Welfare of Sequential Allocation Mechanisms for Indivisible Goods
Paper and Code
Nov 26, 2015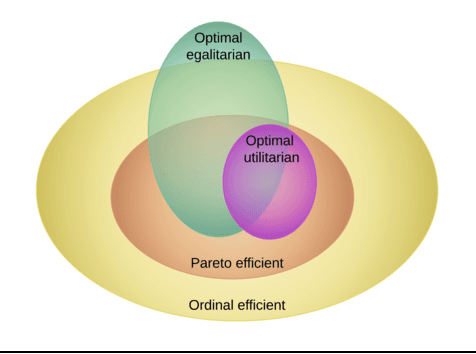
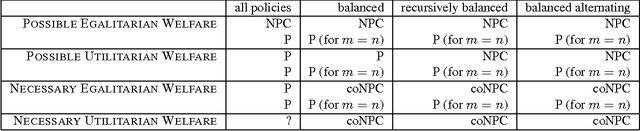
Sequential allocation is a simple and attractive mechanism for the allocation of indivisible goods. Agents take turns, according to a policy, to pick items. Sequential allocation is guaranteed to return an allocation which is efficient but may not have an optimal social welfare. We consider therefore the relation between welfare and efficiency. We study the (computational) questions of what welfare is possible or necessary depending on the choice of policy. We also consider a novel control problem in which the chair chooses a policy to improve social welfare.
* Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, 787-794,
2016
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge