What Causes Optical Flow Networks to be Vulnerable to Physical Adversarial Attacks
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2021
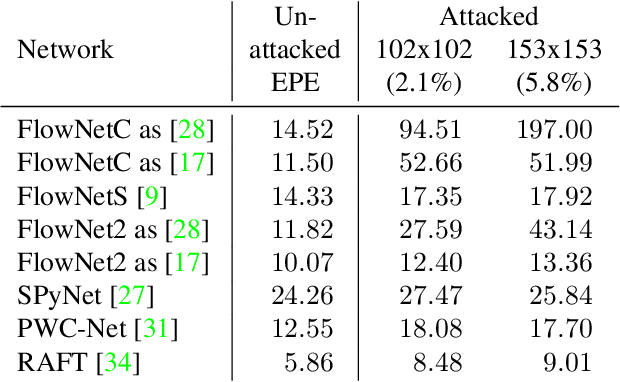


Recent work demonstrated the lack of robustness of optical flow networks to physical, patch-based adversarial attacks. The possibility to physically attack a basic component of automotive systems is a reason for serious concerns. In this paper, we analyze the cause of the problem and show that the lack of robustness is rooted in the classical aperture problem of optical flow estimation in combination with bad choices in the details of the network architecture. We show how these mistakes can be rectified in order to make optical flow networks robust to physical, patch-based attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge