Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Optimal Relay for Extending Coverage in Post-Disaster Scenarios
Paper and Code
Apr 13, 2021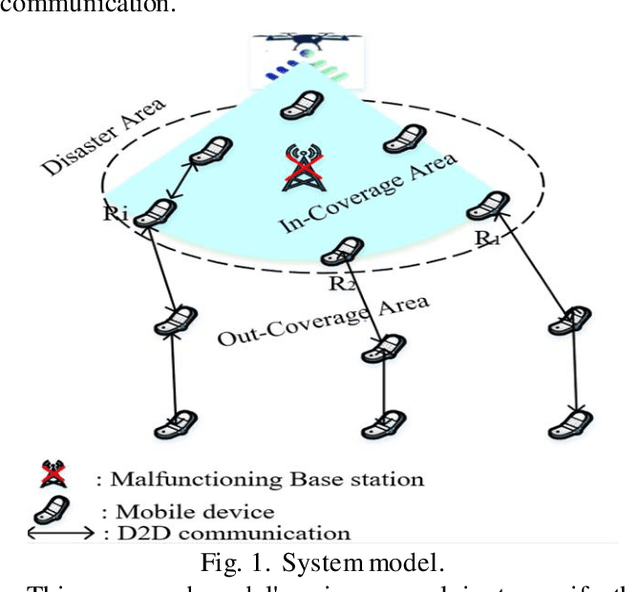
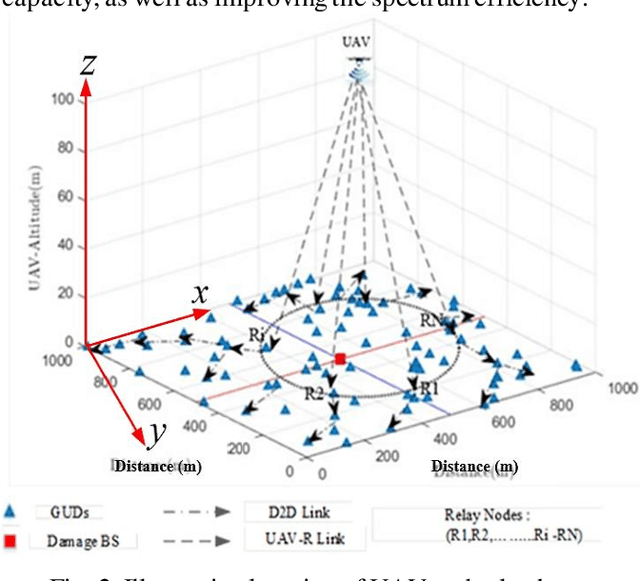
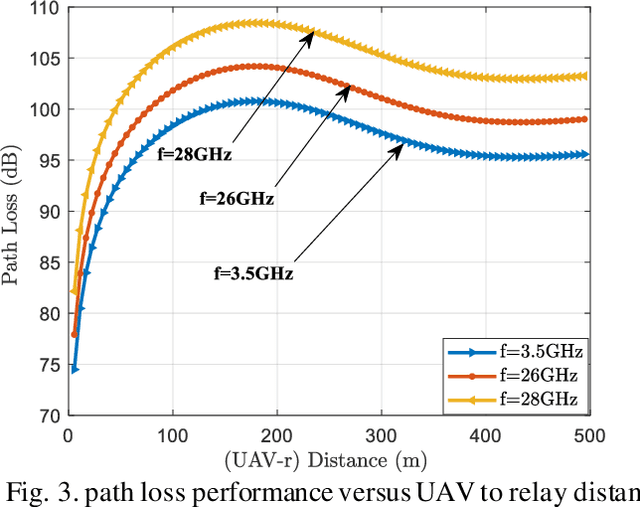
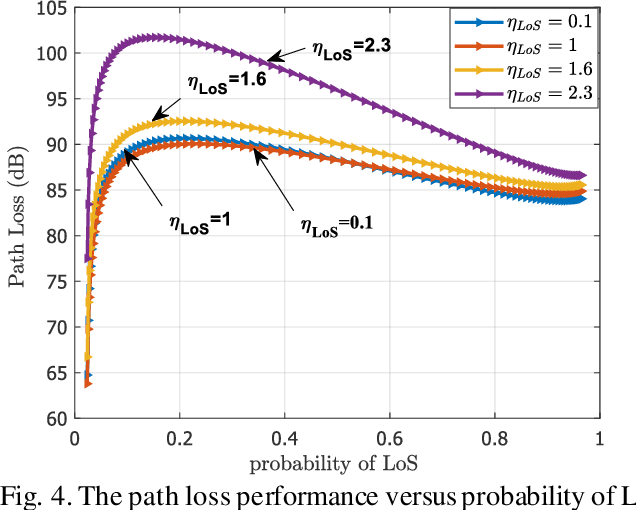
The malfunction or interruption of wireless coverage services has been shown to increase the mortality rate during natural disasters. Wireless coverage by an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) provides network coverage to ground user devices during and post-disaster events. The relay hops receive wireless coverage and can be forwarded to user devices that are out of coverage allowing reliable connectivity for large-scale user devices. This work evaluates the optimal relay hops performance to improve wireless coverage services and establish connectivity in post-disaster scenarios. The results demonstrate the UAV line of sights understanding to select an optimal relay for improving wireless coverage services. The path loss probability and system capacity were all affected by the user device distance and relay densities. The optimal relay hop distance and the UAV positions static are also investigated to improve coverage likelihood which could be especially useful for UAV deployment design. It is found that the dense relays node in UAV systems enhances the capacity coverage area and energy efficiency by decentralized connectivity through a multihop device to device wireless network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge