Unsupervised Transductive Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2016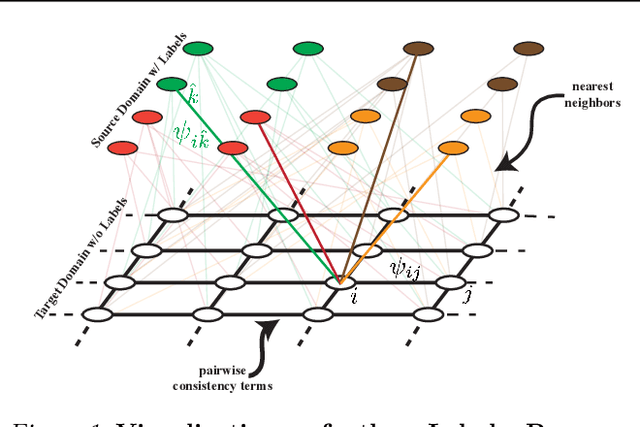
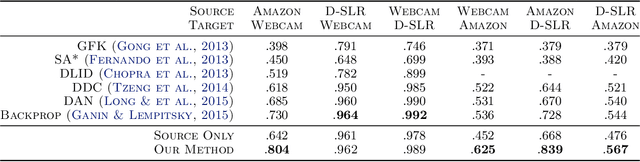
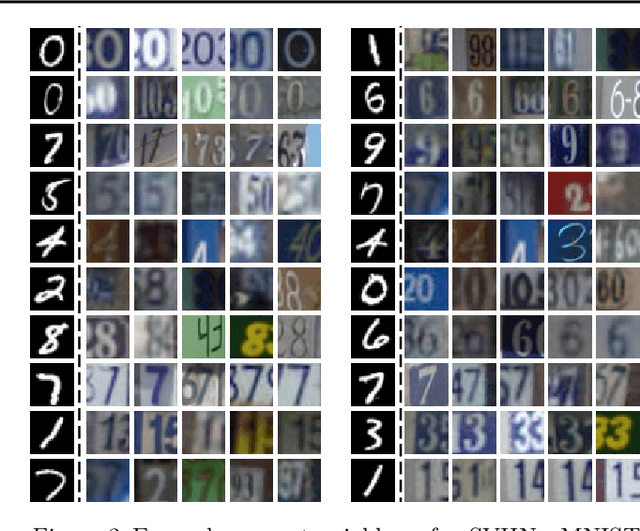
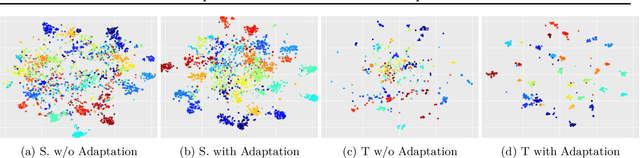
Supervised learning with large scale labeled datasets and deep layered models has made a paradigm shift in diverse areas in learning and recognition. However, this approach still suffers generalization issues under the presence of a domain shift between the training and the test data distribution. In this regard, unsupervised domain adaptation algorithms have been proposed to directly address the domain shift problem. In this paper, we approach the problem from a transductive perspective. We incorporate the domain shift and the transductive target inference into our framework by jointly solving for an asymmetric similarity metric and the optimal transductive target label assignment. We also show that our model can easily be extended for deep feature learning in order to learn features which are discriminative in the target domain. Our experiments show that the proposed method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms in both object recognition and digit classification experiments by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge