constraints at prediction time. Contrary to prior work that enforces fairness only on points around test or train data, we are able to enforce and guarantee fairness on all points in the input domain. Additionally, we propose an in-processing technique to use fairness as an inductive bias by iteratively incorporating fairness counterexamples in the learning process. We have implemented these techniques in a tool called FETA. Empirical evaluation on real-world datasets indicates that FETA is not only able to guarantee fairness on-the-fly at prediction time but also is able to train accurate models exhibiting a much higher degree of individual fairness.
Counterexample-Guided Learning of Monotonic Neural Networks
Jun 16, 2020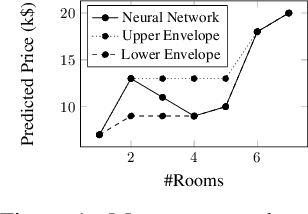
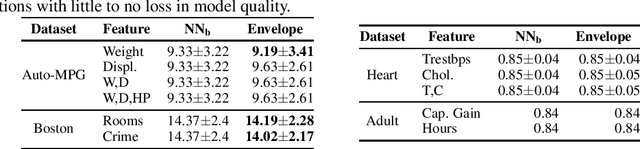
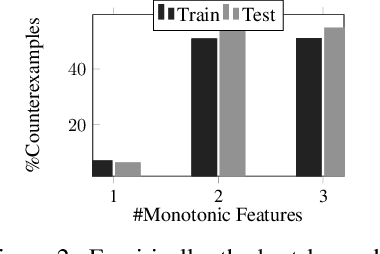
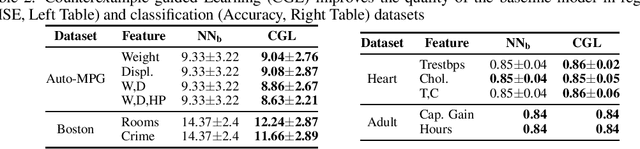
Abstract:The widespread adoption of deep learning is often attributed to its automatic feature construction with minimal inductive bias. However, in many real-world tasks, the learned function is intended to satisfy domain-specific constraints. We focus on monotonicity constraints, which are common and require that the function's output increases with increasing values of specific input features. We develop a counterexample-guided technique to provably enforce monotonicity constraints at prediction time. Additionally, we propose a technique to use monotonicity as an inductive bias for deep learning. It works by iteratively incorporating monotonicity counterexamples in the learning process. Contrary to prior work in monotonic learning, we target general ReLU neural networks and do not further restrict the hypothesis space. We have implemented these techniques in a tool called COMET. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results compared to existing monotonic learners, and can improve the model quality compared to those that were trained without taking monotonicity constraints into account.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge