Adrià Giménez
MLLP-VRAIN UPV system for the IWSLT 2025 Simultaneous Speech Translation Translation task
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:This work describes the participation of the MLLP-VRAIN research group in the shared task of the IWSLT 2025 Simultaneous Speech Translation track. Our submission addresses the unique challenges of real-time translation of long-form speech by developing a modular cascade system that adapts strong pre-trained models to streaming scenarios. We combine Whisper Large-V3-Turbo for ASR with the multilingual NLLB-3.3B model for MT, implementing lightweight adaptation techniques rather than training new end-to-end models from scratch. Our approach employs document-level adaptation with prefix training to enhance the MT model's ability to handle incomplete inputs, while incorporating adaptive emission policies including a wait-$k$ strategy and RALCP for managing the translation stream. Specialized buffer management techniques and segmentation strategies ensure coherent translations across long audio sequences. Experimental results on the ACL60/60 dataset demonstrate that our system achieves a favorable balance between translation quality and latency, with a BLEU score of 31.96 and non-computational-aware StreamLAAL latency of 2.94 seconds. Our final model achieves a preliminary score on the official test set (IWSLT25Instruct) of 29.8 BLEU. Our work demonstrates that carefully adapted pre-trained components can create effective simultaneous translation systems for long-form content without requiring extensive in-domain parallel data or specialized end-to-end training.
Segmentation-Free Streaming Machine Translation
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:Streaming Machine Translation (MT) is the task of translating an unbounded input text stream in real-time. The traditional cascade approach, which combines an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and an MT system, relies on an intermediate segmentation step which splits the transcription stream into sentence-like units. However, the incorporation of a hard segmentation constrains the MT system and is a source of errors. This paper proposes a Segmentation-Free framework that enables the model to translate an unsegmented source stream by delaying the segmentation decision until the translation has been generated. Extensive experiments show how the proposed Segmentation-Free framework has better quality-latency trade-off than competing approaches that use an independent segmentation model. Software, data and models will be released upon paper acceptance.
Europarl-ST: A Multilingual Corpus For Speech Translation Of Parliamentary Debates
Nov 08, 2019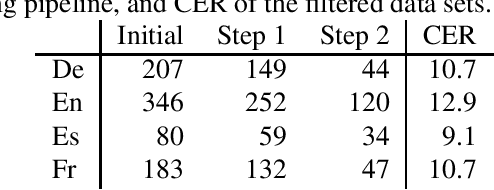
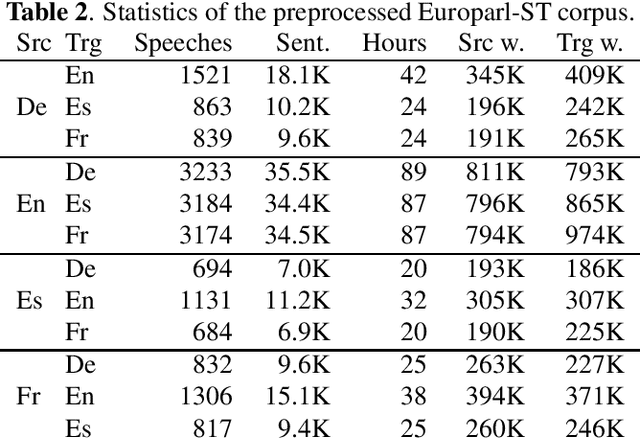
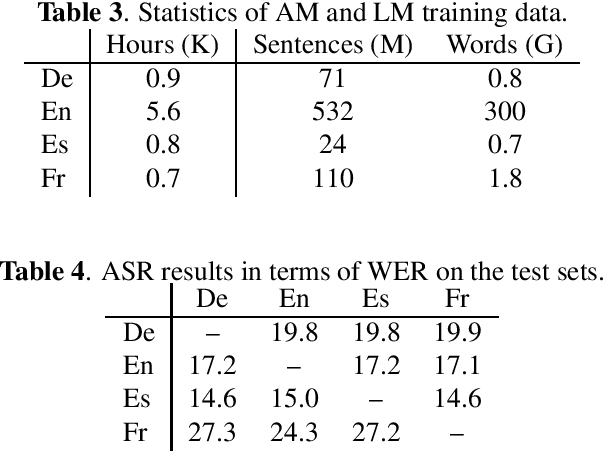
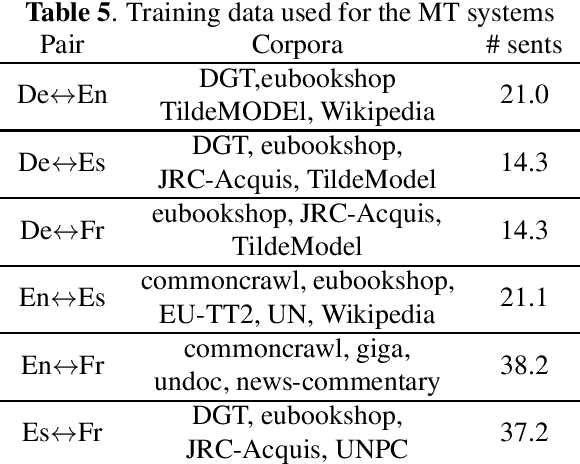
Abstract:Current research into spoken language translation (SLT) is often hampered by the lack of specific data resources for this task, as currently available SLT datasets are restricted to a limited set of language pairs. In this paper we present Europarl-ST, a novel multilingual SLT corpus containing paired audio-text samples for SLT from and into 6 European languages, for a total of 30 different translation directions. This corpus has been compiled using the debates held in the European Parliament in the period between 2008 and 2012. This paper describes the corpus creation process and presents a series of automatic speech recognition, machine translation and spoken language translation experiments that highlight the potential of this new resource. The corpus is released under a Creative Commons license and is freely accessible and downloadable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge