Aditya
Benchmarking Deep Learning Architectures for Urban Vegetation Points Segmentation
Jun 17, 2023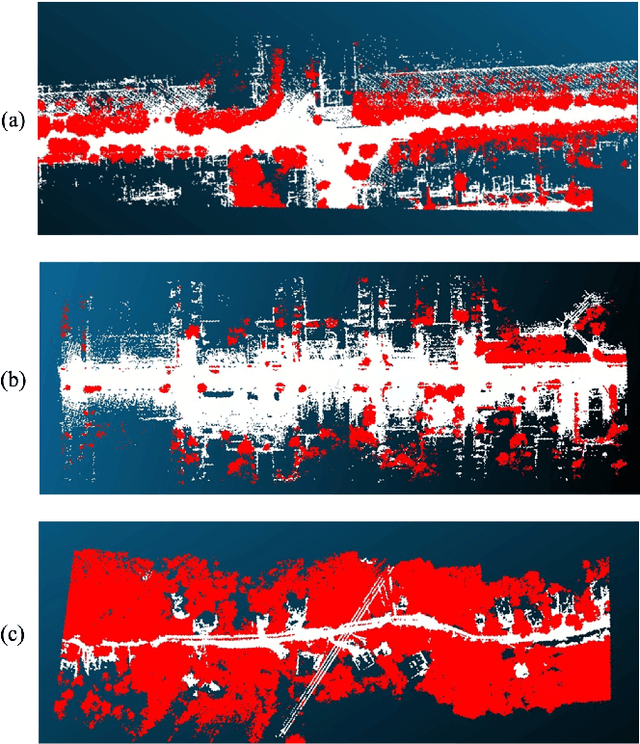
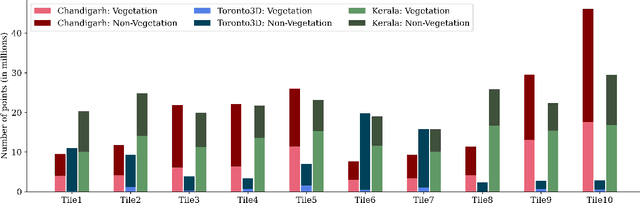
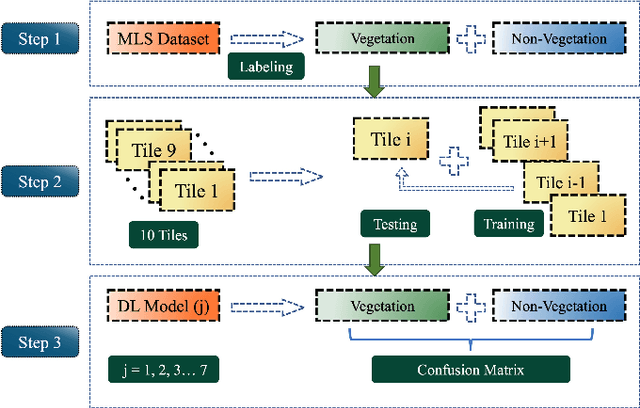
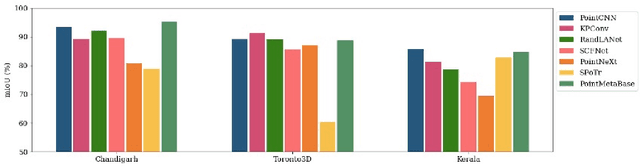
Abstract:Vegetation is crucial for sustainable and resilient cities providing various ecosystem services and well-being of humans. However, vegetation is under critical stress with rapid urbanization and expanding infrastructure footprints. Consequently, mapping of this vegetation is essential in the urban environment. Recently, deep learning for point cloud semantic segmentation has shown significant progress. Advanced models attempt to obtain state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets, comprising multiple classes and representing real world scenarios. However, class specific segmentation with respect to vegetation points has not been explored. Therefore, selection of a deep learning model for vegetation points segmentation is ambiguous. To address this problem, we provide a comprehensive assessment of point-based deep learning models for semantic segmentation of vegetation class. We have selected four representative point-based models, namely PointCNN, KPConv (omni-supervised), RandLANet and SCFNet. These models are investigated on three different datasets, specifically Chandigarh, Toronto3D and Kerala, which are characterized by diverse nature of vegetation, varying scene complexity and changing per-point features. PointCNN achieves the highest mIoU on the Chandigarh (93.32%) and Kerala datasets (85.68%) while KPConv (omni-supervised) provides the highest mIoU on the Toronto3D dataset (91.26%). The paper develops a deeper insight, hitherto not reported, into the working of these models for vegetation segmentation and outlines the ingredients that should be included in a model specifically for vegetation segmentation. This paper is a step towards the development of a novel architecture for vegetation points segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge