Visually Grounded Language Learning: a review of language games, datasets, tasks, and models
Paper and Code
Dec 05, 2023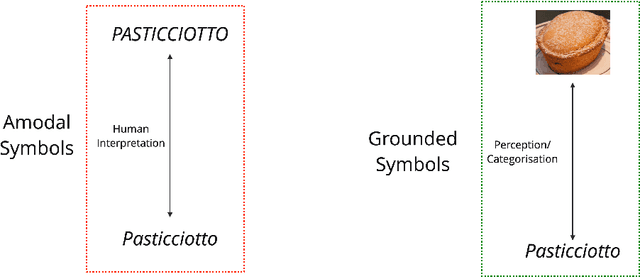
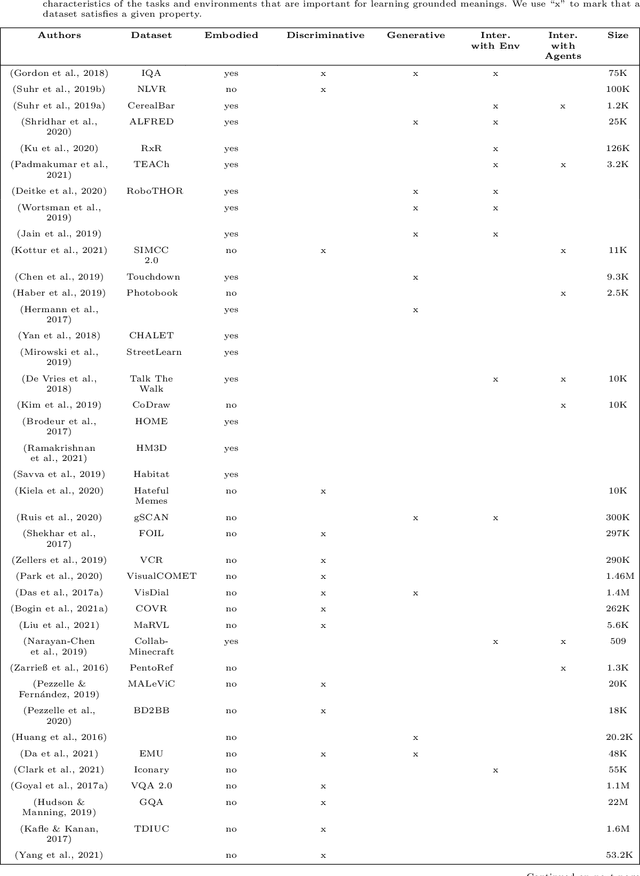
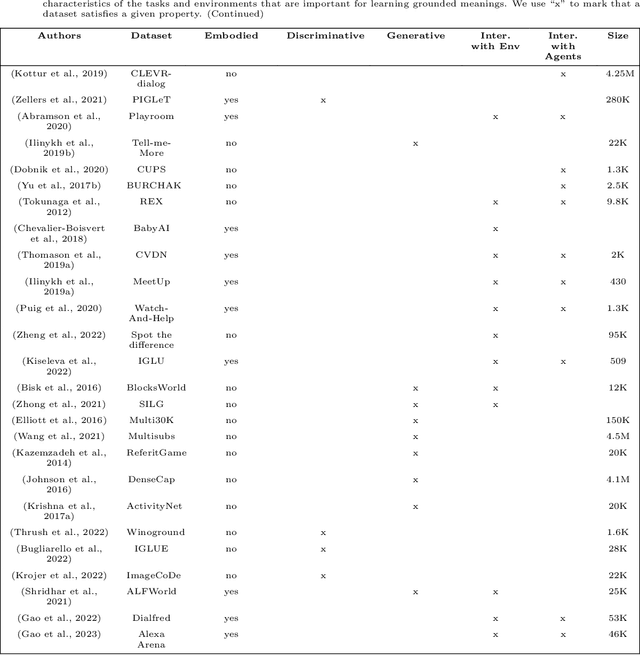
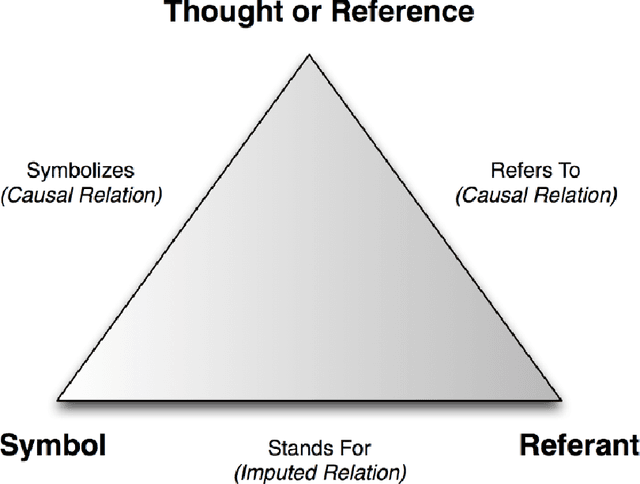
In recent years, several machine learning models have been proposed. They are trained with a language modelling objective on large-scale text-only data. With such pretraining, they can achieve impressive results on many Natural Language Understanding and Generation tasks. However, many facets of meaning cannot be learned by ``listening to the radio" only. In the literature, many Vision+Language (V+L) tasks have been defined with the aim of creating models that can ground symbols in the visual modality. In this work, we provide a systematic literature review of several tasks and models proposed in the V+L field. We rely on Wittgenstein's idea of `language games' to categorise such tasks into 3 different families: 1) discriminative games, 2) generative games, and 3) interactive games. Our analysis of the literature provides evidence that future work should be focusing on interactive games where communication in Natural Language is important to resolve ambiguities about object referents and action plans and that physical embodiment is essential to understand the semantics of situations and events. Overall, these represent key requirements for developing grounded meanings in neural models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge