Abdelouahab Moussaoui
DziriBERT: a Pre-trained Language Model for the Algerian Dialect
Sep 25, 2021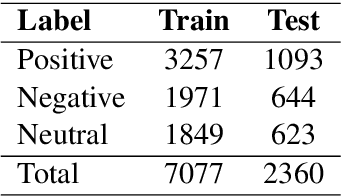
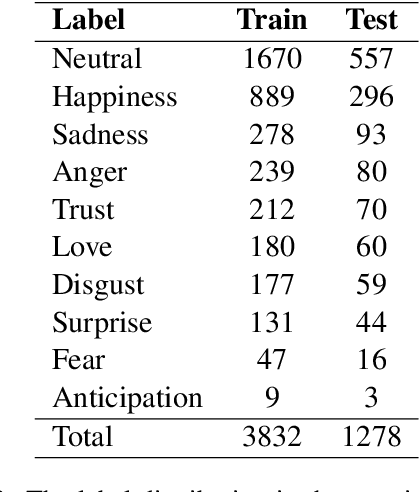
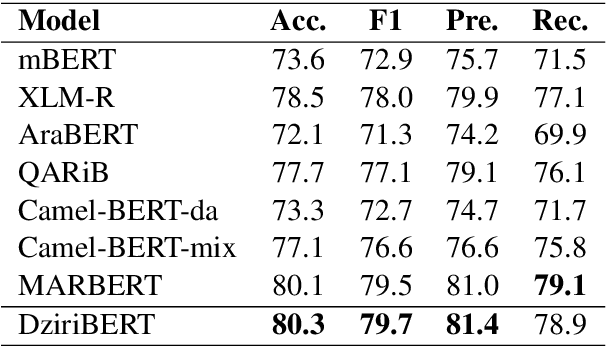
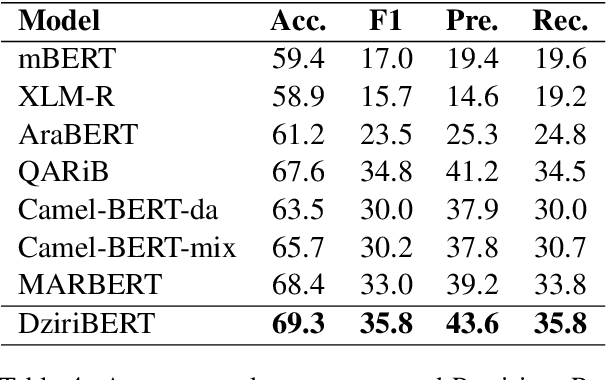
Abstract:Pre-trained transformers are now the de facto models in Natural Language Processing given their state-of-the-art results in many tasks and languages. However, most of the current models have been trained on languages for which large text resources are already available (such as English, French, Arabic, etc.). Therefore, there is still a number of low-resource languages that need more attention from the community. In this paper, we study the Algerian dialect which has several specificities that make the use of Arabic or multilingual models inappropriate. To address this issue, we collected more than one Million Algerian tweets, and pre-trained the first Algerian language model: DziriBERT. When compared to existing models, DziriBERT achieves the best results on two Algerian downstream datasets. The obtained results show that pre-training a dedicated model on a small dataset (150 MB) can outperform existing models that have been trained on much more data (hundreds of GB). Finally, our model is publicly available to the community.
PeSOA: Penguins Search Optimisation Algorithm for Global Optimisation Problems
Sep 27, 2018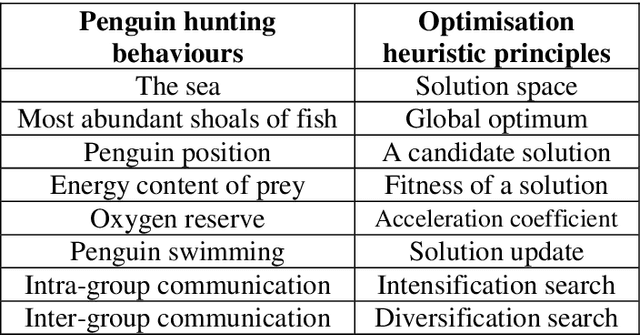
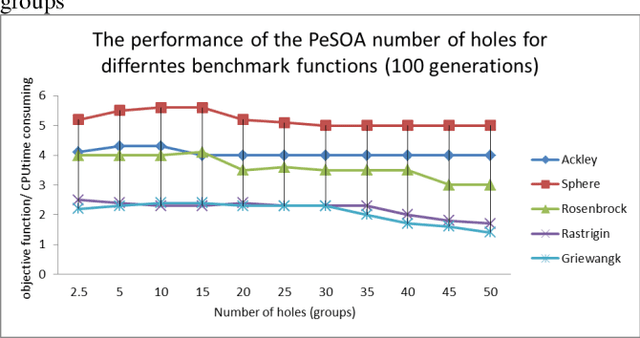
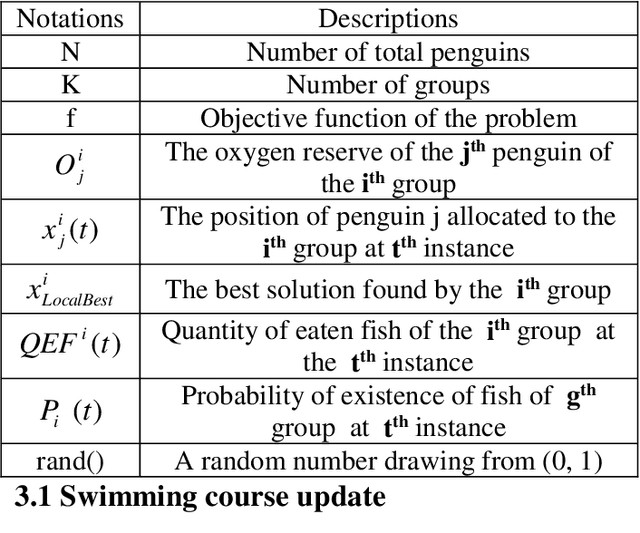
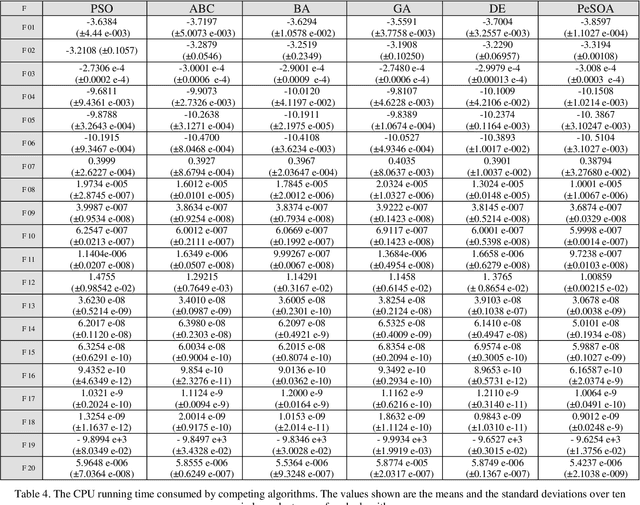
Abstract:This paper develops Penguin search Optimisation Algorithm (PeSOA), a new metaheuristic algorithm which is inspired by the foraging behaviours of penguins. A population of penguins located in the solution space of the given search and optimisation problem is divided into groups and tasked with finding optimal solutions. The penguins of a group perform simultaneous dives and work as a team to collaboratively feed on fish the energy content of which corresponds to the fitness of candidate solutions. Fish stocks have higher fitness and concentration near areas of solution optima and thus drive the search. Penguins can migrate to other places if their original habitat lacks food. We identify two forms of penguin communication both intra-group and inter-group which are useful in designing intensification and diversification strategies. An efficient intensification strategy allows fast convergence to a local optimum, whereas an effective diversification strategy avoids cyclic behaviour around local optima and explores more effectively the space of potential solutions. The proposed PeSOA algorithm has been validated on a well-known set of benchmark functions. Comparative performances with six other nature-inspired metaheuristics show that the PeSOA performs favourably in these tests. A run-time analysis shows that the performance obtained by the PeSOA is very stable at any time of the evolution horizon, making the PeSOA a viable approach for real world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge