Vector-Valued Least-Squares Regression under Output Regularity Assumptions
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2022
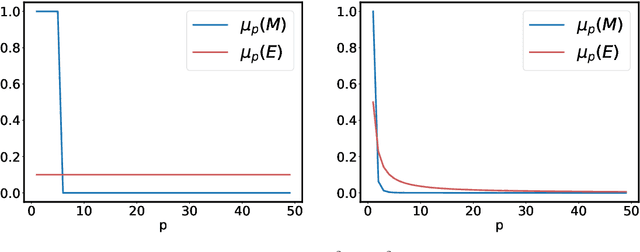

We propose and analyse a reduced-rank method for solving least-squares regression problems with infinite dimensional output. We derive learning bounds for our method, and study under which setting statistical performance is improved in comparison to full-rank method. Our analysis extends the interest of reduced-rank regression beyond the standard low-rank setting to more general output regularity assumptions. We illustrate our theoretical insights on synthetic least-squares problems. Then, we propose a surrogate structured prediction method derived from this reduced-rank method. We assess its benefits on three different problems: image reconstruction, multi-label classification, and metabolite identification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge