We Have a Package for You! A Comprehensive Analysis of Package Hallucinations by Code Generating LLMs
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2024
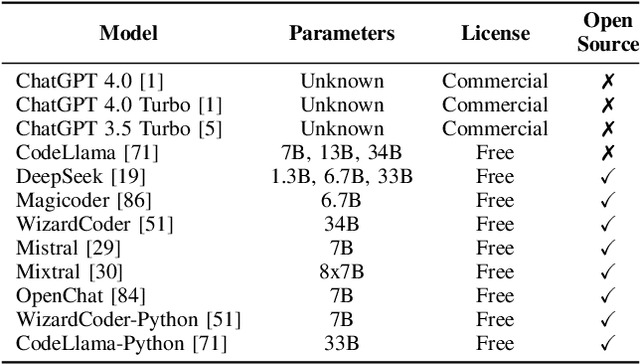


The reliance of popular programming languages such as Python and JavaScript on centralized package repositories and open-source software, combined with the emergence of code-generating Large Language Models (LLMs), has created a new type of threat to the software supply chain: package hallucinations. These hallucinations, which arise from fact-conflicting errors when generating code using LLMs, represent a novel form of package confusion attack that poses a critical threat to the integrity of the software supply chain. This paper conducts a rigorous and comprehensive evaluation of package hallucinations across different programming languages, settings, and parameters, exploring how different configurations of LLMs affect the likelihood of generating erroneous package recommendations and identifying the root causes of this phenomena. Using 16 different popular code generation models, across two programming languages and two unique prompt datasets, we collect 576,000 code samples which we analyze for package hallucinations. Our findings reveal that 19.7% of generated packages across all the tested LLMs are hallucinated, including a staggering 205,474 unique examples of hallucinated package names, further underscoring the severity and pervasiveness of this threat. We also implemented and evaluated mitigation strategies based on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), self-detected feedback, and supervised fine-tuning. These techniques demonstrably reduced package hallucinations, with hallucination rates for one model dropping below 3%. While the mitigation efforts were effective in reducing hallucination rates, our study reveals that package hallucinations are a systemic and persistent phenomenon that pose a significant challenge for code generating LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge