Working Memory Graphs
Paper and Code
Nov 17, 2019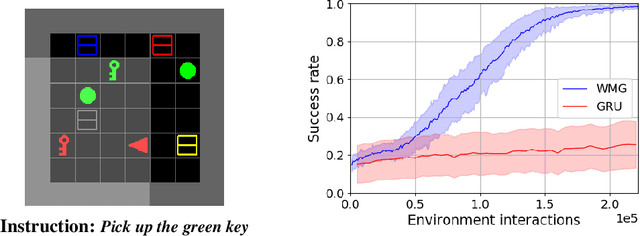
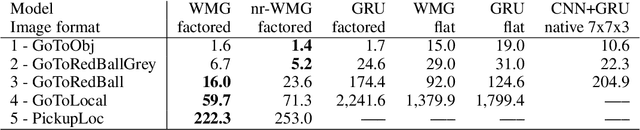
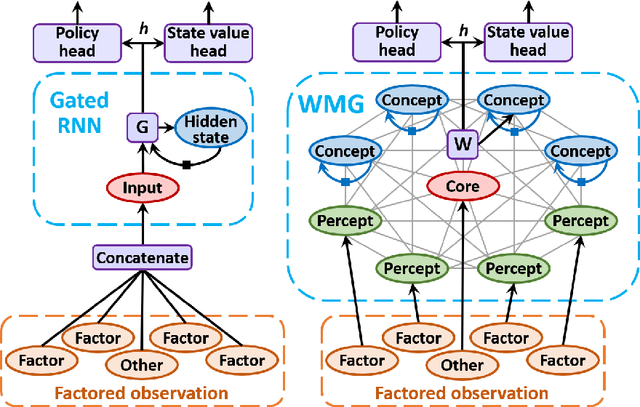
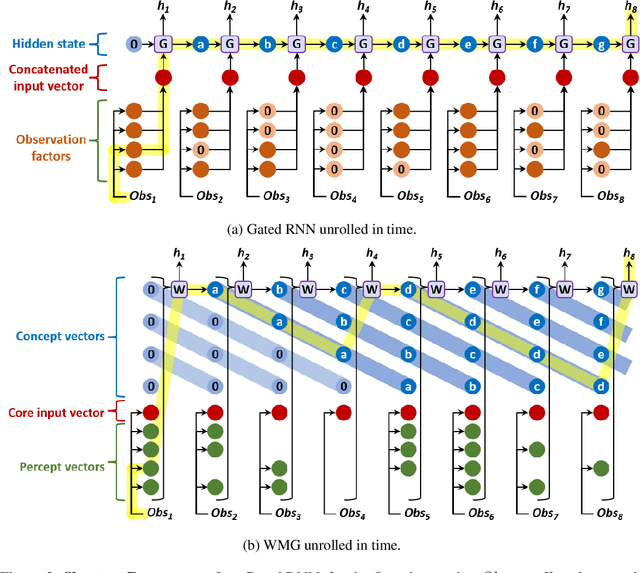
Transformers have increasingly outperformed gated RNNs in obtaining new state-of-the-art results on supervised tasks involving text sequences. Inspired by this trend, we study the question of how Transformer-based models can improve the performance of sequential decision-making agents. We present the Working Memory Graph (WMG), an agent that employs multi-head self-attention to reason over a dynamic set of vectors representing observed and recurrent state. We evaluate WMG in two partially observable environments, one that requires complex reasoning over past observations, and another that features factored observations. We find that WMG significantly outperforms gated RNNs on these tasks, supporting the hypothesis that WMG's inductive bias in favor of learning and leveraging factored representations can dramatically boost sample efficiency in environments featuring such structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge