Özge Drama
A Control Method to Compensate Ground Level Changes for Running Bipedal Robots
Jun 06, 2020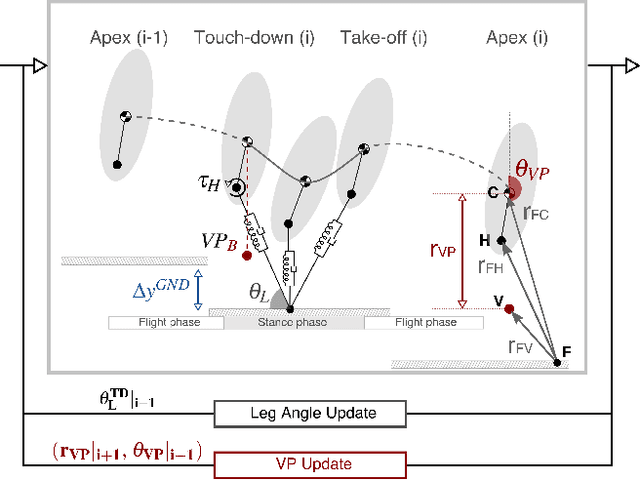
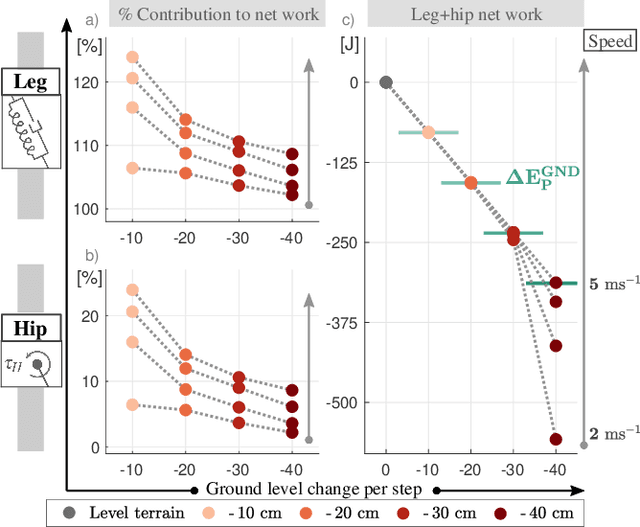
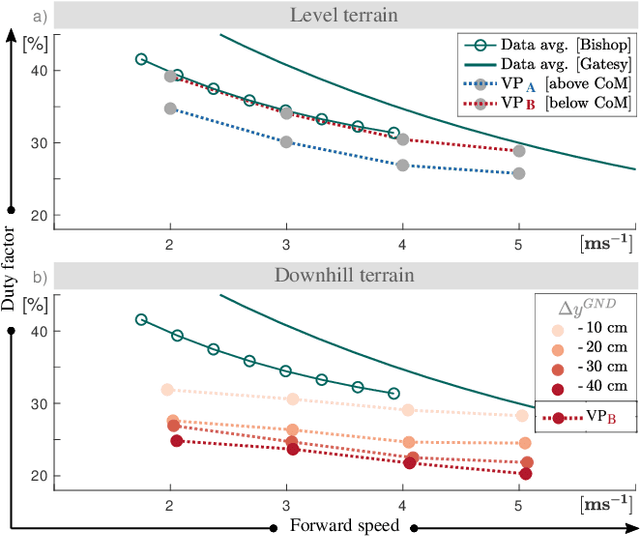
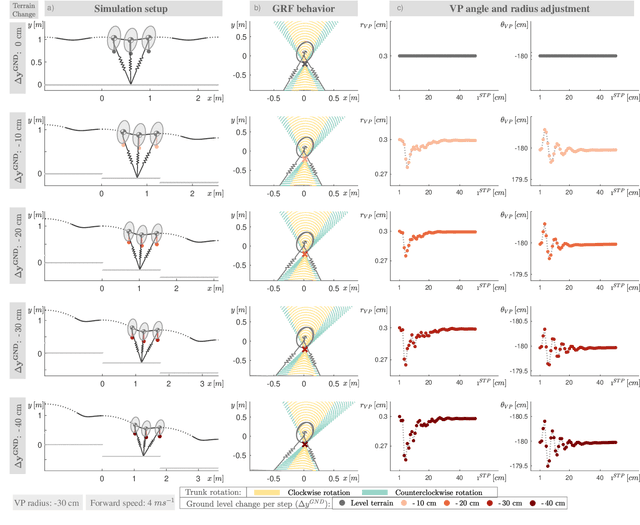
Abstract:Bipedal running is a difficult task to realize in robots, since the trunk is underactuated and control is limited by intermittent ground contacts. Stabilizing the trunk becomes even more challenging if the terrain is uneven and causes perturbations. One bio-inspired method to achieve postural stability is the virtual point (VP) control, which is able to generate natural motion. However, so far it has only been studied for level running. In this work, we investigate whether the VP control method can accommodate single step-downs and downhill terrains. We provide guidelines on the model and controller parameterizations for handling varying terrain conditions. Next, we show that the VP method is able to stabilize single step-down perturbations up to 40 cm, and downhill grades up to 20-10{\deg} corresponding to running speeds of 2-5m/s. Our results suggest that VP control is a promising candidate for terrain-adaptive running control of bipedal robots.
Postural Stability in Human Running with Step-down Perturbations: An Experimental and Numerical Study
Apr 06, 2020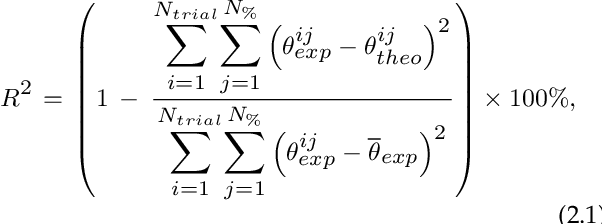
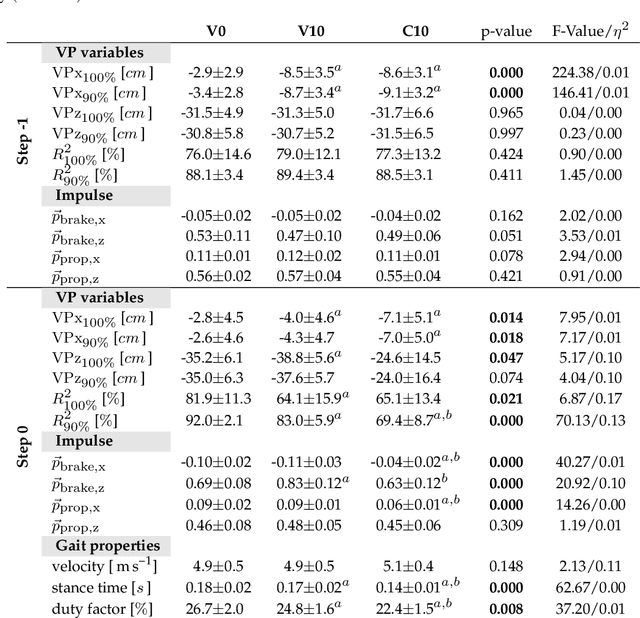
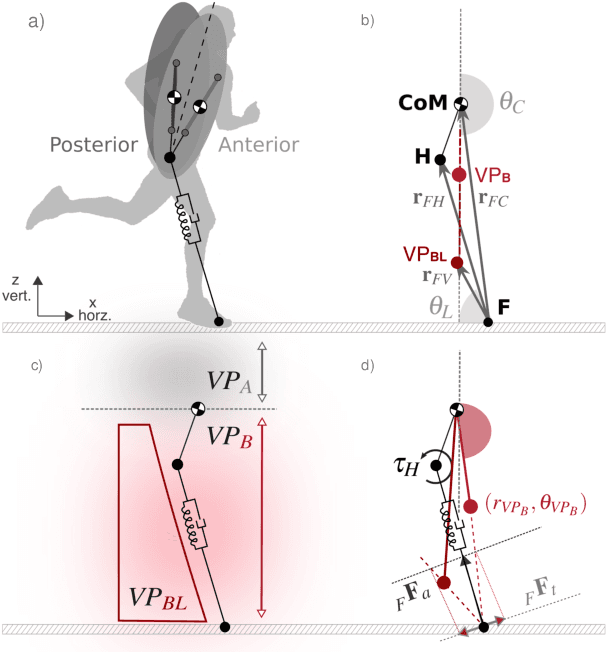
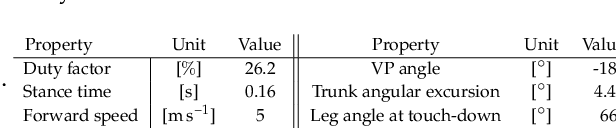
Abstract:Postural stability is one of the most crucial elements in bipedal locomotion. Bipeds are dynamically unstable and need to maintain their trunk upright against the rotations induced by the ground reaction forces (GRFs), especially when running. Gait studies report that the GRF vectors focus around a virtual point above the center of mass (VPA), while the trunk moves forward in pitch axis during the stance phase of human running. However, a recent simulation study suggests that a virtual point below the center of mass (VPB) might be present in human running, since a VPA yields backward trunk rotation during the stance phase. In this work, we perform a gait analysis to investigate the existence and location of the VP in human running at 5 ms-1, and support our findings numerically using the spring-loaded inverted pendulum model with a trunk (TSLIP). We extend our analysis to include perturbations in terrain height (visible and camouflaged), and investigate the response of the VP mechanism to step-down perturbations both experimentally and numerically. Our experimental results show that the human running gait displays a VPB of ~-30cm and a forward trunk motion during the stance phase. The camouflaged step-down perturbations affect the location of the VPB. Our simulation results suggest that the VPB is able to encounter the step-down perturbations and bring the system back to its initial equilibrium state.
Trunk Pitch Oscillations to Improve Energetics in Bipedal Running Birds and Robots
Sep 20, 2019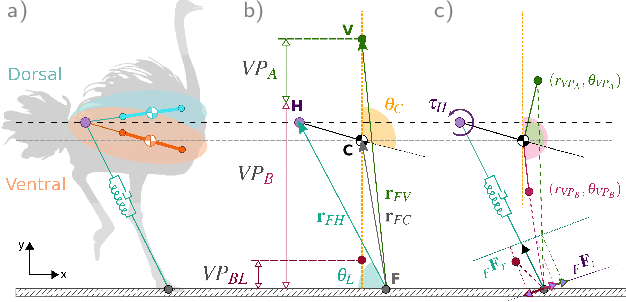
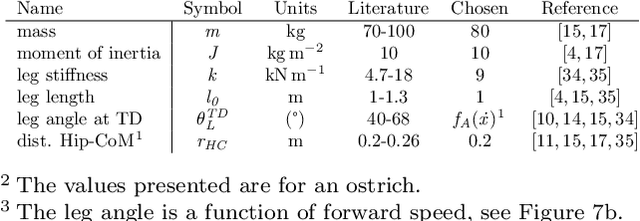
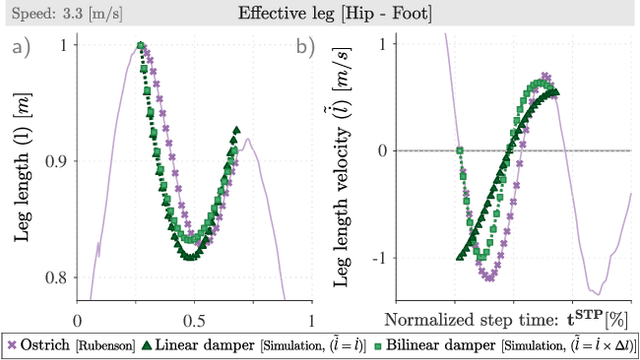
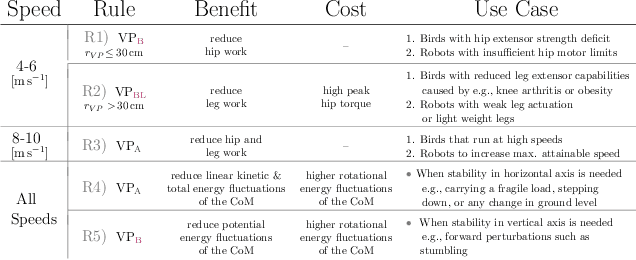
Abstract:Bipedal animals have diverse morphologies and advanced locomotion abilities. Terrestrial birds in particular, display agile, efficient, and robust running motion, in which they exploit the interplay between the body segment masses and moment of inertias. On the other hand, most legged robots are not able to generate such versatile and energy efficient motion and often disregard trunk movements as a means to enhance their locomotion capabilities. Recent research investigated how trunk motions affect the gait characteristics of humans, but there is a lack of analysis across different bipedal morphologies. To address this issue, we analyze avian running based on a spring-loaded inverted pendulum model with a pronograde (horizontal) trunk. We use a virtual point based control scheme and modify the alignment of the ground reaction forces to assess how our control strategy influences the trunk pitch oscillations and energetics of the locomotion. We derive three potential key strategies to leverage trunk pitch motions that minimize either the energy fluctuations of the center of mass or the work performed by the hip and leg. We show that these strategies are also valid for human-like trunks, and could be used in legged robotics.
Trunk Pitch Oscillations for Joint Load Redistribution in Humans and Humanoid Robots
Sep 09, 2019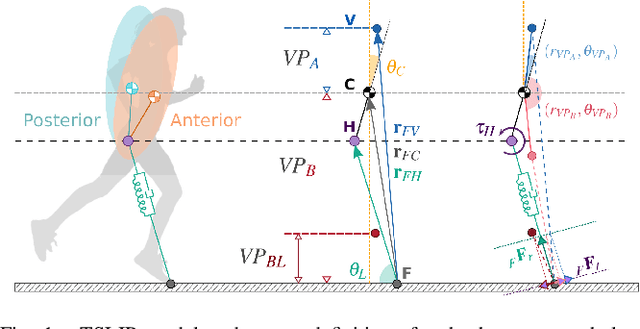
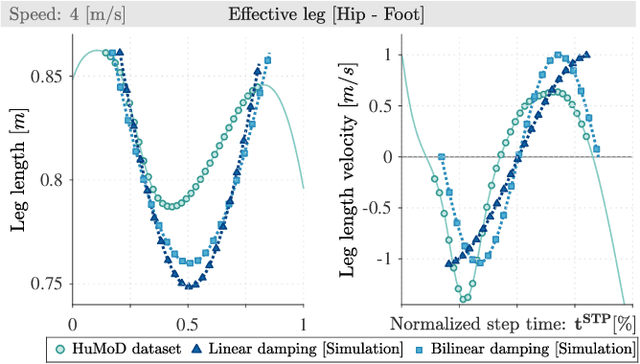
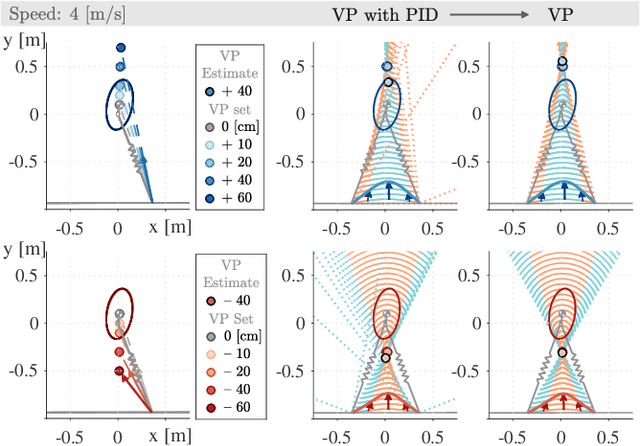
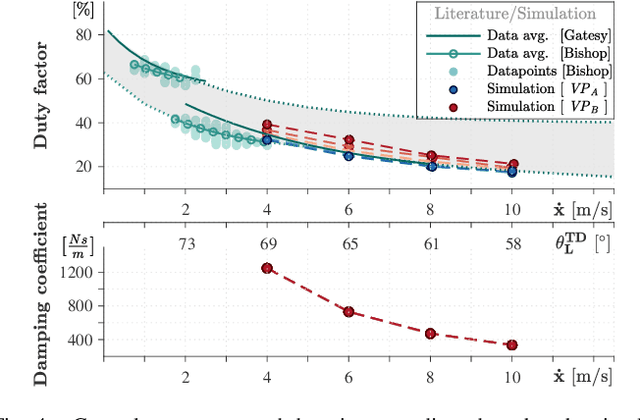
Abstract:Creating natural-looking running gaits for humanoid robots is a complex task due to the underactuated degree of freedom in the trunk, which makes the motion planning and control difficult. The research on trunk movements in human locomotion is insufficient, and no formalism is known to transfer human motion patterns onto robots. Related work mostly focuses on the lower extremities, and simplifies the problem by stabilizing the trunk at a fixed angle. In contrast, humans display significant trunk motions that follow the natural dynamics of the gait. In this work, we use a spring-loaded inverted pendulum model with a trunk (TSLIP) together with a virtual point (VP) target to create trunk oscillations and investigate the impact of these movements. We analyze how the VP location and forward speed determine the direction and magnitude of the trunk oscillations. We show that positioning the VP below the center of mass (CoM) can explain the forward trunk pitching observed in human running. The VP below the CoM leads to a synergistic work between the hip and leg, reducing the leg loading. However, it comes at the cost of increased peak hip torque. Our results provide insights for leveraging the trunk motion to redistribute joint loads and potentially improve the energy efficiency in humanoid robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge