UPB at SemEval-2021 Task 1: Combining Deep Learning and Hand-Crafted Features for Lexical Complexity Prediction
Paper and Code
Apr 14, 2021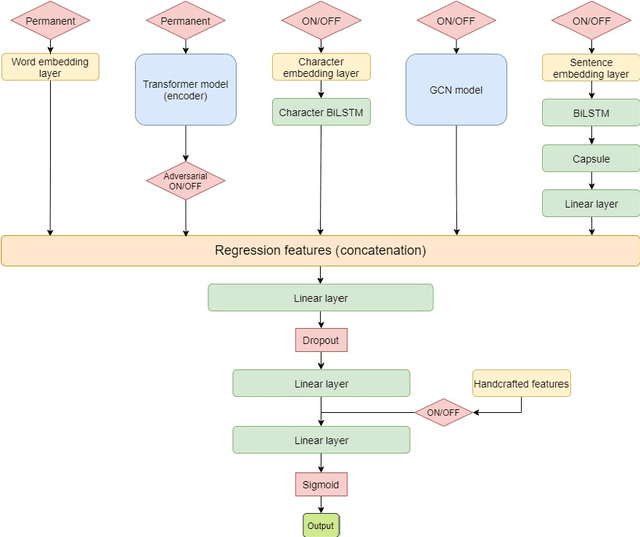

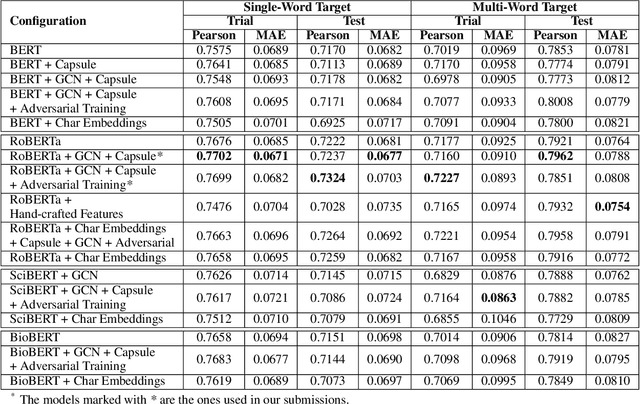
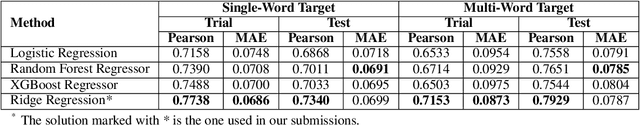
Reading is a complex process which requires proper understanding of texts in order to create coherent mental representations. However, comprehension problems may arise due to hard-to-understand sections, which can prove troublesome for readers, while accounting for their specific language skills. As such, steps towards simplifying these sections can be performed, by accurately identifying and evaluating difficult structures. In this paper, we describe our approach for the SemEval-2021 Task 1: Lexical Complexity Prediction competition that consists of a mixture of advanced NLP techniques, namely Transformer-based language models, pre-trained word embeddings, Graph Convolutional Networks, Capsule Networks, as well as a series of hand-crafted textual complexity features. Our models are applicable on both subtasks and achieve good performance results, with a MAE below 0.07 and a Person correlation of .73 for single word identification, as well as a MAE below 0.08 and a Person correlation of .79 for multiple word targets. Our results are just 5.46% and 6.5% lower than the top scores obtained in the competition on the first and the second subtasks, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge