Understanding MCMC Dynamics as Flows on the Wasserstein Space
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2019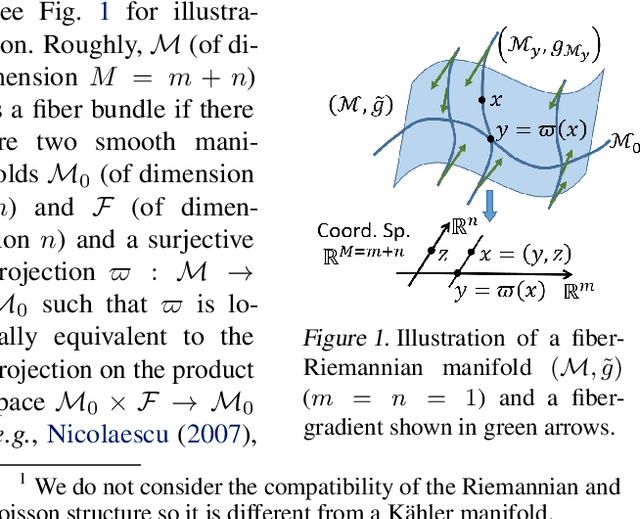
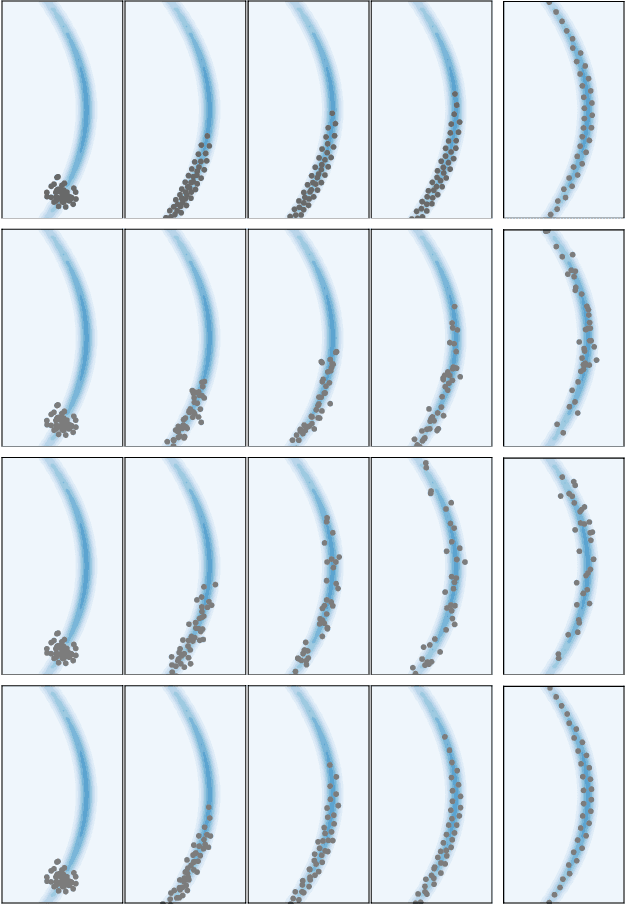
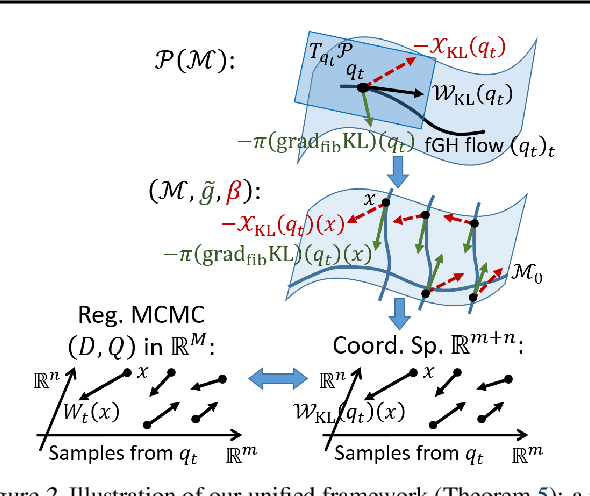

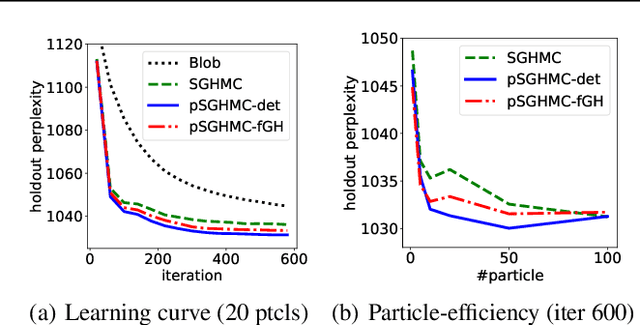
It is known that the Langevin dynamics used in MCMC is the gradient flow of the KL divergence on the Wasserstein space, which helps convergence analysis and inspires recent particle-based variational inference methods (ParVIs). But no more MCMC dynamics is understood in this way. In this work, by developing novel concepts, we propose a theoretical framework that recognizes a general MCMC dynamics as the fiber-gradient Hamiltonian flow on the Wasserstein space of a fiber-Riemannian Poisson manifold. The "conservation + convergence" structure of the flow gives a clear picture on the behavior of general MCMC dynamics. We analyse existing MCMC instances under the framework. The framework also enables ParVI simulation of MCMC dynamics, which enriches the ParVI family with more efficient dynamics, and also adapts ParVI advantages to MCMCs. We develop two ParVI methods for a particular MCMC dynamics and demonstrate the benefits in experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge