Aaron D Ames
Distributed Data-Driven Predictive Control for Multi-Agent Collaborative Legged Locomotion
Nov 13, 2022



Abstract:The aim of this work is to define a planner that enables robust legged locomotion for complex multi-agent systems consisting of several holonomically constrained quadrupeds. To this end, we employ a methodology based on behavioral systems theory to model the sophisticated and high-dimensional structure induced by the holonomic constraints. The resulting model is then used in tandem with distributed control techniques such that the computational burden is shared across agents while the coupling between agents is preserved. Finally, this distributed model is framed in the context of a predictive controller, resulting in a robustly stable method for trajectory planning. This methodology is tested in simulation with up to five agents and is further experimentally validated on three A1 quadrupedal robots subject to various uncertainties, including payloads, rough terrain, and push disturbances.
Layered Control for Cooperative Locomotion of Two Quadrupedal Robots: Centralized and Distributed Approaches
Nov 13, 2022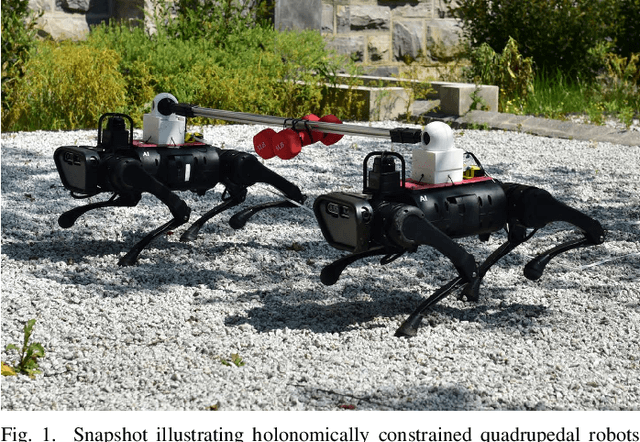
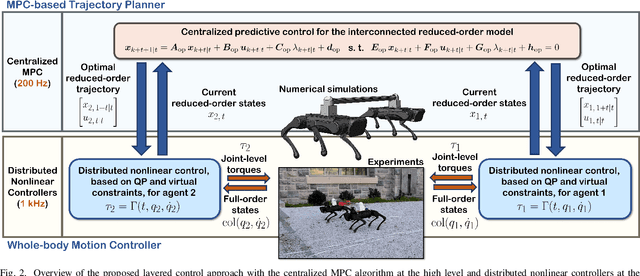
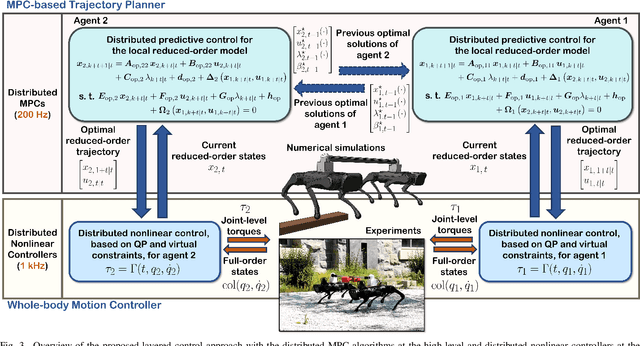
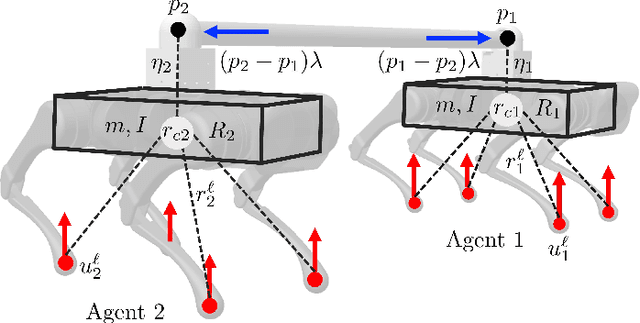
Abstract:This paper presents a layered control approach for real-time trajectory planning and control of robust cooperative locomotion by two holonomically constrained quadrupedal robots. A novel interconnected network of reduced-order models, based on the single rigid body (SRB) dynamics, is developed for trajectory planning purposes. At the higher level of the control architecture, two different model predictive control (MPC) algorithms are proposed to address the optimal control problem of the interconnected SRB dynamics: centralized and distributed MPCs. The distributed MPC assumes two local quadratic programs that share their optimal solutions according to a one-step communication delay and an agreement protocol. At the lower level of the control scheme, distributed nonlinear controllers are developed to impose the full-order dynamics to track the prescribed reduced-order trajectories generated by MPCs. The effectiveness of the control approach is verified with extensive numerical simulations and experiments for the robust and cooperative locomotion of two holonomically constrained A1 robots with different payloads on variable terrains and in the presence of disturbances. It is shown that the distributed MPC has a performance similar to that of the centralized MPC, while the computation time is reduced significantly.
From Bipedal Walking to Quadrupedal Locomotion: Full-Body Dynamics Decomposition for Rapid Gait Generation
Sep 30, 2019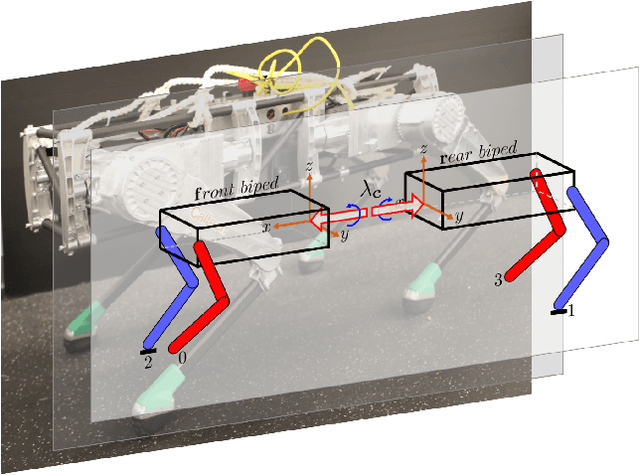
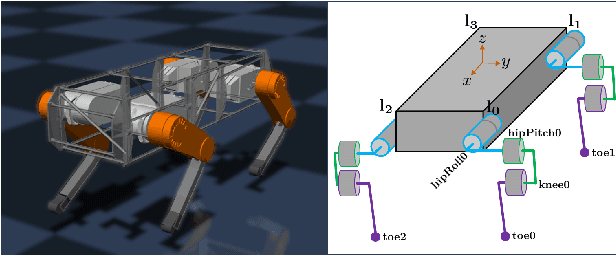
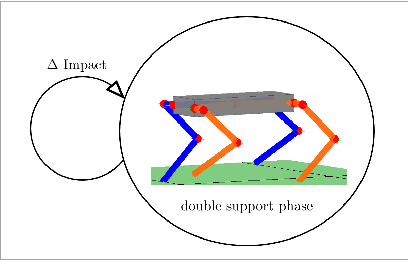
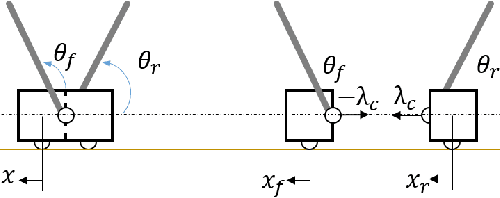
Abstract:This paper systematically decomposes quadrupeds into bipeds to rapidly generate walking gaits, and then recomposes these gaits to obtain quadrupedal locomotion. We begin by decomposing the full-order, nonlinear and hybrid dynamics of a three-dimensional quadrupedal robot, including its continuous and discrete dynamics, into two bipedal systems that are subject to external forces. Using the hybrid zero dynamics (HZD) framework, gaits for these bipedal robots can be rapidly generated (on the order of seconds) along with corresponding controllers. The decomposition is performed in such a way that the bipedal walking gaits and controllers can be composed to yield dynamic walking gaits for the original quadrupedal robot --- the result, therefore, is the rapid generation of dynamic quadruped gaits utilizing the full-order dynamics. This methodology is demonstrated through the rapid generation (3.96 seconds on average) of four stepping-in-place gaits and one ambling gait at 0.35 m/s on a quadrupedal robot --- the Vision 60, with 36 state variables and 12 control inputs --- both in simulation and through outdoor experiments. This suggested a new approach for fast quadrupedal trajectory planning using full-body dynamics, without the need for empirical model simplification, wherein methods from dynamic bipedal walking can be directly applied to quadrupeds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge