Variable and value elimination in binary constraint satisfaction via forbidden patterns
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2015
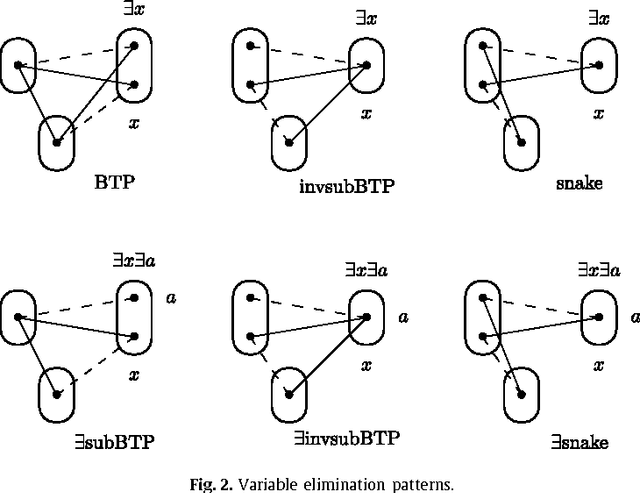
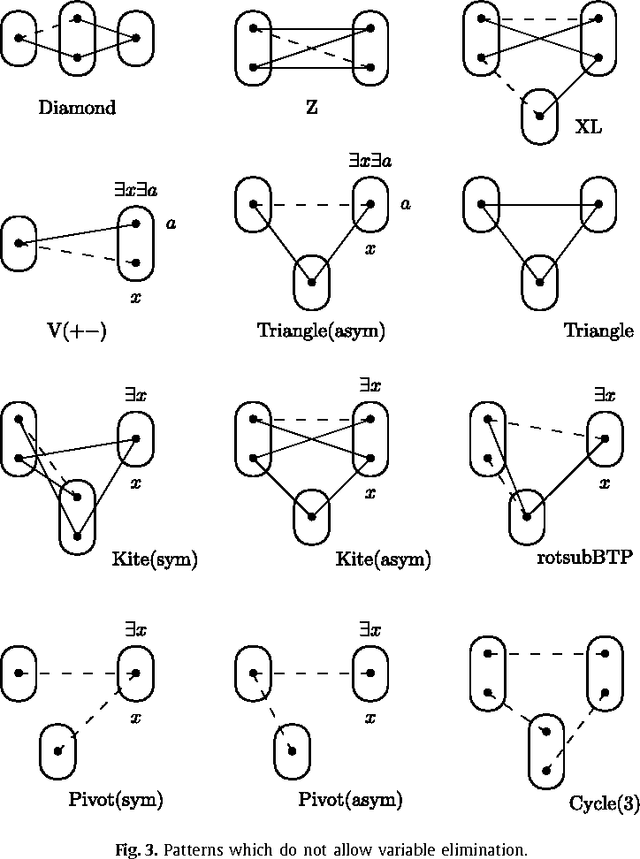
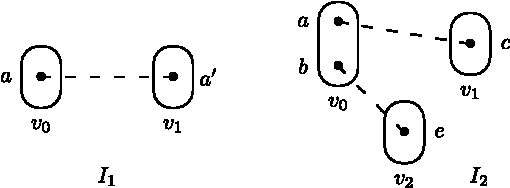
Variable or value elimination in a constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) can be used in preprocessing or during search to reduce search space size. A variable elimination rule (value elimination rule) allows the polynomial-time identification of certain variables (domain elements) whose elimination, without the introduction of extra compensatory constraints, does not affect the satisfiability of an instance. We show that there are essentially just four variable elimination rules and three value elimination rules defined by forbidding generic sub-instances, known as irreducible existential patterns, in arc-consistent CSP instances. One of the variable elimination rules is the already-known Broken Triangle Property, whereas the other three are novel. The three value elimination rules can all be seen as strict generalisations of neighbourhood substitution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge