Abhishek Ray
IMBWatch -- a Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network approach to detect Illicit Massage Business
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Illicit Massage Businesses (IMBs) are a covert and persistent form of organized exploitation that operate under the facade of legitimate wellness services while facilitating human trafficking, sexual exploitation, and coerced labor. Detecting IMBs is difficult due to encoded digital advertisements, frequent changes in personnel and locations, and the reuse of shared infrastructure such as phone numbers and addresses. Traditional approaches, including community tips and regulatory inspections, are largely reactive and ineffective at revealing the broader operational networks traffickers rely on. To address these challenges, we introduce IMBWatch, a spatio-temporal graph neural network (ST-GNN) framework for large-scale IMB detection. IMBWatch constructs dynamic graphs from open-source intelligence, including scraped online advertisements, business license records, and crowdsourced reviews. Nodes represent heterogeneous entities such as businesses, aliases, phone numbers, and locations, while edges capture spatio-temporal and relational patterns, including co-location, repeated phone usage, and synchronized advertising. The framework combines graph convolutional operations with temporal attention mechanisms to model the evolution of IMB networks over time and space, capturing patterns such as intercity worker movement, burner phone rotation, and coordinated advertising surges. Experiments on real-world datasets from multiple U.S. cities show that IMBWatch outperforms baseline models, achieving higher accuracy and F1 scores. Beyond performance gains, IMBWatch offers improved interpretability, providing actionable insights to support proactive and targeted interventions. The framework is scalable, adaptable to other illicit domains, and released with anonymized data and open-source code to support reproducible research.
Bayesian Model Averaging for Data Driven Decision Making when Causality is Partially Known
May 12, 2021
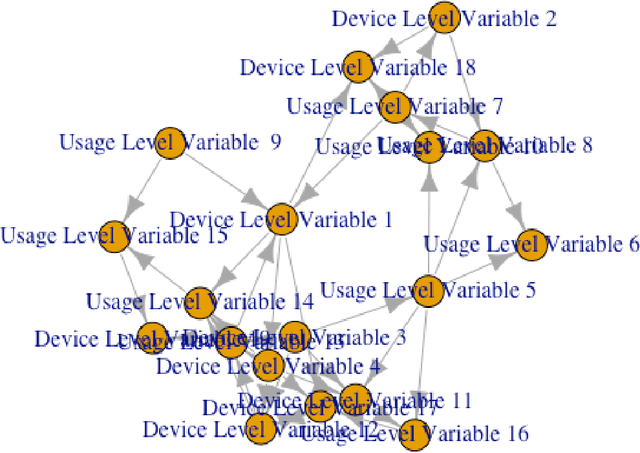
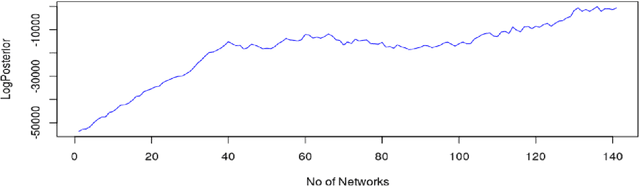
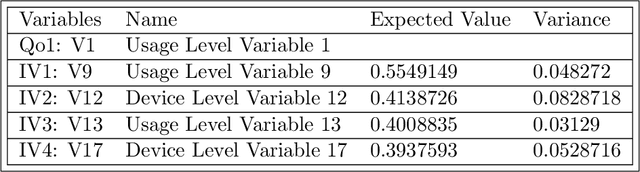
Abstract:Probabilistic machine learning models are often insufficient to help with decisions on interventions because those models find correlations - not causal relationships. If observational data is only available and experimentation are infeasible, the correct approach to study the impact of an intervention is to invoke Pearl's causality framework. Even that framework assumes that the underlying causal graph is known, which is seldom the case in practice. When the causal structure is not known, one may use out-of-the-box algorithms to find causal dependencies from observational data. However, there exists no method that also accounts for the decision-maker's prior knowledge when developing the causal structure either. The objective of this paper is to develop rational approaches for making decisions from observational data in the presence of causal graph uncertainty and prior knowledge from the decision-maker. We use ensemble methods like Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA) to infer set of causal graphs that can represent the data generation process. We provide decisions by computing the expected value and risk of potential interventions explicitly. We demonstrate our approach by applying them in different example contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge