Abdurrahim Yilmaz
DermaBench: A Clinician-Annotated Benchmark Dataset for Dermatology Visual Question Answering and Reasoning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) are increasingly important in medical applications; however, their evaluation in dermatology remains limited by datasets that focus primarily on image-level classification tasks such as lesion recognition. While valuable for recognition, such datasets cannot assess the full visual understanding, language grounding, and clinical reasoning capabilities of multimodal models. Visual question answering (VQA) benchmarks are required to evaluate how models interpret dermatological images, reason over fine-grained morphology, and generate clinically meaningful descriptions. We introduce DermaBench, a clinician-annotated dermatology VQA benchmark built on the Diverse Dermatology Images (DDI) dataset. DermaBench comprises 656 clinical images from 570 unique patients spanning Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI. Using a hierarchical annotation schema with 22 main questions (single-choice, multi-choice, and open-ended), expert dermatologists annotated each image for diagnosis, anatomic site, lesion morphology, distribution, surface features, color, and image quality, together with open-ended narrative descriptions and summaries, yielding approximately 14.474 VQA-style annotations. DermaBench is released as a metadata-only dataset to respect upstream licensing and is publicly available at Harvard Dataverse.
A Hierarchical Benchmark of Foundation Models for Dermatology
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Foundation models have transformed medical image analysis by providing robust feature representations that reduce the need for large-scale task-specific training. However, current benchmarks in dermatology often reduce the complex diagnostic taxonomy to flat, binary classification tasks, such as distinguishing melanoma from benign nevi. This oversimplification obscures a model's ability to perform fine-grained differential diagnoses, which is critical for clinical workflow integration. This study evaluates the utility of embeddings derived from ten foundation models, spanning general computer vision, general medical imaging, and dermatology-specific domains, for hierarchical skin lesion classification. Using the DERM12345 dataset, which comprises 40 lesion subclasses, we calculated frozen embeddings and trained lightweight adapter models using a five-fold cross-validation. We introduce a hierarchical evaluation framework that assesses performance across four levels of clinical granularity: 40 Subclasses, 15 Main Classes, 2 and 4 Superclasses, and Binary Malignancy. Our results reveal a "granularity gap" in model capabilities: MedImageInsights achieved the strongest overall performance (97.52% weighted F1-Score on Binary Malignancy detection) but declined to 65.50% on fine-grained 40-class subtype classification. Conversely, MedSigLip (69.79%) and dermatology-specific models (Derm Foundation and MONET) excelled at fine-grained 40-class subtype discrimination while achieving lower overall performance than MedImageInsights on broader classification tasks. Our findings suggest that while general medical foundation models are highly effective for high-level screening, specialized modeling strategies are necessary for the granular distinctions required in diagnostic support systems.
An ensemble deep learning approach to detect tumors on Mohs micrographic surgery slides
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is the gold standard technique for removing high risk nonmelanoma skin cancer however, intraoperative histopathological examination demands significant time, effort, and professionality. The objective of this study is to develop a deep learning model to detect basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and artifacts on Mohs slides. A total of 731 Mohs slides from 51 patients with BCCs were used in this study, with 91 containing tumor and 640 without tumor which was defined as non-tumor. The dataset was employed to train U-Net based models that segment tumor and non-tumor regions on the slides. The segmented patches were classified as tumor, or non-tumor to produce predictions for whole slide images (WSIs). For the segmentation phase, the deep learning model success was measured using a Dice score with 0.70 and 0.67 value, area under the curve (AUC) score with 0.98 and 0.96 for tumor and non-tumor, respectively. For the tumor classification, an AUC of 0.98 for patch-based detection, and AUC of 0.91 for slide-based detection was obtained on the test dataset. We present an AI system that can detect tumors and non-tumors in Mohs slides with high success. Deep learning can aid Mohs surgeons and dermatopathologists in making more accurate decisions.
DERM12345: A Large, Multisource Dermatoscopic Skin Lesion Dataset with 38 Subclasses
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:Skin lesion datasets provide essential information for understanding various skin conditions and developing effective diagnostic tools. They aid the artificial intelligence-based early detection of skin cancer, facilitate treatment planning, and contribute to medical education and research. Published large datasets have partially coverage the subclassifications of the skin lesions. This limitation highlights the need for more expansive and varied datasets to reduce false predictions and help improve the failure analysis for skin lesions. This study presents a diverse dataset comprising 12,345 dermatoscopic images with 38 subclasses of skin lesions collected in Turkiye which comprises different skin types in the transition zone between Europe and Asia. Each subgroup contains high-resolution photos and expert annotations, providing a strong and reliable basis for future research. The detailed analysis of each subgroup provided in this study facilitates targeted research endeavors and enhances the depth of understanding regarding the skin lesions. This dataset distinguishes itself through a diverse structure with 5 super classes, 15 main classes, 38 subclasses and its 12,345 high-resolution dermatoscopic images.
Benchmarking of Lightweight Deep Learning Architectures for Skin Cancer Classification using ISIC 2017 Dataset
Oct 23, 2021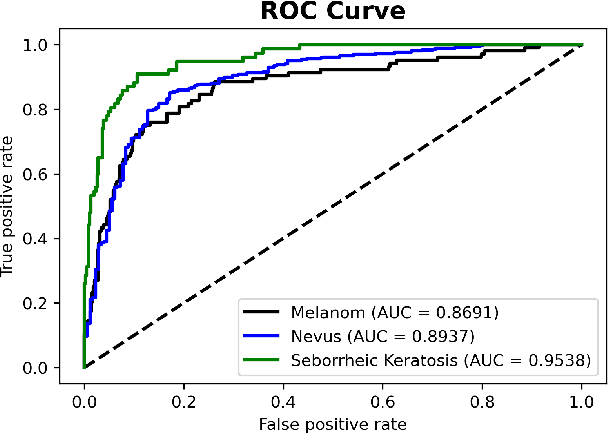



Abstract:Skin cancer is one of the deadly types of cancer and is common in the world. Recently, there has been a huge jump in the rate of people getting skin cancer. For this reason, the number of studies on skin cancer classification with deep learning are increasing day by day. For the growth of work in this area, the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) organization was established and they created an open dataset archive. In this study, images were taken from ISIC 2017 Challenge. The skin cancer images taken were preprocessed and data augmented. Later, these images were trained with transfer learning and fine-tuning approach and deep learning models were created in this way. 3 different mobile deep learning models and 3 different batch size values were determined for each, and a total of 9 models were created. Among these models, the NASNetMobile model with 16 batch size got the best result. The accuracy value of this model is 82.00%, the precision value is 81.77% and the F1 score value is 0.8038. Our method is to benchmark mobile deep learning models which have few parameters and compare the results of the models.
Mechatronic Investigation of Wound Healing Process by Using Micro Robot
Aug 05, 2021



Abstract:The purpose of this study is to find ideal forces for reducing cell stress in wound healing process by micro robots. Because of this aim, we made two simulations on COMSOL Multiphysics with micro robot to find correct force. As a result of these simulation, we created force curves to obtain the minimum force and friction force that could lift the cells from the surface will be determined. As the potential of the system for two micro robots that have 2 mm x 0.25 mm x 0.4 mm dimension SU-8 body with 3 NdFeB that have 0.25 thickness and diameter, simulation results at maximum force in the x-axis calculated with 4.640 mN, the distance between the two robots is 150 um.
Automated Onychomycosis Detection Using Deep Neural Networks
Jul 13, 2021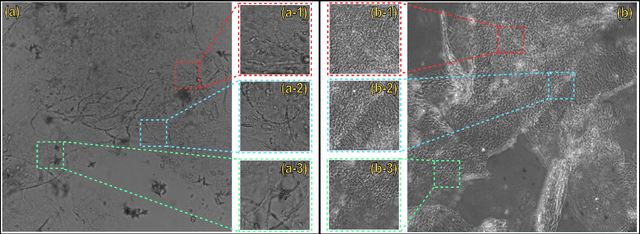
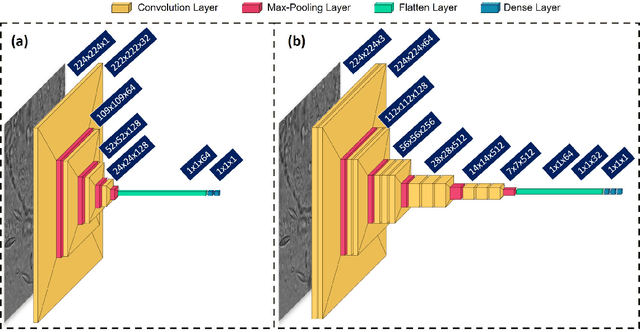
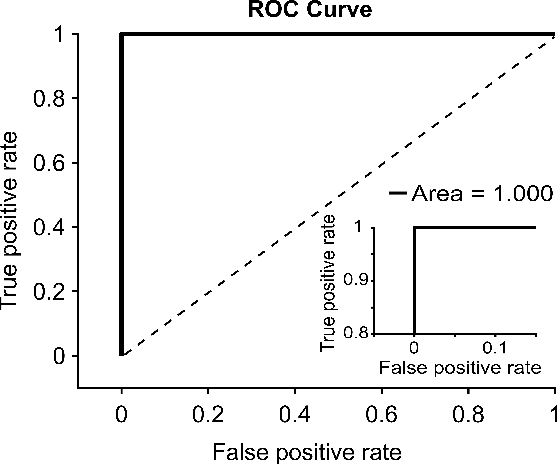

Abstract:Clinical dermatology, still relies heavily on manual introspection of fungi within a Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) solution using a brightfield microscope. However, this method takes a long time, is based on the experience of the clinician, and has a low accuracy. With the increase of neural network applications in the field of clinical microscopy it is now possible to automate such manual processes increasing both efficiency and accuracy. This study presents a deep neural network structure that enables the rapid solutions for these problems and can perform automatic fungi detection in grayscale images without colorants. Microscopic images of 81 fungi and 235 ceratine were collected. Then, smaller patches were extracted containing 2062 fungi and 2142 ceratine. In order to detect fungus and ceratine, two models were created one of which was a custom neural network and the other was based on the VGG16 architecture. The developed custom model had 99.84% accuracy, and an area under the curve (AUC) value of 1.00, while the VGG16 model had 98.89% accuracy and an AUC value of 0.99. However, average accuracy and AUC value of clinicians is 72.8% and 0.87 respectively. This deep learning model allows the development of an automated system that can detect fungi within microscopic images.
The Effect of Pore Structure in Flapping Wings on Flight Performance
Jun 03, 2021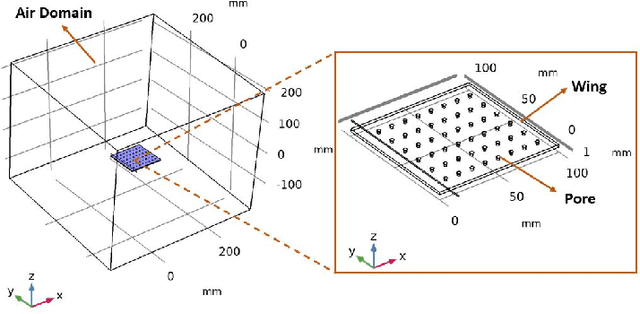
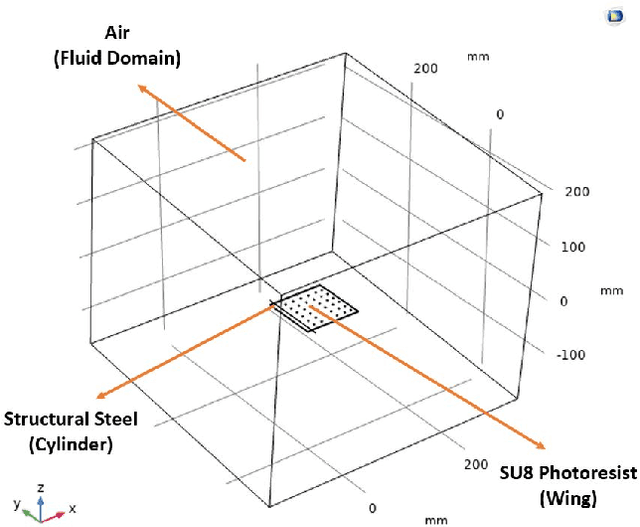


Abstract:This study investigates the effects of porosity on flying creatures such as dragonflies, moths, hummingbirds, etc. wing and shows that pores can affect wing performance. These studies were performed by 3D porous flapping wing flow analyses on Comsol Multiphysics. In this study, we analyzed different numbers of the porous wing at different angles of inclination in order to see the effect of pores on lift and drag forces. To compare the results 9 different analyses were performed. In these analyses, airflow velocity was taken as 5 m/s, angle of attack as 5 degrees, frequency as 25 Hz, and flapping angle as 30 degrees. By keeping these values constant, the number of pores was changed to 36, 48, and 60, and the pore angles of inclination to 60, 70, and 80 degrees. Analyses were carried out by giving laminar flow to this wing designed in the Comsol Multiphysics program. The importance of pores was investigated by comparing the results of these analyses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge