Value-Decomposition Multi-Agent Actor-Critics
Paper and Code
Aug 01, 2020
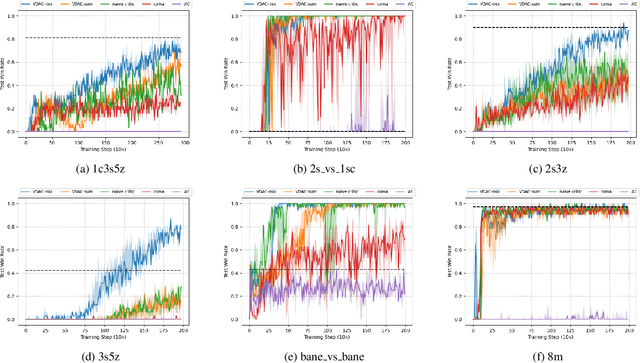
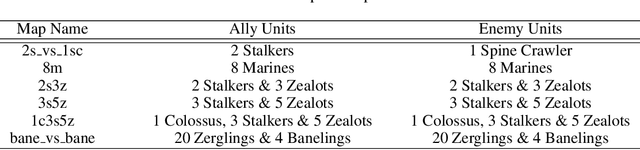
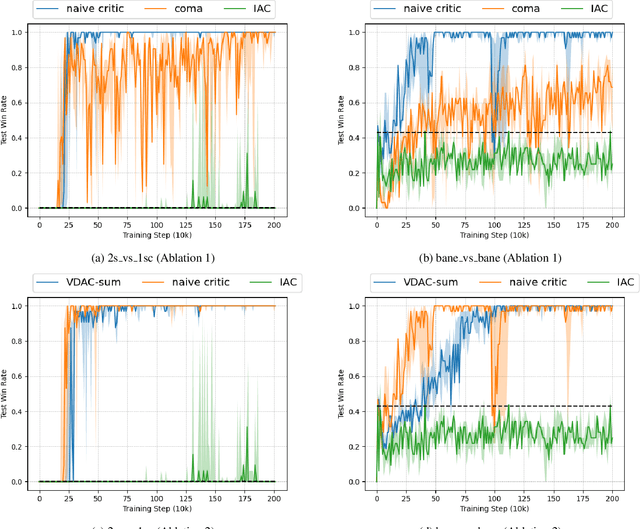
The exploitation of extra state information has been an active research area in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). QMIX represents the joint action-value using a non-negative function approximator and achieves the best performance, by far, on multi-agent benchmarks, StarCraft II micromanagement tasks. However, our experiments show that, in some cases, QMIX is incompatible with A2C, a training paradigm that promotes algorithm training efficiency. To obtain a reasonable trade-off between training efficiency and algorithm performance, we extend value-decomposition to actor-critics that are compatible with A2C and propose a novel actor-critic framework, value-decomposition actor-critics (VDACs). We evaluate VDACs on the testbed of StarCraft II micromanagement tasks and demonstrate that the proposed framework improves median performance over other actor-critic methods. Furthermore, we use a set of ablation experiments to identify the key factors that contribute to the performance of VDACs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge