Underwater image filtering: methods, datasets and evaluation
Paper and Code
Dec 22, 2020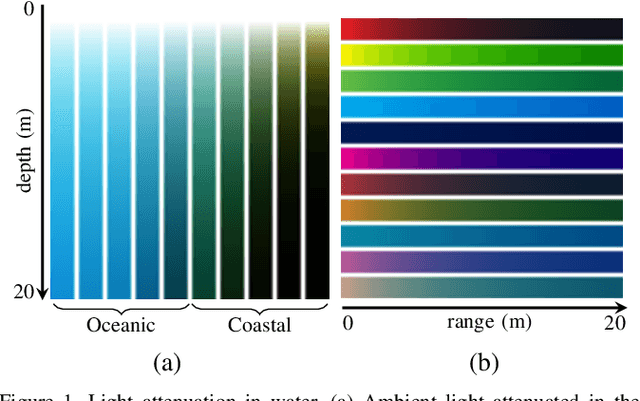
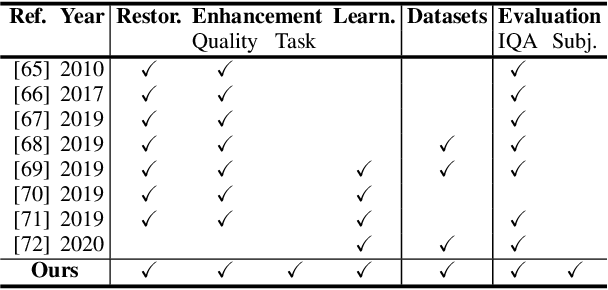
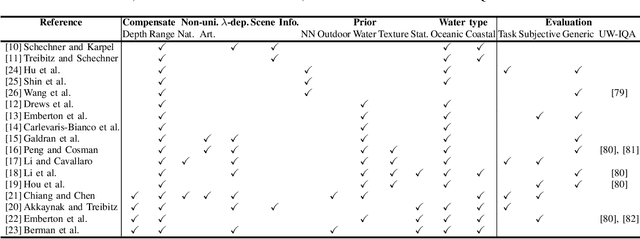
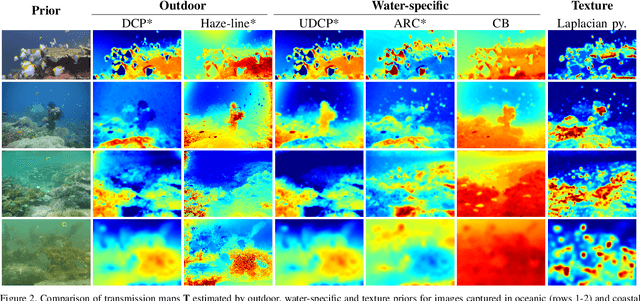
Underwater images are degraded by the selective attenuation of light that distorts colours and reduces contrast. The degradation extent depends on the water type, the distance between an object and the camera, and the depth under the water surface the object is at. Underwater image filtering aims to restore or to enhance the appearance of objects captured in an underwater image. Restoration methods compensate for the actual degradation, whereas enhancement methods improve either the perceived image quality or the performance of computer vision algorithms. The growing interest in underwater image filtering methods--including learning-based approaches used for both restoration and enhancement--and the associated challenges call for a comprehensive review of the state of the art. In this paper, we review the design principles of filtering methods and revisit the oceanology background that is fundamental to identify the degradation causes. We discuss image formation models and the results of restoration methods in various water types. Furthermore, we present task-dependent enhancement methods and categorise datasets for training neural networks and for method evaluation. Finally, we discuss evaluation strategies, including subjective tests and quality assessment measures. We complement this survey with a platform ( https://puiqe.eecs.qmul.ac.uk/ ), which hosts state-of-the-art underwater filtering methods and facilitates comparisons.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge