Abhinav Rai
Maximizing Success Rate of Payment Routing using Non-stationary Bandits
Aug 02, 2023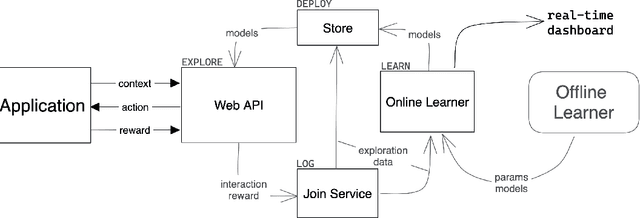
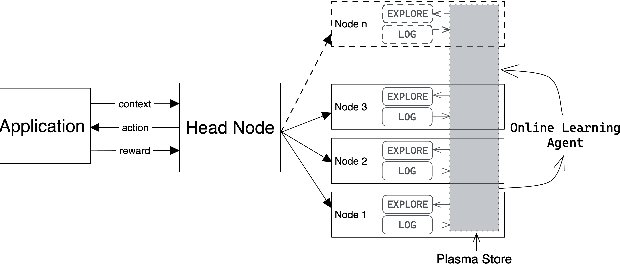
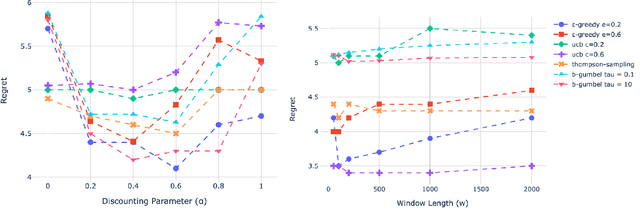
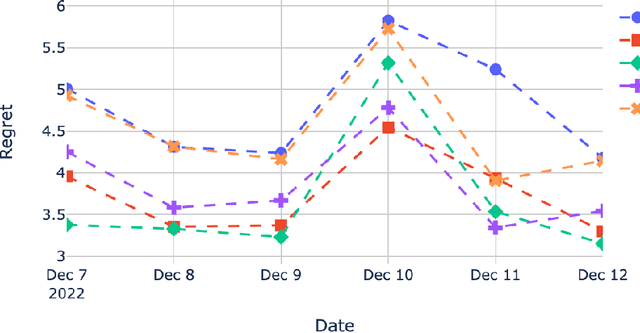
Abstract:This paper discusses the system architecture design and deployment of non-stationary multi-armed bandit approaches to determine a near-optimal payment routing policy based on the recent history of transactions. We propose a Routing Service architecture using a novel Ray-based implementation for optimally scaling bandit-based payment routing to over 10000 transactions per second, adhering to the system design requirements and ecosystem constraints with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). We first evaluate the effectiveness of multiple bandit-based payment routing algorithms on a custom simulator to benchmark multiple non-stationary bandit approaches and identify the best hyperparameters. We then conducted live experiments on the payment transaction system on a fantasy sports platform Dream11. In the live experiments, we demonstrated that our non-stationary bandit-based algorithm consistently improves the success rate of transactions by 0.92\% compared to the traditional rule-based methods over one month.
Transformed ROIs for Capturing Visual Transformations in Videos
Jun 06, 2021



Abstract:Modeling the visual changes that an action brings to a scene is critical for video understanding. Currently, CNNs process one local neighbourhood at a time, so contextual relationships over longer ranges, while still learnable, are indirect. We present TROI, a plug-and-play module for CNNs to reason between mid-level feature representations that are otherwise separated in space and time. The module relates localized visual entities such as hands and interacting objects and transforms their corresponding regions of interest directly in the feature maps of convolutional layers. With TROI, we achieve state-of-the-art action recognition results on the large-scale datasets Something-Something-V2 and Epic-Kitchens-100.
Multi-Stage Fusion for One-Click Segmentation
Oct 20, 2020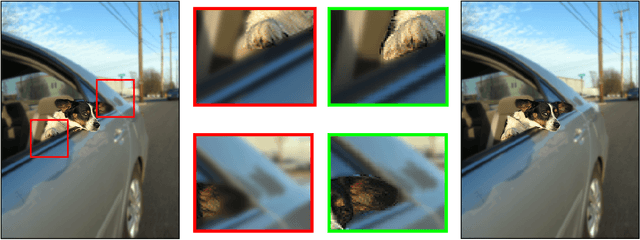
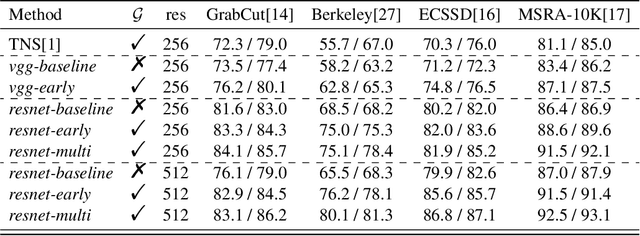
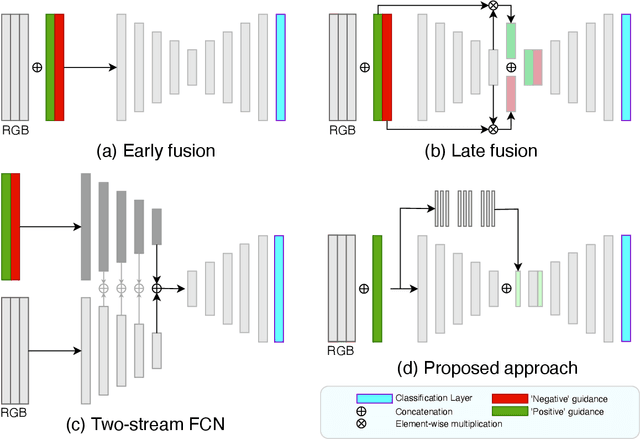
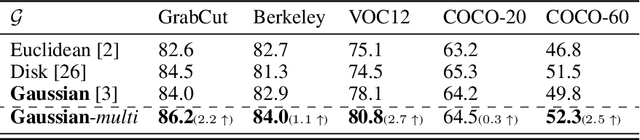
Abstract:Segmenting objects of interest in an image is an essential building block of applications such as photo-editing and image analysis. Under interactive settings, one should achieve good segmentations while minimizing user input. Current deep learning-based interactive segmentation approaches use early fusion and incorporate user cues at the image input layer. Since segmentation CNNs have many layers, early fusion may weaken the influence of user interactions on the final prediction results. As such, we propose a new multi-stage guidance framework for interactive segmentation. By incorporating user cues at different stages of the network, we allow user interactions to impact the final segmentation output in a more direct way. Our proposed framework has a negligible increase in parameter count compared to early-fusion frameworks. We perform extensive experimentation on the standard interactive instance segmentation and one-click segmentation benchmarks and report state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge