Agnieszka Dobrowolska
pMCT: Patched Multi-Condition Training for Robust Speech Recognition
Jul 11, 2022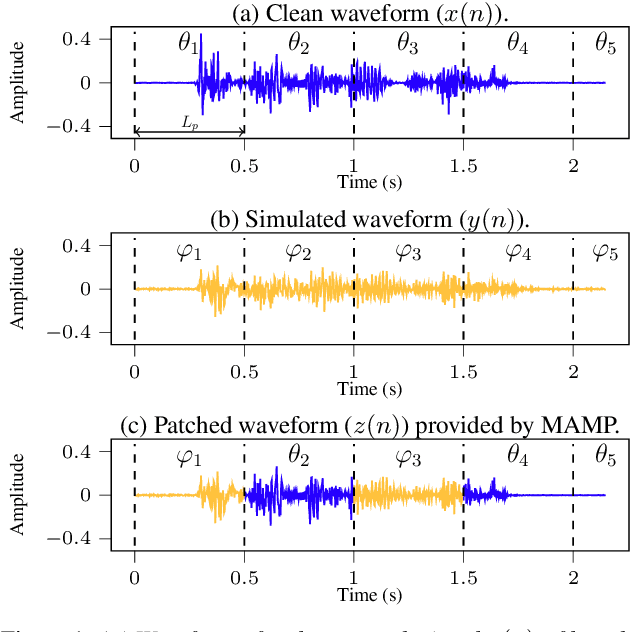
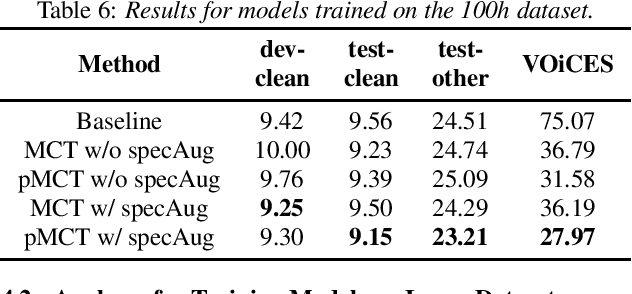
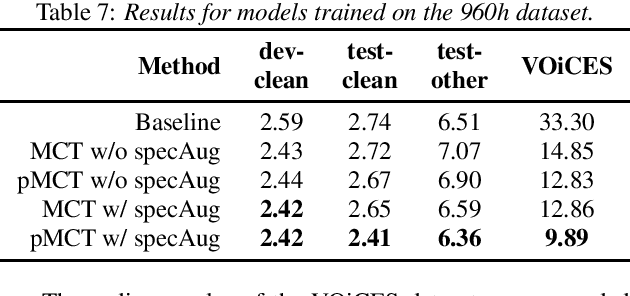
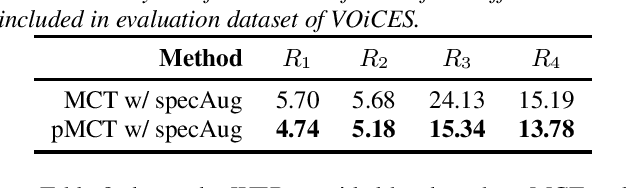
Abstract:We propose a novel Patched Multi-Condition Training (pMCT) method for robust Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). pMCT employs Multi-condition Audio Modification and Patching (MAMP) via mixing {\it patches} of the same utterance extracted from clean and distorted speech. Training using patch-modified signals improves robustness of models in noisy reverberant scenarios. Our proposed pMCT is evaluated on the LibriSpeech dataset showing improvement over using vanilla Multi-Condition Training (MCT). For analyses on robust ASR, we employed pMCT on the VOiCES dataset which is a noisy reverberant dataset created using utterances from LibriSpeech. In the analyses, pMCT achieves 23.1% relative WER reduction compared to the MCT.
FedNST: Federated Noisy Student Training for Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 06, 2022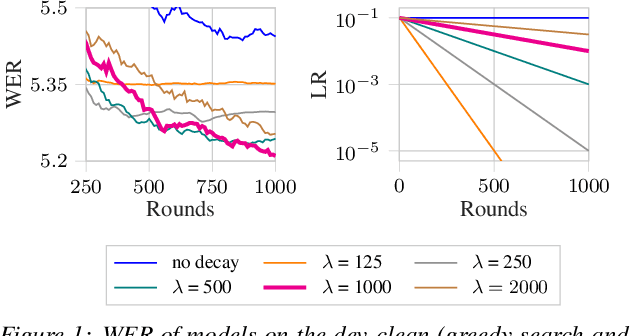
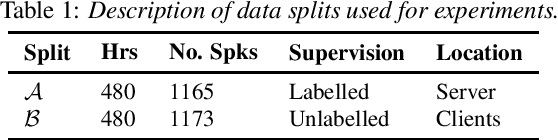
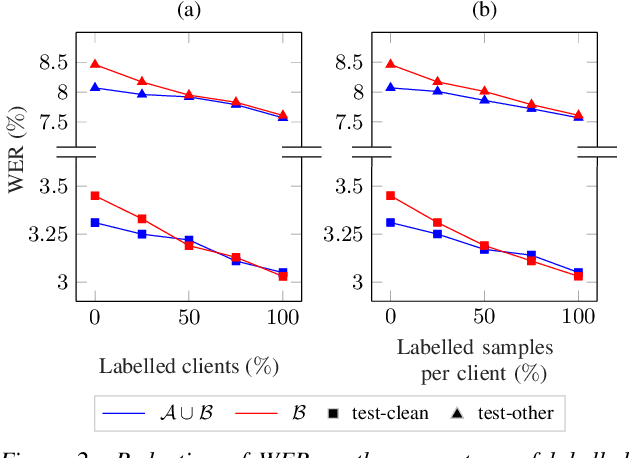
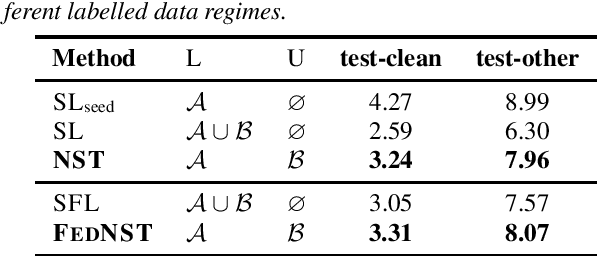
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables training state-of-the-art Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models on user devices (clients) in distributed systems, hence preventing transmission of raw user data to a central server. A key challenge facing practical adoption of FL for ASR is obtaining ground-truth labels on the clients. Existing approaches rely on clients to manually transcribe their speech, which is impractical for obtaining large training corpora. A promising alternative is using semi-/self-supervised learning approaches to leverage unlabelled user data. To this end, we propose a new Federated ASR method called FedNST for noisy student training of distributed ASR models with private unlabelled user data. We explore various facets of FedNST , such as training models with different proportions of unlabelled and labelled data, and evaluate the proposed approach on 1173 simulated clients. Evaluating FedNST on LibriSpeech, where 960 hours of speech data is split equally into server (labelled) and client (unlabelled) data, showed a 22.5% relative word error rate reduction (WERR) over a supervised baseline trained only on server data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge