Watch out! There may be a Human. Addressing Invisible Humans in Social Navigation
Paper and Code
Nov 22, 2022
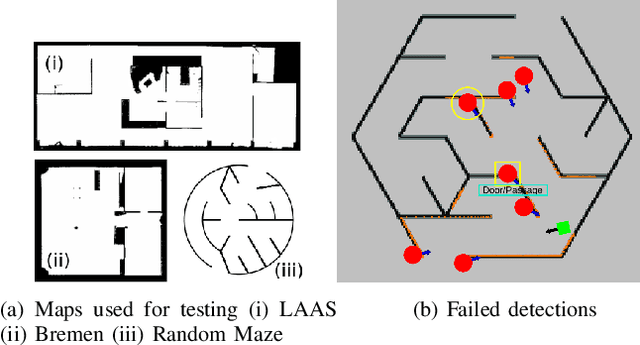

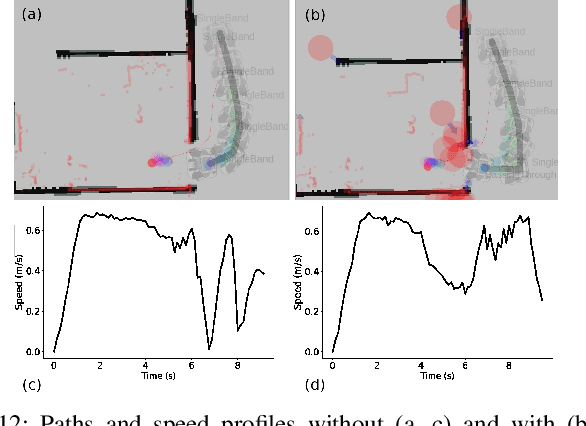
Current approaches in human-aware or social robot navigation address the humans that are visible to the robot. However, it is also important to address the possible emergences of humans to avoid shocks or surprises to humans and erratic behavior of the robot planner. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to detect and address these human emergences called `invisible humans'. We determine the places from which a human, currently not visible to the robot, can appear suddenly and then adapt the path and speed of the robot with the anticipation of potential collisions. This is done while still considering and adapting humans present in the robot's field of view. We also show how this detection can be exploited to identify and address the doorways or narrow passages. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed methodology is shown through several simulated and real-world experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge