Bayesian Model Averaging for Data Driven Decision Making when Causality is Partially Known
Paper and Code
May 12, 2021
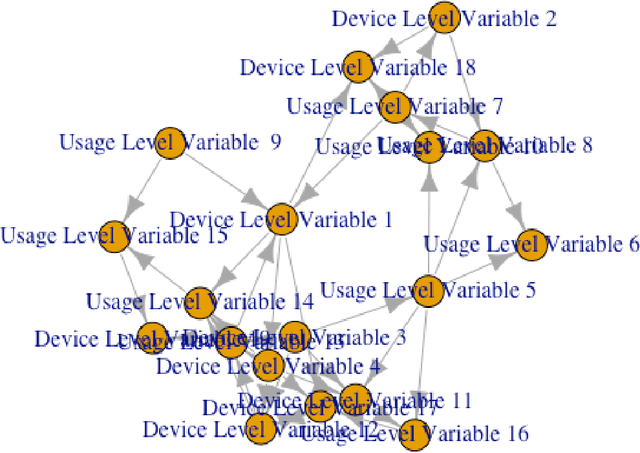
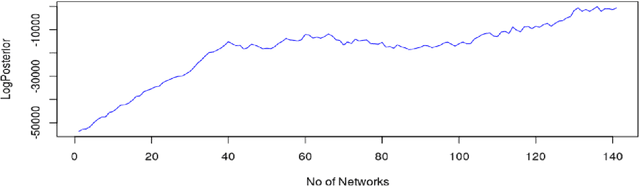
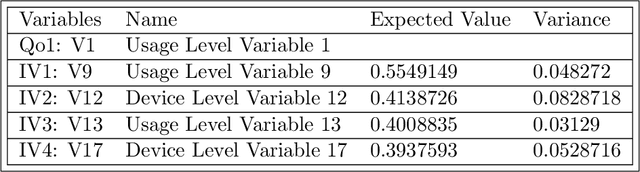
Probabilistic machine learning models are often insufficient to help with decisions on interventions because those models find correlations - not causal relationships. If observational data is only available and experimentation are infeasible, the correct approach to study the impact of an intervention is to invoke Pearl's causality framework. Even that framework assumes that the underlying causal graph is known, which is seldom the case in practice. When the causal structure is not known, one may use out-of-the-box algorithms to find causal dependencies from observational data. However, there exists no method that also accounts for the decision-maker's prior knowledge when developing the causal structure either. The objective of this paper is to develop rational approaches for making decisions from observational data in the presence of causal graph uncertainty and prior knowledge from the decision-maker. We use ensemble methods like Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA) to infer set of causal graphs that can represent the data generation process. We provide decisions by computing the expected value and risk of potential interventions explicitly. We demonstrate our approach by applying them in different example contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge