Aaron Call
ALOJA: A Framework for Benchmarking and Predictive Analytics in Big Data Deployments
Nov 06, 2015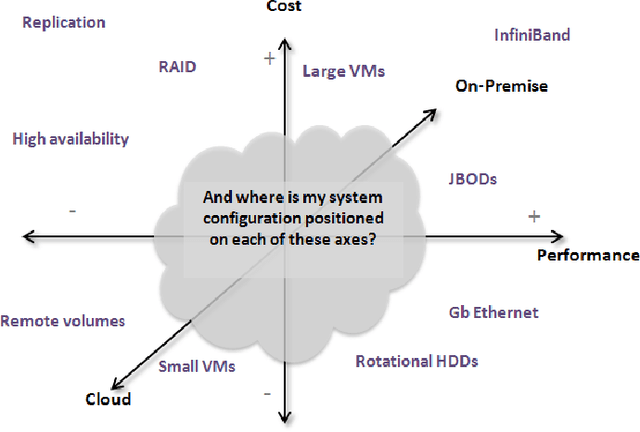
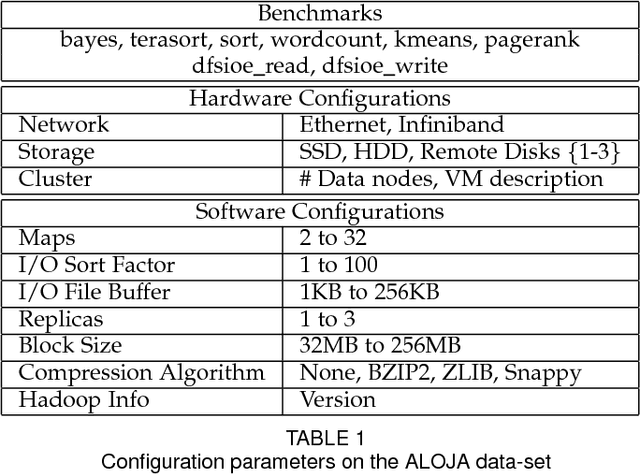

Abstract:This article presents the ALOJA project and its analytics tools, which leverages machine learning to interpret Big Data benchmark performance data and tuning. ALOJA is part of a long-term collaboration between BSC and Microsoft to automate the characterization of cost-effectiveness on Big Data deployments, currently focusing on Hadoop. Hadoop presents a complex run-time environment, where costs and performance depend on a large number of configuration choices. The ALOJA project has created an open, vendor-neutral repository, featuring over 40,000 Hadoop job executions and their performance details. The repository is accompanied by a test-bed and tools to deploy and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different hardware configurations, parameters and Cloud services. Despite early success within ALOJA, a comprehensive study requires automation of modeling procedures to allow an analysis of large and resource-constrained search spaces. The predictive analytics extension, ALOJA-ML, provides an automated system allowing knowledge discovery by modeling environments from observed executions. The resulting models can forecast execution behaviors, predicting execution times for new configurations and hardware choices. That also enables model-based anomaly detection or efficient benchmark guidance by prioritizing executions. In addition, the community can benefit from ALOJA data-sets and framework to improve the design and deployment of Big Data applications.
ALOJA-ML: A Framework for Automating Characterization and Knowledge Discovery in Hadoop Deployments
Nov 06, 2015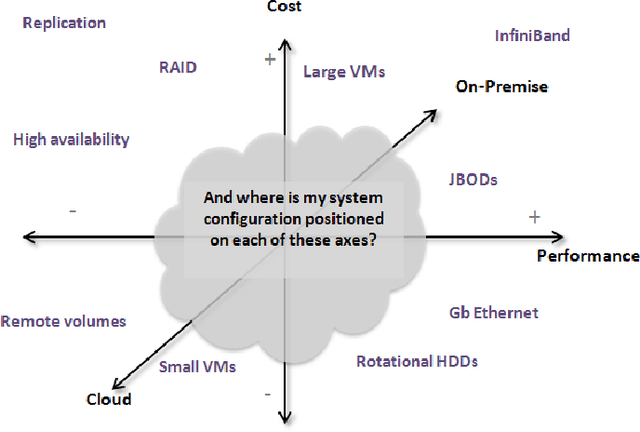
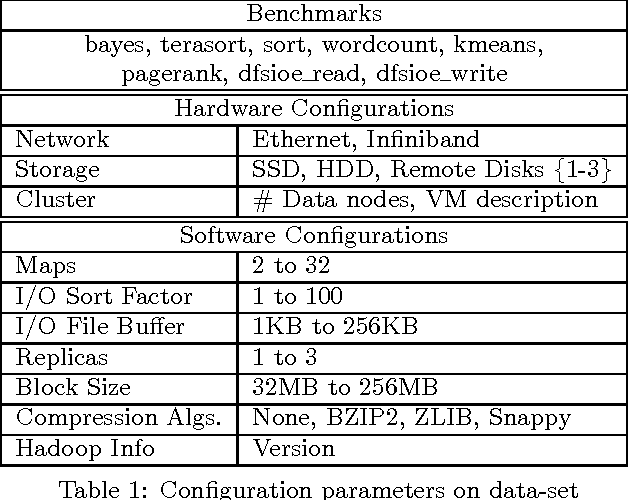

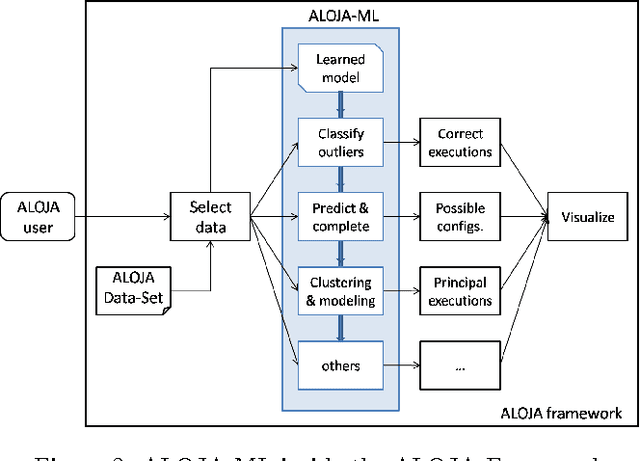
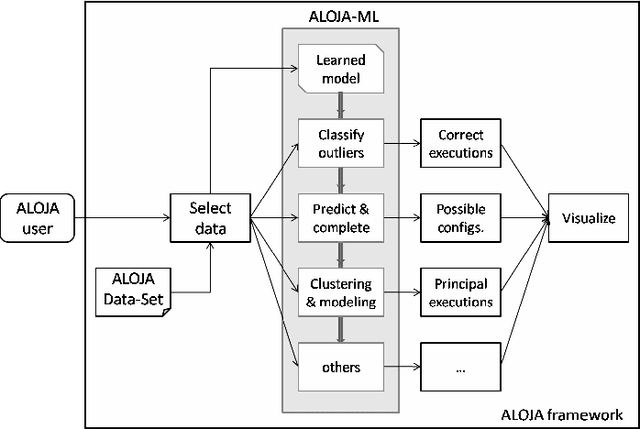
Abstract:This article presents ALOJA-Machine Learning (ALOJA-ML) an extension to the ALOJA project that uses machine learning techniques to interpret Hadoop benchmark performance data and performance tuning; here we detail the approach, efficacy of the model and initial results. Hadoop presents a complex execution environment, where costs and performance depends on a large number of software (SW) configurations and on multiple hardware (HW) deployment choices. These results are accompanied by a test bed and tools to deploy and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the different hardware configurations, parameter tunings, and Cloud services. Despite early success within ALOJA from expert-guided benchmarking, it became clear that a genuinely comprehensive study requires automation of modeling procedures to allow a systematic analysis of large and resource-constrained search spaces. ALOJA-ML provides such an automated system allowing knowledge discovery by modeling Hadoop executions from observed benchmarks across a broad set of configuration parameters. The resulting performance models can be used to forecast execution behavior of various workloads; they allow 'a-priori' prediction of the execution times for new configurations and HW choices and they offer a route to model-based anomaly detection. In addition, these models can guide the benchmarking exploration efficiently, by automatically prioritizing candidate future benchmark tests. Insights from ALOJA-ML's models can be used to reduce the operational time on clusters, speed-up the data acquisition and knowledge discovery process, and importantly, reduce running costs. In addition to learning from the methodology presented in this work, the community can benefit in general from ALOJA data-sets, framework, and derived insights to improve the design and deployment of Big Data applications.
* Submitted to KDD'2015. Part of the Aloja Project. Partially funded by European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 639595) - HiEST Project
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge