Adam Diamant
The importance of evaluating the complete automated knowledge-based planning pipeline
Oct 31, 2019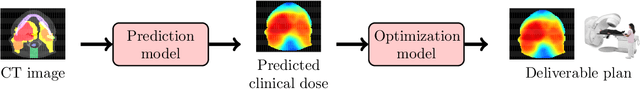
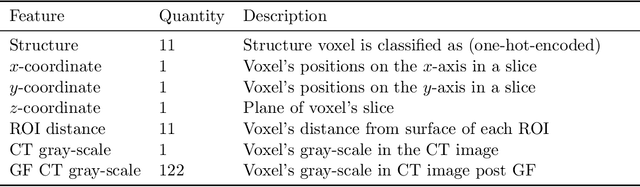
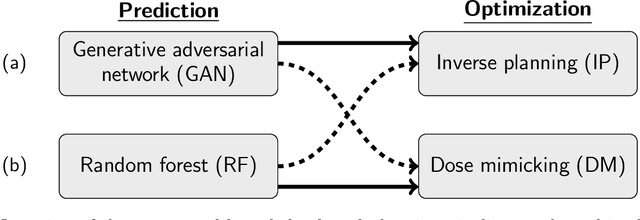
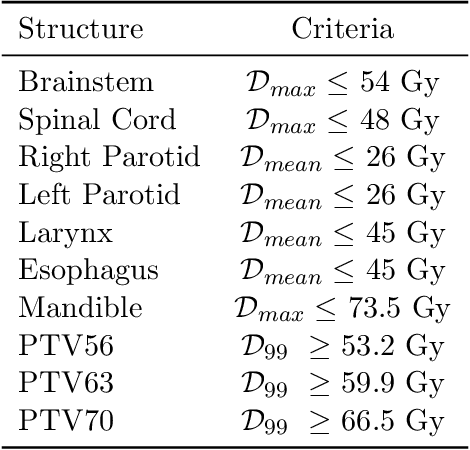
Abstract:We determine how prediction methods combine with optimization methods in two-stage knowledge-based planning (KBP) pipelines to produce radiation therapy treatment plans. We trained two dose prediction methods, a generative adversarial network (GAN) and a random forest (RF) with the same 130 treatment plans. The models were applied to 87 out-of-sample patients to create two sets of predicted dose distributions that were used as input to two optimization models. The first optimization model, inverse planning (IP), estimates weights for dose-objectives from a predicted dose distribution and generates new plans using conventional inverse planning. The second optimization model, dose mimicking (DM), minimizes the sum of one-sided quadratic penalties between the predictions and the generated plans using several dose-objectives. Altogether, four KBP pipelines (GAN-IP, GAN-DM, RF-IP, and RF-DM) were constructed and benchmarked against the corresponding clinical plans using clinical criteria; the error of both prediction methods was also evaluated. The best performing plans were GAN-IP plans, which satisfied the same criteria as their corresponding clinical plans (78%) more often than any other KBP pipeline. However, GAN did not necessarily provide the best prediction for the second-stage optimization models. Specifically, both the RF-IP and RF-DM plans satisfied all clinical criteria 25% and 15% more often than GAN-DM plans (the worst performing planning), respectively. GAN predictions also had a higher mean absolute error (3.9 Gy) than those from RF (3.6 Gy). We find that state-of-the-art prediction methods when paired with different optimization algorithms, produce treatment plans with considerable variation in quality.
Automated Treatment Planning in Radiation Therapy using Generative Adversarial Networks
Jul 17, 2018
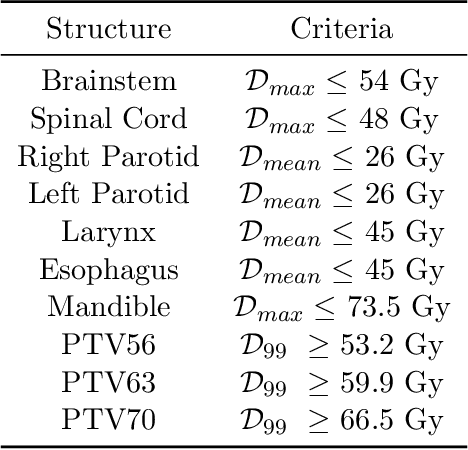
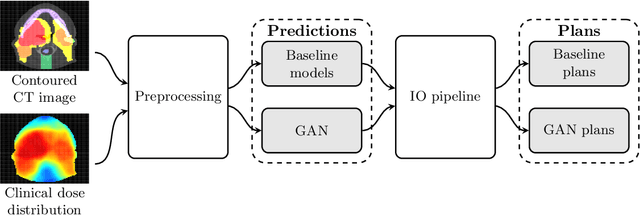
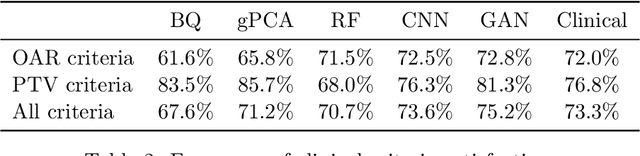
Abstract:Knowledge-based planning (KBP) is an automated approach to radiation therapy treatment planning that involves predicting desirable treatment plans before they are then corrected to deliverable ones. We propose a generative adversarial network (GAN) approach for predicting desirable 3D dose distributions that eschews the previous paradigms of site-specific feature engineering and predicting low-dimensional representations of the plan. Experiments on a dataset of oropharyngeal cancer patients show that our approach significantly outperforms previous methods on several clinical satisfaction criteria and similarity metrics.
Interior Point Methods with Adversarial Networks
May 23, 2018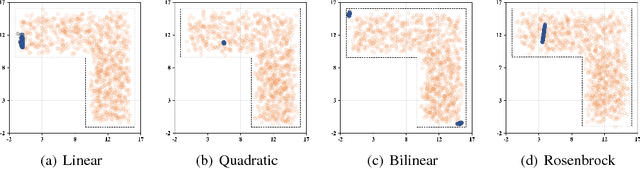
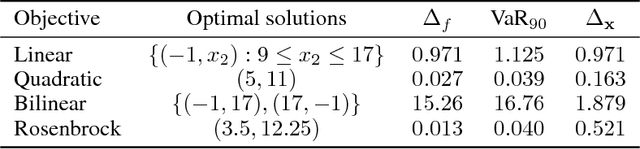

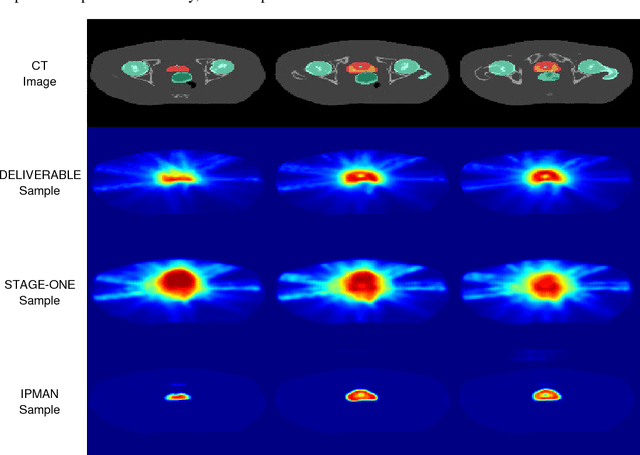
Abstract:We present a new methodology, called IPMAN, that combines interior point methods and generative adversarial networks to solve constrained optimization problems with feasible sets that are non-convex or not explicitly defined. Our methodology produces {\epsilon}-optimal solutions and demonstrates that, when there are multiple global optima, it learns a distribution over the optimal set. We apply our approach to synthetic examples to demonstrate its effectiveness and to a problem in radiation therapy treatment optimization with a non-convex feasible set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge