Wasserstein Collaborative Filtering for Item Cold-start Recommendation
Paper and Code
Sep 10, 2019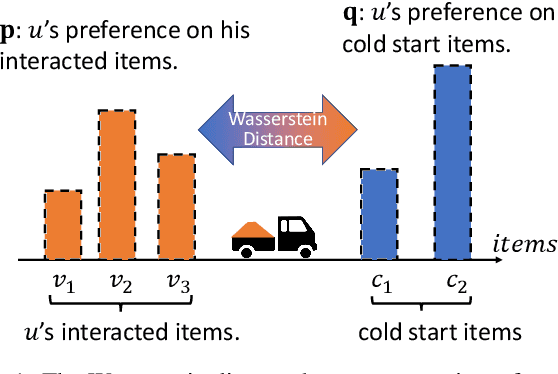
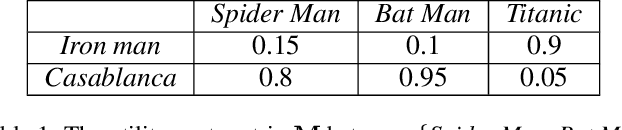
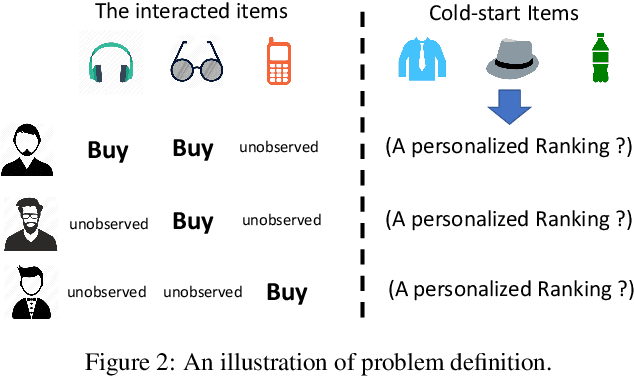
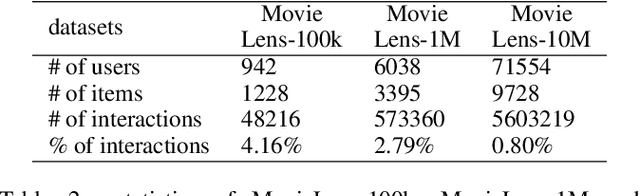
The item cold-start problem seriously limits the recommendation performance of Collaborative Filtering (CF) methods when new items have either none or very little interactions. To solve this issue, many modern Internet applications propose to predict a new item's interaction from the possessing contents. However, it is difficult to design and learn a map between the item's interaction history and the corresponding contents. In this paper, we apply the Wasserstein distance to address the item cold-start problem. Given item content information, we can calculate the similarity between the interacted items and cold-start ones, so that a user's preference on cold-start items can be inferred by minimizing the Wasserstein distance between the distributions over these two types of items. We further adopt the idea of CF and propose Wasserstein CF (WCF) to improve the recommendation performance on cold-start items. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of WCF over state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge