WAKE: Wavelet Decomposition Coupled with Adaptive Kalman Filtering for Pathological Tremor Extraction
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2018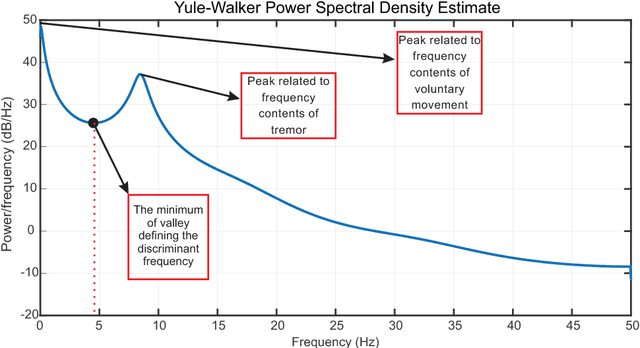
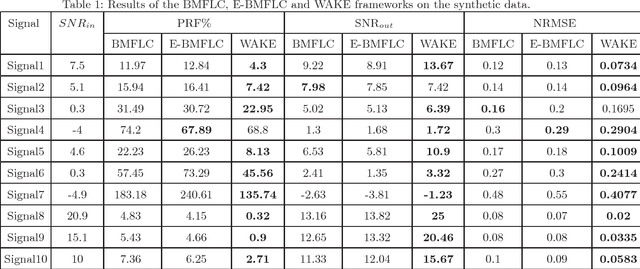

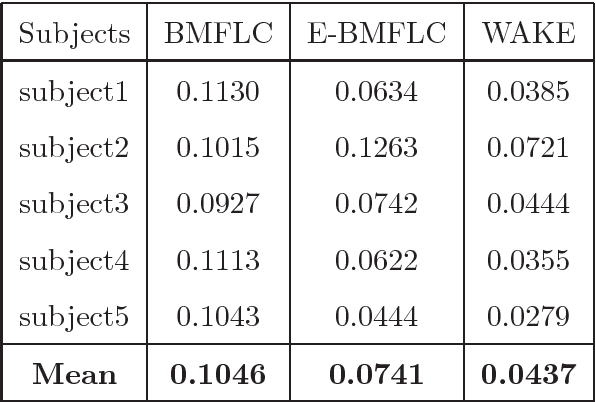
Pathological Hand Tremor (PHT) is among common symptoms of several neurological movement disorders, which can significantly degrade quality of life of affected individuals. Beside pharmaceutical and surgical therapies, mechatronic technologies have been utilized to control PHTs. Most of these technologies function based on estimation, extraction, and characterization of tremor movement signals. Real-time extraction of tremor signal is of paramount importance because of its application in assistive and rehabilitative devices. In this paper, we propose a novel on-line adaptive method which can adjust the hyper-parameters of the filter to the variable characteristics of the tremor. The proposed "WAKE: Wavelet decomposition coupled with Adaptive Kalman filtering technique for pathological tremor Extraction, referred to as the WAKE framework" is composed of a new adaptive Kalman filter and a wavelet transform core to provide indirect prediction of the tremor, one sample ahead of time, to be used for its suppression. In this paper, the design, implementation and evaluation of WAKE are given. The performance is evaluated based on three different datasets, the first one is a synthetic dataset, developed in this work, that simulates hand tremor under ten different conditions. The second and third ones are real datasets recorded from patients with PHTs. The results obtained from the proposed WAKE framework demonstrate significant improvements in the estimation accuracy in comparison with two well regarded techniques in the literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge