Aditi Singh
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women, Delhi, India
Agentic AI in Healthcare & Medicine: A Seven-Dimensional Taxonomy for Empirical Evaluation of LLM-based Agents
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents that plan, use tools and act has begun to shape healthcare and medicine. Reported studies demonstrate competence on various tasks ranging from EHR analysis and differential diagnosis to treatment planning and research workflows. Yet the literature largely consists of overviews which are either broad surveys or narrow dives into a single capability (e.g., memory, planning, reasoning), leaving healthcare work without a common frame. We address this by reviewing 49 studies using a seven-dimensional taxonomy: Cognitive Capabilities, Knowledge Management, Interaction Patterns, Adaptation & Learning, Safety & Ethics, Framework Typology and Core Tasks & Subtasks with 29 operational sub-dimensions. Using explicit inclusion and exclusion criteria and a labeling rubric (Fully Implemented, Partially Implemented, Not Implemented), we map each study to the taxonomy and report quantitative summaries of capability prevalence and co-occurrence patterns. Our empirical analysis surfaces clear asymmetries. For instance, the External Knowledge Integration sub-dimension under Knowledge Management is commonly realized (~76% Fully Implemented) whereas Event-Triggered Activation sub-dimenison under Interaction Patterns is largely absent (~92% Not Implemented) and Drift Detection & Mitigation sub-dimension under Adaptation & Learning is rare (~98% Not Implemented). Architecturally, Multi-Agent Design sub-dimension under Framework Typology is the dominant pattern (~82% Fully Implemented) while orchestration layers remain mostly partial. Across Core Tasks & Subtasks, information centric capabilities lead e.g., Medical Question Answering & Decision Support and Benchmarking & Simulation, while action and discovery oriented areas such as Treatment Planning & Prescription still show substantial gaps (~59% Not Implemented).
Critical Insights into Leading Conversational AI Models
Oct 26, 2025



Abstract:Big Language Models (LLMs) are changing the way businesses use software, the way people live their lives and the way industries work. Companies like Google, High-Flyer, Anthropic, OpenAI and Meta are making better LLMs. So, it's crucial to look at how each model is different in terms of performance, moral behaviour and usability, as these differences are based on the different ideas that built them. This study compares five top LLMs: Google's Gemini, High-Flyer's DeepSeek, Anthropic's Claude, OpenAI's GPT models and Meta's LLaMA. It performs this by analysing three important factors: Performance and Accuracy, Ethics and Bias Mitigation and Usability and Integration. It was found that Claude has good moral reasoning, Gemini is better at multimodal capabilities and has strong ethical frameworks. DeepSeek is great at reasoning based on facts, LLaMA is good for open applications and ChatGPT delivers balanced performance with a focus on usage. It was concluded that these models are different in terms of how well they work, how easy they are to use and how they treat people ethically, making it a point that each model should be utilised by the user in a way that makes the most of its strengths.
Multilingual Prompt Engineering in Large Language Models: A Survey Across NLP Tasks
May 16, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance across a wide range of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. However, ensuring their effectiveness across multiple languages presents unique challenges. Multilingual prompt engineering has emerged as a key approach to enhance LLMs' capabilities in diverse linguistic settings without requiring extensive parameter re-training or fine-tuning. With growing interest in multilingual prompt engineering over the past two to three years, researchers have explored various strategies to improve LLMs' performance across languages and NLP tasks. By crafting structured natural language prompts, researchers have successfully extracted knowledge from LLMs across different languages, making these techniques an accessible pathway for a broader audience, including those without deep expertise in machine learning, to harness the capabilities of LLMs. In this paper, we survey and categorize different multilingual prompting techniques based on the NLP tasks they address across a diverse set of datasets that collectively span around 250 languages. We further highlight the LLMs employed, present a taxonomy of approaches and discuss potential state-of-the-art (SoTA) methods for specific multilingual datasets. Additionally, we derive a range of insights across language families and resource levels (high-resource vs. low-resource), including analyses such as the distribution of NLP tasks by language resource type and the frequency of prompting methods across different language families. Our survey reviews 36 research papers covering 39 prompting techniques applied to 30 multilingual NLP tasks, with the majority of these studies published in the last two years.
A survey of agent interoperability protocols: Model Context Protocol (MCP), Agent Communication Protocol (ACP), Agent-to-Agent Protocol (A2A), and Agent Network Protocol (ANP)
May 04, 2025



Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-powered autonomous agents demand robust, standardized protocols to integrate tools, share contextual data, and coordinate tasks across heterogeneous systems. Ad-hoc integrations are difficult to scale, secure, and generalize across domains. This survey examines four emerging agent communication protocols: Model Context Protocol (MCP), Agent Communication Protocol (ACP), Agent-to-Agent Protocol (A2A), and Agent Network Protocol (ANP), each addressing interoperability in distinct deployment contexts. MCP provides a JSON-RPC client-server interface for secure tool invocation and typed data exchange. ACP introduces REST-native messaging via multi-part messages and asynchronous streaming to support multimodal agent responses. A2A enables peer-to-peer task outsourcing through capability-based Agent Cards, facilitating enterprise-scale workflows. ANP supports open-network agent discovery and secure collaboration using decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and JSON-LD graphs. The protocols are compared across multiple dimensions, including interaction modes, discovery mechanisms, communication patterns, and security models. Based on the comparative analysis, a phased adoption roadmap is proposed: beginning with MCP for tool access, followed by ACP for multimodal messaging, A2A for collaborative task execution, and extending to ANP for decentralized agent marketplaces. This work provides a comprehensive foundation for designing secure, interoperable, and scalable ecosystems of LLM-powered agents.
Pediatric Asthma Detection with Googles HeAR Model: An AI-Driven Respiratory Sound Classifier
Apr 28, 2025



Abstract:Early detection of asthma in children is crucial to prevent long-term respiratory complications and reduce emergency interventions. This work presents an AI-powered diagnostic pipeline that leverages Googles Health Acoustic Representations (HeAR) model to detect early signs of asthma from pediatric respiratory sounds. The SPRSound dataset, the first open-access collection of annotated respiratory sounds in children aged 1 month to 18 years, is used to extract 2-second audio segments labeled as wheeze, crackle, rhonchi, stridor, or normal. Each segment is embedded into a 512-dimensional representation using HeAR, a foundation model pretrained on 300 million health-related audio clips, including 100 million cough sounds. Multiple classifiers, including SVM, Random Forest, and MLP, are trained on these embeddings to distinguish between asthma-indicative and normal sounds. The system achieves over 91\% accuracy, with strong performance on precision-recall metrics for positive cases. In addition to classification, learned embeddings are visualized using PCA, misclassifications are analyzed through waveform playback, and ROC and confusion matrix insights are provided. This method demonstrates that short, low-resource pediatric recordings, when powered by foundation audio models, can enable fast, noninvasive asthma screening. The approach is especially promising for digital diagnostics in remote or underserved healthcare settings.
Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey on Agentic RAG
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized artificial intelligence (AI) by enabling human like text generation and natural language understanding. However, their reliance on static training data limits their ability to respond to dynamic, real time queries, resulting in outdated or inaccurate outputs. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a solution, enhancing LLMs by integrating real time data retrieval to provide contextually relevant and up-to-date responses. Despite its promise, traditional RAG systems are constrained by static workflows and lack the adaptability required for multistep reasoning and complex task management. Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Agentic RAG) transcends these limitations by embedding autonomous AI agents into the RAG pipeline. These agents leverage agentic design patterns reflection, planning, tool use, and multiagent collaboration to dynamically manage retrieval strategies, iteratively refine contextual understanding, and adapt workflows to meet complex task requirements. This integration enables Agentic RAG systems to deliver unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and context awareness across diverse applications. This survey provides a comprehensive exploration of Agentic RAG, beginning with its foundational principles and the evolution of RAG paradigms. It presents a detailed taxonomy of Agentic RAG architectures, highlights key applications in industries such as healthcare, finance, and education, and examines practical implementation strategies. Additionally, it addresses challenges in scaling these systems, ensuring ethical decision making, and optimizing performance for real-world applications, while providing detailed insights into frameworks and tools for implementing Agentic RAG
A Survey of Large Language Model-Based Generative AI for Text-to-SQL: Benchmarks, Applications, Use Cases, and Challenges
Dec 06, 2024

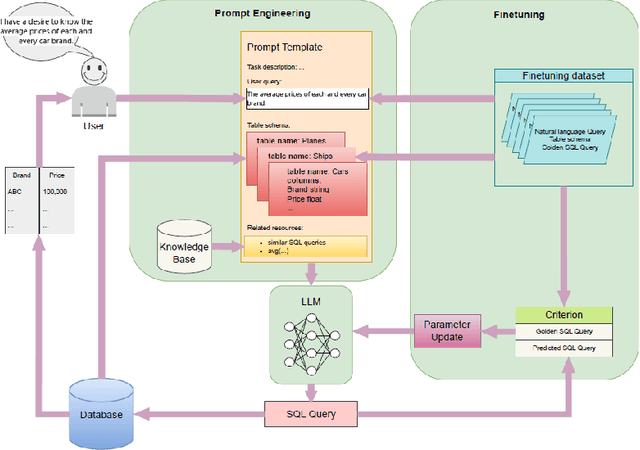

Abstract:Text-to-SQL systems facilitate smooth interaction with databases by translating natural language queries into Structured Query Language (SQL), bridging the gap between non-technical users and complex database management systems. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of AI-driven text-to-SQL systems, highlighting their foundational components, advancements in large language model (LLM) architectures, and the critical role of datasets such as Spider, WikiSQL, and CoSQL in driving progress. We examine the applications of text-to-SQL in domains like healthcare, education, and finance, emphasizing their transformative potential for improving data accessibility. Additionally, we analyze persistent challenges, including domain generalization, query optimization, support for multi-turn conversational interactions, and the limited availability of datasets tailored for NoSQL databases and dynamic real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we outline future research directions, such as extending text-to-SQL capabilities to support NoSQL databases, designing datasets for dynamic multi-turn interactions, and optimizing systems for real-world scalability and robustness. By surveying current advancements and identifying key gaps, this paper aims to guide the next generation of research and applications in LLM-based text-to-SQL systems.
A Survey of Sustainability in Large Language Models: Applications, Economics, and Challenges
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed numerous domains by providing advanced capabilities in natural language understanding, generation, and reasoning. Despite their groundbreaking applications across industries such as research, healthcare, and creative media, their rapid adoption raises critical concerns regarding sustainability. This survey paper comprehensively examines the environmental, economic, and computational challenges associated with LLMs, focusing on energy consumption, carbon emissions, and resource utilization in data centers. By synthesizing insights from existing literature, this work explores strategies such as resource-efficient training, sustainable deployment practices, and lifecycle assessments to mitigate the environmental impacts of LLMs. Key areas of emphasis include energy optimization, renewable energy integration, and balancing performance with sustainability. The findings aim to guide researchers, practitioners, and policymakers in developing actionable strategies for sustainable AI systems, fostering a responsible and environmentally conscious future for artificial intelligence.
Movie Gen: SWOT Analysis of Meta's Generative AI Foundation Model for Transforming Media Generation, Advertising, and Entertainment Industries
Dec 05, 2024

Abstract:Generative AI is reshaping the media landscape, enabling unprecedented capabilities in video creation, personalization, and scalability. This paper presents a comprehensive SWOT analysis of Metas Movie Gen, a cutting-edge generative AI foundation model designed to produce 1080p HD videos with synchronized audio from simple text prompts. We explore its strengths, including high-resolution video generation, precise editing, and seamless audio integration, which make it a transformative tool across industries such as filmmaking, advertising, and education. However, the analysis also addresses limitations, such as constraints on video length and potential biases in generated content, which pose challenges for broader adoption. In addition, we examine the evolving regulatory and ethical considerations surrounding generative AI, focusing on issues like content authenticity, cultural representation, and responsible use. Through comparative insights with leading models like DALL-E and Google Imagen, this paper highlights Movie Gens unique features, such as video personalization and multimodal synthesis, while identifying opportunities for innovation and areas requiring further research. Our findings provide actionable insights for stakeholders, emphasizing both the opportunities and challenges of deploying generative AI in media production. This work aims to guide future advancements in generative AI, ensuring scalability, quality, and ethical integrity in this rapidly evolving field.
Architectural Flaw Detection in Civil Engineering Using GPT-4
Oct 26, 2024



Abstract:The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in civil engineering presents a transformative approach to enhancing design quality and safety. This paper investigates the potential of the advanced LLM GPT4 Turbo vision model in detecting architectural flaws during the design phase, with a specific focus on identifying missing doors and windows. The study evaluates the model's performance through metrics such as precision, recall, and F1 score, demonstrating AI's effectiveness in accurately detecting flaws compared to human-verified data. Additionally, the research explores AI's broader capabilities, including identifying load-bearing issues, material weaknesses, and ensuring compliance with building codes. The findings highlight how AI can significantly improve design accuracy, reduce costly revisions, and support sustainable practices, ultimately revolutionizing the civil engineering field by ensuring safer, more efficient, and aesthetically optimized structures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge