Vertex-reinforced Random Walk for Network Embedding
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2020
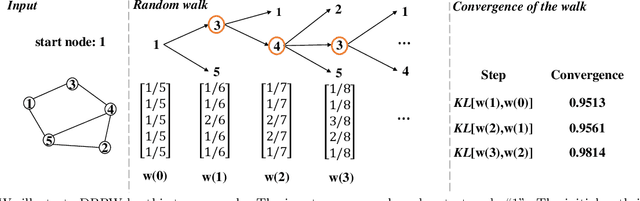
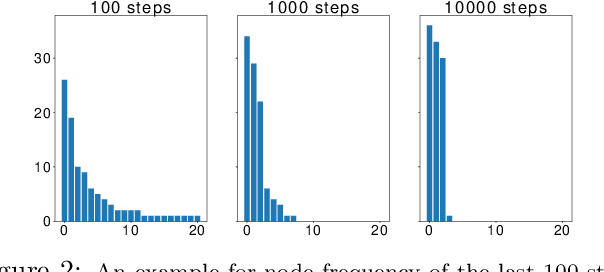
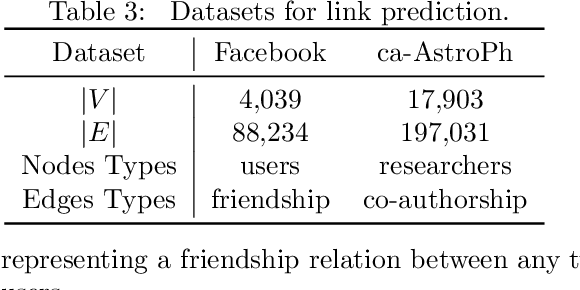
In this paper, we study the fundamental problem of random walk for network embedding. We propose to use non-Markovian random walk, variants of vertex-reinforced random walk (VRRW), to fully use the history of a random walk path. To solve the getting stuck problem of VRRW, we introduce an exploitation-exploration mechanism to help the random walk jump out of the stuck set. The new random walk algorithms share the same convergence property of VRRW and thus can be used to learn stable network embeddings. Experimental results on two link prediction benchmark datasets and three node classification benchmark datasets show that our proposed approach reinforce2vec can outperform state-of-the-art random walk based embedding methods by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge