Using Pre-training and Interaction Modeling for ancestry-specific disease prediction in UK Biobank
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2024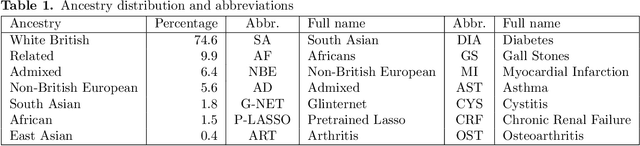
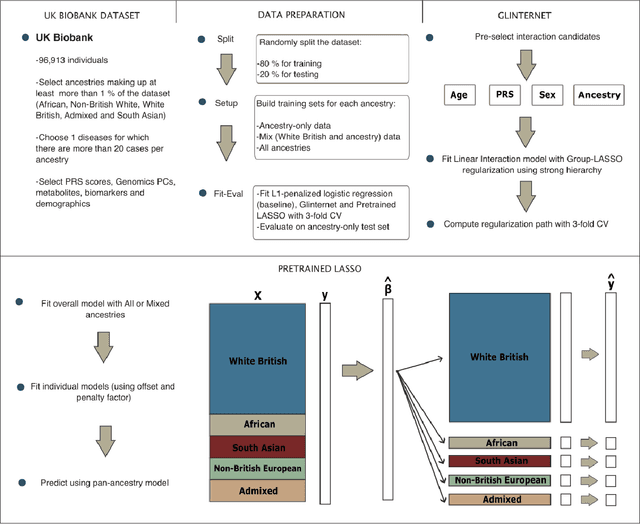
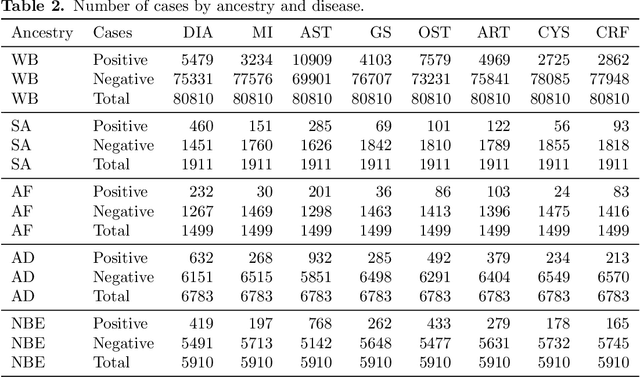
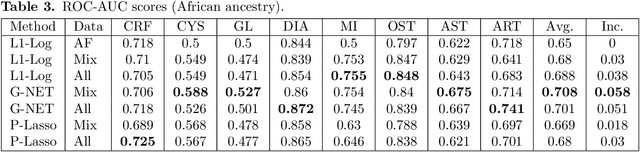
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have uncovered the genetic basis of complex traits, but show an under-representation of non-European descent individuals, underscoring a critical gap in genetic research. Here, we assess whether we can improve disease prediction across diverse ancestries using multiomic data. We evaluate the performance of Group-LASSO INTERaction-NET (glinternet) and pretrained lasso in disease prediction focusing on diverse ancestries in the UK Biobank. Models were trained on data from White British and other ancestries and validated across a cohort of over 96,000 individuals for 8 diseases. Out of 96 models trained, we report 16 with statistically significant incremental predictive performance in terms of ROC-AUC scores. These findings suggest that advanced statistical methods that borrow information across multiple ancestries may improve disease risk prediction, but with limited benefit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge