Aart Stuurman
The Effects of Learning in Morphologically Evolving Robot Systems
Nov 18, 2021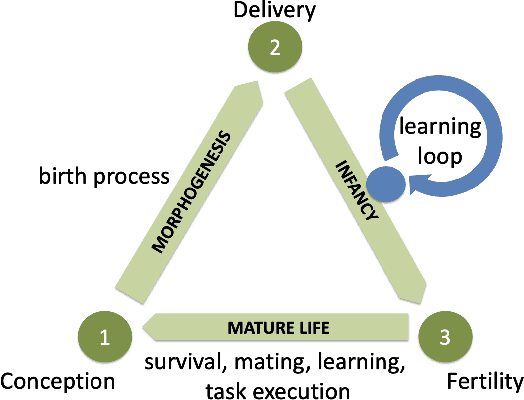
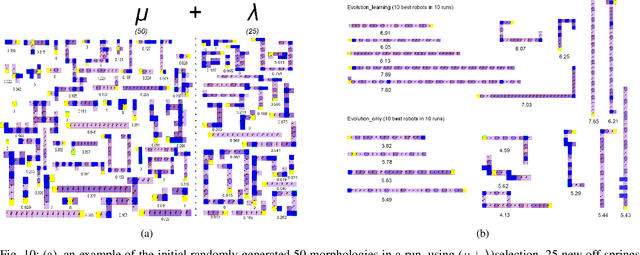

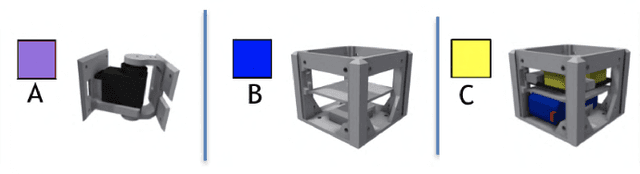
Abstract:Simultaneously evolving morphologies (bodies) and controllers (brains) of robots can cause a mismatch between the inherited body and brain in the offspring. To mitigate this problem, the addition of an infant learning period by the so-called Triangle of Life framework has been proposed relatively long ago. However, an empirical assessment is still lacking to-date. In this paper we investigate the effects of such a learning mechanism from different perspectives. Using extensive simulations we show that learning can greatly increase task performance and reduce the number of generations required to reach a certain fitness level compared to the purely evolutionary approach. Furthermore, although learning only directly affects the controllers, we demonstrate that the evolved morphologies will be also different. This provides a quantitative demonstration that changes in the brain can induce changes in the body. Finally, we examine the concept of morphological intelligence quantified by the ability of a given body to learn. We observe that the learning delta, the performance difference between the inherited and the learned brain, is growing throughout the evolutionary process. This shows that evolution is producing robots with an increasing plasticity, that is, consecutive generations are becoming better and better learners which in turn makes them better and better at the given task. All in all, our results demonstrate that the Triangle of Life is not only a concept of theoretical interest, but a system architecture with practical benefits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge