Aidan Furlong
Prediction of Critical Heat Flux in Rod Bundles Using Tube-Based Hybrid Machine Learning Models in CTF
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The prediction of critical heat flux (CHF) using machine learning (ML) approaches has become a highly active research activity in recent years, the goal of which is to build models more accurate than current conventional approaches such as empirical correlations or lookup tables (LUTs). Previous work developed and deployed tube-based pure and hybrid ML models in the CTF subchannel code, however, full-scale reactor core simulations require the use of rod bundle geometries. Unlike isolated subchannels, rod bundles experience complex thermal hydraulic phenomena such as channel crossflow, spacer grid losses, and effects from unheated conductors. This study investigates the generalization of ML-based CHF prediction models in rod bundles after being trained on tube-based CHF data. A purely data-driven DNN and two hybrid bias-correction models were implemented in the CTF subchannel code and used to predict CHF location and magnitude in the Combustion Engineering 5-by-5 bundle CHF test series. The W-3 correlation, Bowring correlation, and Groeneveld LUT were used as baseline comparators. On average, all three ML-based approaches produced magnitude and location predictions more accurate than the baseline models, with the hybrid LUT model exhibiting the most favorable performance metrics.
A Three-Stage Bayesian Transfer Learning Framework to Improve Predictions in Data-Scarce Domains
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:The use of ML in engineering has grown steadily to support a wide array of applications. Among these methods, deep neural networks have been widely adopted due to their performance and accessibility, but they require large, high-quality datasets. Experimental data are often sparse, noisy, or insufficient to build resilient data-driven models. Transfer learning, which leverages relevant data-abundant source domains to assist learning in data-scarce target domains, has shown efficacy. Parameter transfer, where pretrained weights are reused, is common but degrades under large domain shifts. Domain-adversarial neural networks (DANNs) help address this issue by learning domain-invariant representations, thereby improving transfer under greater domain shifts in a semi-supervised setting. However, DANNs can be unstable during training and lack a native means for uncertainty quantification. This study introduces a fully-supervised three-stage framework, the staged Bayesian domain-adversarial neural network (staged B-DANN), that combines parameter transfer and shared latent space adaptation. In Stage 1, a deterministic feature extractor is trained on the source domain. This feature extractor is then adversarially refined using a DANN in Stage 2. In Stage 3, a Bayesian neural network is built on the adapted feature extractor for fine-tuning on the target domain to handle conditional shifts and yield calibrated uncertainty estimates. This staged B-DANN approach was first validated on a synthetic benchmark, where it was shown to significantly outperform standard transfer techniques. It was then applied to the task of predicting critical heat flux in rectangular channels, leveraging data from tube experiments as the source domain. The results of this study show that the staged B-DANN method can improve predictive accuracy and generalization, potentially assisting other domains in nuclear engineering.
Physics-Based Hybrid Machine Learning for Critical Heat Flux Prediction with Uncertainty Quantification
Feb 26, 2025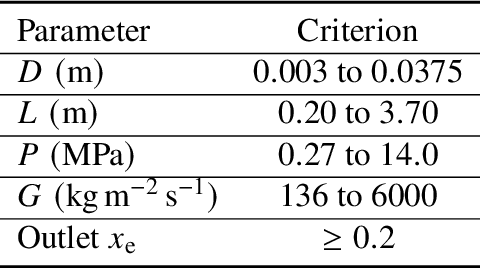
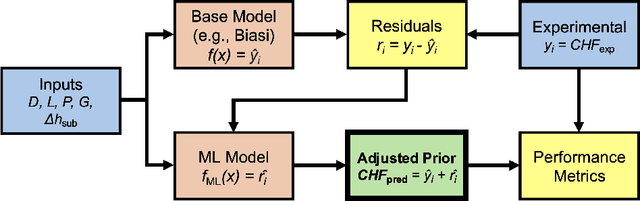
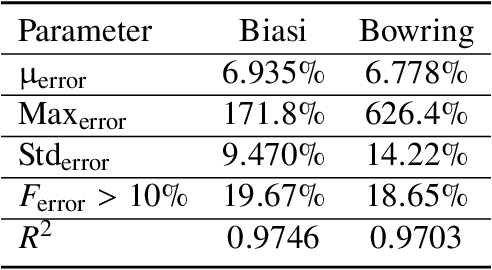
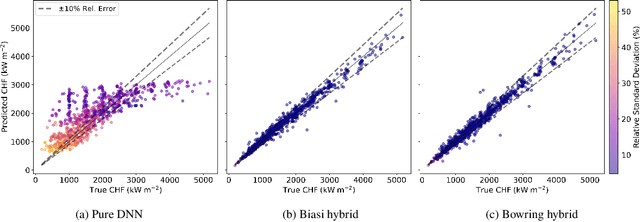
Abstract:Critical heat flux is a key quantity in boiling system modeling due to its impact on heat transfer and component temperature and performance. This study investigates the development and validation of an uncertainty-aware hybrid modeling approach that combines machine learning with physics-based models in the prediction of critical heat flux in nuclear reactors for cases of dryout. Two empirical correlations, Biasi and Bowring, were employed with three machine learning uncertainty quantification techniques: deep neural network ensembles, Bayesian neural networks, and deep Gaussian processes. A pure machine learning model without a base model served as a baseline for comparison. This study examines the performance and uncertainty of the models under both plentiful and limited training data scenarios using parity plots, uncertainty distributions, and calibration curves. The results indicate that the Biasi hybrid deep neural network ensemble achieved the most favorable performance (with a mean absolute relative error of 1.846% and stable uncertainty estimates), particularly in the plentiful data scenario. The Bayesian neural network models showed slightly higher error and uncertainty but superior calibration. By contrast, deep Gaussian process models underperformed by most metrics. All hybrid models outperformed pure machine learning configurations, demonstrating resistance against data scarcity.
Native Fortran Implementation of TensorFlow-Trained Deep and Bayesian Neural Networks
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Over the past decade, the investigation of machine learning (ML) within the field of nuclear engineering has grown significantly. With many approaches reaching maturity, the next phase of investigation will determine the feasibility and usefulness of ML model implementation in a production setting. Several of the codes used for reactor design and assessment are primarily written in the Fortran language, which is not immediately compatible with TensorFlow-trained ML models. This study presents a framework for implementing deep neural networks (DNNs) and Bayesian neural networks (BNNs) in Fortran, allowing for native execution without TensorFlow's C API, Python runtime, or ONNX conversion. Designed for ease of use and computational efficiency, the framework can be implemented in any Fortran code, supporting iterative solvers and UQ via ensembles or BNNs. Verification was performed using a two-input, one-output test case composed of a noisy sinusoid to compare Fortran-based predictions to those from TensorFlow. The DNN predictions showed negligible differences and achieved a 19.6x speedup, whereas the BNN predictions exhibited minor disagreement, plausibly due to differences in random number generation. An 8.0x speedup was noted for BNN inference. The approach was then further verified on a nuclear-relevant problem predicting critical heat flux (CHF), which demonstrated similar behavior along with significant computational gains. Discussion regarding the framework's successful integration into the CTF thermal-hydraulics code is also included, outlining its practical usefulness. Overall, this framework was shown to be effective at implementing both DNN and BNN model inference within Fortran, allowing for the continued study of ML-based methods in real-world nuclear applications.
Predicting Critical Heat Flux with Uncertainty Quantification and Domain Generalization Using Conditional Variational Autoencoders and Deep Neural Networks
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Deep generative models (DGMs) have proven to be powerful in generating realistic data samples. Their capability to learn the underlying distribution of a dataset enable them to generate synthetic data samples that closely resemble the original training dataset, thus addressing the challenge of data scarcity. In this work, we investigated the capabilities of DGMs by developing a conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) model to augment the critical heat flux (CHF) measurement data that was used to generate the 2006 Groeneveld lookup table. To determine how this approach compared to traditional methods, a fine-tuned deep neural network (DNN) regression model was created and evaluated with the same dataset. Both the CVAE and DNN models achieved small mean absolute relative errors, with the CVAE model maintaining more favorable results. To quantify the uncertainty in the model's predictions, uncertainty quantification (UQ) was performed with repeated sampling of the CVAE model and ensembling of the DNN model. Following UQ, the DNN ensemble notably improved performance when compared to the baseline DNN model, while the CVAE model achieved similar results to its non-UQ results. The CVAE model was shown to have significantly less variability and a higher confidence after assessment of the prediction-wise relative standard deviations. Evaluating domain generalization, both models achieved small mean error values when predicting both inside and outside the training domain, with predictions outside the training domain showing slightly larger errors. Overall, the CVAE model was comparable to the DNN regression model in predicting CHF values but with better uncertainty behavior.
Data-Driven Prediction and Uncertainty Quantification of PWR Crud-Induced Power Shift Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jun 27, 2024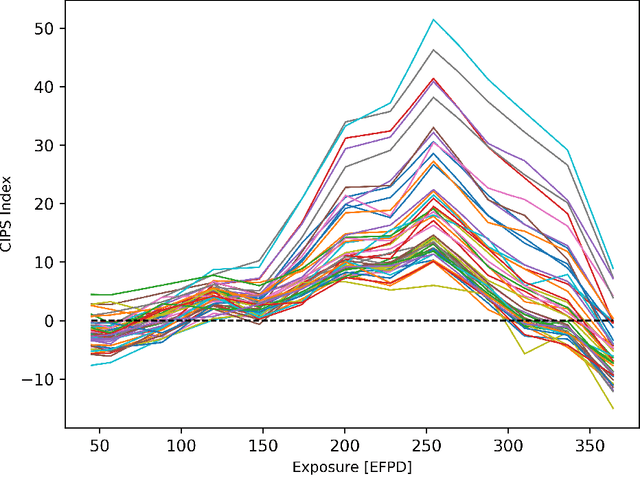
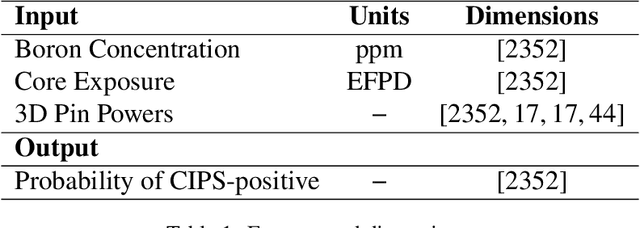
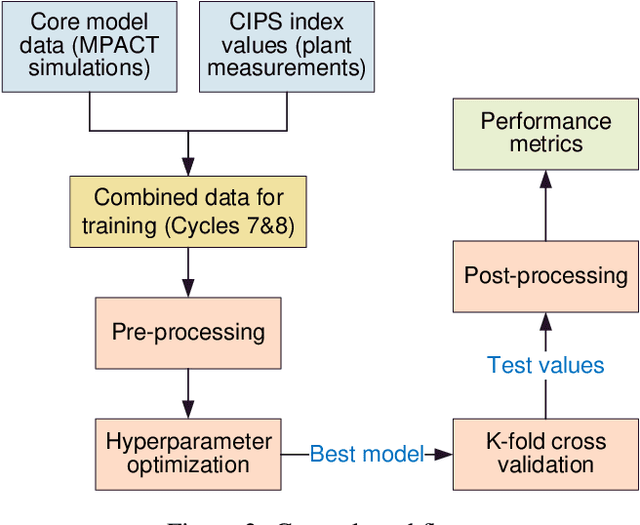

Abstract:The development of Crud-Induced Power Shift (CIPS) is an operational challenge in Pressurized Water Reactors that is due to the development of crud on the fuel rod cladding. The available predictive tools developed previously, usually based on fundamental physics, are computationally expensive and have shown differing degrees of accuracy. This work proposes a completely top-down approach to predict CIPS instances on an assembly level with reactor-specific calibration built-in. Built using artificial neural networks, this work uses a three-dimensional convolutional approach to leverage the image-like layout of the input data. As a classifier, the convolutional neural network model predicts whether a given assembly will experience CIPS as well as the time of occurrence during a given cycle. This surrogate model is both trained and tested using a combination of calculated core model parameters and measured plant data from Unit 1 of the Catawba Nuclear Station. After the evaluation of its performance using various metrics, Monte Carlo dropout is employed for extensive uncertainty quantification of the model predictions. The results indicate that this methodology could be a viable approach in predicting CIPS with an assembly-level resolution across both clean and afflicted cycles, while using limited computational resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge