Understanding Text Classification Data and Models Using Aggregated Input Salience
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2022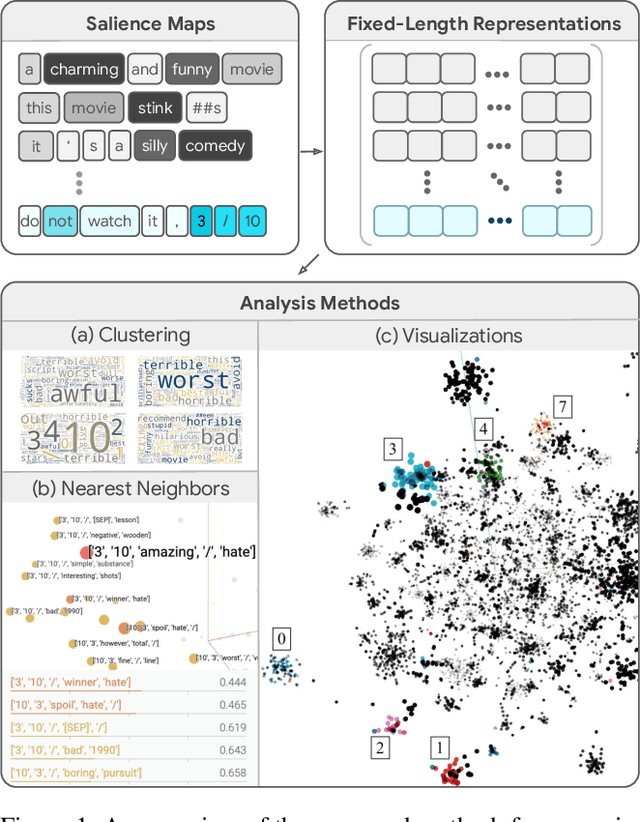
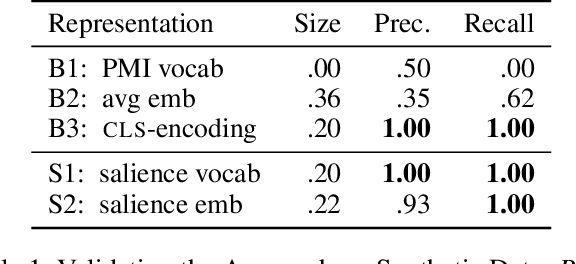

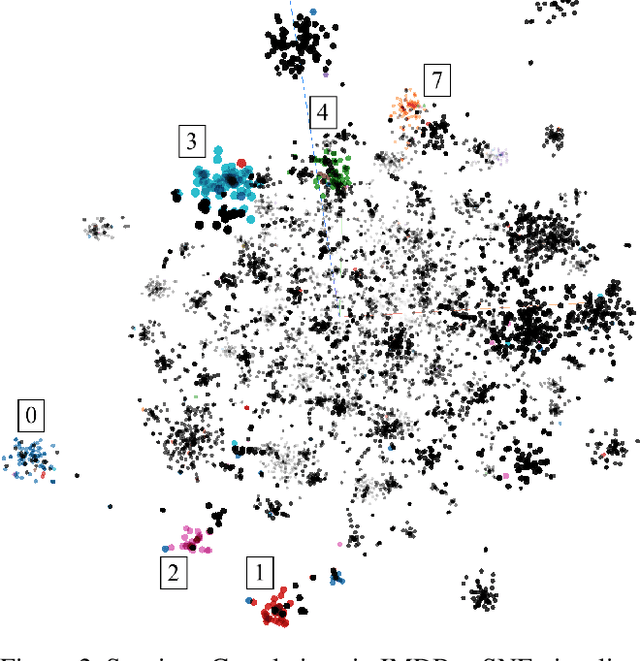
Realizing when a model is right for a wrong reason is not trivial and requires a significant effort by model developers. In some cases, an input salience method, which highlights the most important parts of the input, may reveal problematic reasoning. But scrutinizing highlights over many data instances is tedious and often infeasible. Furthermore, analyzing examples in isolation does not reveal general patterns in the data or in the model's behavior. In this paper we aim to address these issues and go from understanding single examples to understanding entire datasets and models. The methodology we propose is based on aggregated salience maps. Using this methodology we address multiple distinct but common model developer needs by showing how problematic data and model behavior can be identified -- a necessary first step for improving the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge