Afifa Ishtiaq
BeamSec: A Practical mmWave Physical Layer Security Scheme Against Strong Adversaries
Sep 19, 2023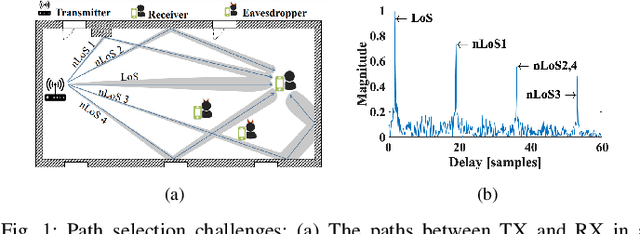
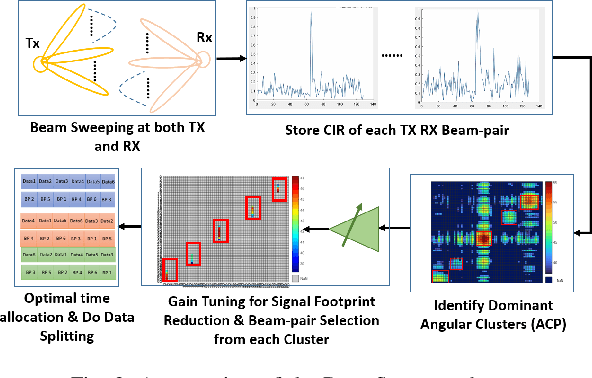
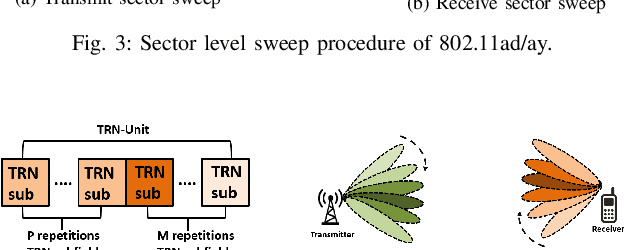
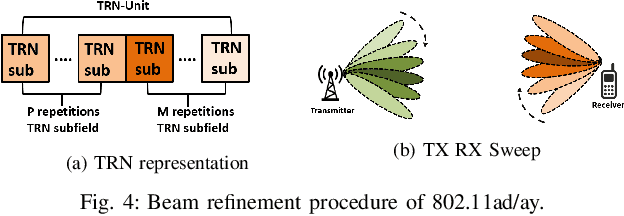
Abstract:The high directionality of millimeter-wave (mmWave) communication systems has proven effective in reducing the attack surface against eavesdropping, thus improving the physical layer security. However, even with highly directional beams, the system is still exposed to eavesdropping against adversaries located within the main lobe. In this paper, we propose \acrshort{BSec}, a solution to protect the users even from adversaries located in the main lobe. The key feature of BeamSec are: (i) Operating without the knowledge of eavesdropper's location/channel; (ii) Robustness against colluding eavesdropping attack and (iii) Standard compatibility, which we prove using experiments via our IEEE 802.11ad/ay-compatible 60 GHz phased-array testbed. Methodologically, BeamSec first identifies uncorrelated and diverse beam-pairs between the transmitter and receiver by analyzing signal characteristics available through standard-compliant procedures. Next, it encodes the information jointly over all selected beam-pairs to minimize information leakage. We study two methods for allocating transmission time among different beams, namely uniform allocation (no knowledge of the wireless channel) and optimal allocation for maximization of the secrecy rate (with partial knowledge of the wireless channel). Our experiments show that \acrshort{BSec} outperforms the benchmark schemes against single and colluding eavesdroppers and enhances the secrecy rate by 79.8% over a random paths selection benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge